Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Pshenichnikov, A.; Zubekhina, B.; Ogi, Hiroshi; Pham, V. H.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
Oikawa, Kenichi; Harjo, S.; Pham, A. H.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Morito, Shigekazu*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oba, Takuya*; Ito, Masakazu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011062_1 - 011062_6, 2021/03
Yamazaki, Saishun; Pshenichnikov, A.; Pham, V. H.; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Tokushima, Kazuyuki*; Aomi, Masaki*; Sakamoto, Kan*
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on Reactor Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2018) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/10
It is predictively evaluated that degradation of fuel assembly proceeded in a certain steam-starved condition at the early stage of a SA at 1F unit 2 (BWR). As for PWR fuel assembly, effective steam flow rate was properly indicated by normalizing to a unit of g-H O/sec/rod which is used as an important parameter for evaluating fuel degradation progression. Due to the inhomogeneous configuration of BWR fuel assembly, the difference of Zry oxidation and hydrogen uptake between the inside and outside of the channel box cannot be properly evaluated by this normalization. Instead of g-H
O/sec/rod which is used as an important parameter for evaluating fuel degradation progression. Due to the inhomogeneous configuration of BWR fuel assembly, the difference of Zry oxidation and hydrogen uptake between the inside and outside of the channel box cannot be properly evaluated by this normalization. Instead of g-H O/sec/rod, proper evaluation unit for BWR configuration is necessary. To accumulate Zry oxidation and hydrogen uptake data for steam-starved conditions, high temperature oxidation tests were performed using a simulated BWR fuel bundle sample. The use of equivalent diameter of the cross section of BWR fuel assembly was proposed for normalization of effective steam flow rate.
O/sec/rod, proper evaluation unit for BWR configuration is necessary. To accumulate Zry oxidation and hydrogen uptake data for steam-starved conditions, high temperature oxidation tests were performed using a simulated BWR fuel bundle sample. The use of equivalent diameter of the cross section of BWR fuel assembly was proposed for normalization of effective steam flow rate.
Povinec, P. P.*; Aoyama, Michio*; Biddulph, D.*; Breier, R.*; Buesseler, K. O.*; Chang, C. C.*; Golser, R.*; Hou, X. L.*; Je kovsk
kovsk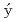 , M.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; et al.
, M.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; et al.
Biogeosciences, 10(8), p.5481 - 5496, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:94.03(Ecology)Radionuclide impact of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident on the distribution of radionuclides in seawater of the NW Pacific Ocean is compared with global fallout from atmospheric tests of nuclear weapons. Surface and water column seawater samples collected during the international expedition in June 2011 were analyzed for  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  I and
I and  H. The
H. The  Cs,
Cs,  I and
I and  H levels in surface seawater offshore Fukushima varied between 0.002-3.5 Bq/L, 0.01-0.8
H levels in surface seawater offshore Fukushima varied between 0.002-3.5 Bq/L, 0.01-0.8  Bq/L, and 0.05-0.15 Bq/L, respectively. At the sampling site about 40 km from the coast, where all three radionuclides were analyzed, the Fukushima impact on the levels of these three radionuclides represent an increase above the global fallout background by factors of about 1000, 30 and 3, respectively. The water column data indicate that the transport of Fukushima-derived radionuclides downward to the depth of 300 m has already occurred. The observed
Bq/L, and 0.05-0.15 Bq/L, respectively. At the sampling site about 40 km from the coast, where all three radionuclides were analyzed, the Fukushima impact on the levels of these three radionuclides represent an increase above the global fallout background by factors of about 1000, 30 and 3, respectively. The water column data indicate that the transport of Fukushima-derived radionuclides downward to the depth of 300 m has already occurred. The observed  Cs levels in surface waters and in the water column are in reasonable agreement with predictions obtained from the Ocean General Circulation Model, which indicates that the radionuclides have been transported from the Fukushima coast eastward. Due to a suitable residence time in the ocean, Fukushima-derived radionuclides will provide useful tracers for isotope oceanography studies on the transport of water masses in the NW Pacific Ocean.
Cs levels in surface waters and in the water column are in reasonable agreement with predictions obtained from the Ocean General Circulation Model, which indicates that the radionuclides have been transported from the Fukushima coast eastward. Due to a suitable residence time in the ocean, Fukushima-derived radionuclides will provide useful tracers for isotope oceanography studies on the transport of water masses in the NW Pacific Ocean.
 He,
He,  B,
B,  Y,
Y, 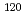 In and
In and  Tl observed in the (
Tl observed in the ( Li,
Li,  Be) charge-exchange reaction
Be) charge-exchange reactionAnnakkage, T.*; J necke, J.*; Winfield, J. S.*; Berg, G. P. A.*; Brown, J. A.*; Gawley, G. A.*; Danczyk, S.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Mercer, D. J.*; Pham, K.*; et al.
necke, J.*; Winfield, J. S.*; Berg, G. P. A.*; Brown, J. A.*; Gawley, G. A.*; Danczyk, S.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Mercer, D. J.*; Pham, K.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 648(1-2), p.3 - 44, 1999/03
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:44.59(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Mohamad, A. B.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Soma, Yasutaka; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tomonori; Ioka, Ikuo; Pham, V. H.; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; et al.
no journal, ,
JAEA is conducting research on various coating technologies for fuel cladding tubes aimed at improving accident resistance. In the lecture, we will introduce new equipment development at JAEA aimed at using these studies in addition to an overview of the entire project.
Kawai, Keito*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Fujimura, Yuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Abe, Yosuke; Mohamad, A. B.; Pham, V. H.; Ishikawa, Norito; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ioka, Ikuo; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mohamad, A. B.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Soma, Yasutaka; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tomonori; Ioka, Ikuo; Pham, V. H.; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mohamad, A. B.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Soma, Yasutaka; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tomonori; Ioka, Ikuo; Pham, V. H.; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
JAEA is promoting the characterization of various coating tubes as part of fundamental research that contributes to the practical application of coated fuel cladding aiming at improving accident tolerance. In this presentation, overall outline, the new test equipment under construction, and highlight results of the vapor oxidation characteristic evaluation test for coated claddings will be presented.
Mohamad, A. B.; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Soma, Yasutaka; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Pham, V. H.; Abe, Yosuke; Ioka, Ikuo; Sato, Tomonori; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Miwa, Shuhei; et al.
no journal, ,
Yamazaki, Saishun; Pshenichnikov, A.; Pham, V. H.; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English