Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 isomers in
isomers in  Cf
CfOrlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Ito, Yuta; Suzaki, Fumi; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064301_1 - 064301_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear)Nguyen, T. H.*; Le Ba, T.*; Tran, C. T.*; Nguyen, T. T.*; Doan, T. T. T.*; Do, V. K.; Watanabe, Masayuki; Pham, Q. M.*; Hoang, S. T.*; Nguyen, D. V.*; et al.
Hydrometallurgy, 213, p.105933_1 - 105933_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:80.29(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)A continuous counter-current extraction for the selective recovery of thorium (Th) and uranium (U) from the Yen Phu (Vietnam) rare earth concentrate leach solutions was systematically studied. The primary amine N1923 was used as an extractant which was prepared in the isoparaffin IP-2028 diluent. Thorium and uranium were selectively recovered in a hydrometallurgical circuit established by continuous mixer-settler extraction, scrubbing, and back-extraction at the laboratory scale. The desired purity of Th and U can be achieved by managing the volume ratio of organic to aqueous phase (O/A ratio) in the corresponding steps. Highly pure Th and U were recovered from the pregnant back-extraction liquor and the raffinate, respectively, which have satisfactory properties for further processing of the subsequent nuclear materials.
Povinec, P. P.*; Aoyama, Michio*; Biddulph, D.*; Breier, R.*; Buesseler, K. O.*; Chang, C. C.*; Golser, R.*; Hou, X. L.*; Je kovsk
kovsk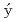 , M.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; et al.
, M.*; Jull, A. J. T.*; et al.
Biogeosciences, 10(8), p.5481 - 5496, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:93.94(Ecology)Radionuclide impact of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident on the distribution of radionuclides in seawater of the NW Pacific Ocean is compared with global fallout from atmospheric tests of nuclear weapons. Surface and water column seawater samples collected during the international expedition in June 2011 were analyzed for  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  I and
I and  H. The
H. The  Cs,
Cs,  I and
I and  H levels in surface seawater offshore Fukushima varied between 0.002-3.5 Bq/L, 0.01-0.8
H levels in surface seawater offshore Fukushima varied between 0.002-3.5 Bq/L, 0.01-0.8  Bq/L, and 0.05-0.15 Bq/L, respectively. At the sampling site about 40 km from the coast, where all three radionuclides were analyzed, the Fukushima impact on the levels of these three radionuclides represent an increase above the global fallout background by factors of about 1000, 30 and 3, respectively. The water column data indicate that the transport of Fukushima-derived radionuclides downward to the depth of 300 m has already occurred. The observed
Bq/L, and 0.05-0.15 Bq/L, respectively. At the sampling site about 40 km from the coast, where all three radionuclides were analyzed, the Fukushima impact on the levels of these three radionuclides represent an increase above the global fallout background by factors of about 1000, 30 and 3, respectively. The water column data indicate that the transport of Fukushima-derived radionuclides downward to the depth of 300 m has already occurred. The observed  Cs levels in surface waters and in the water column are in reasonable agreement with predictions obtained from the Ocean General Circulation Model, which indicates that the radionuclides have been transported from the Fukushima coast eastward. Due to a suitable residence time in the ocean, Fukushima-derived radionuclides will provide useful tracers for isotope oceanography studies on the transport of water masses in the NW Pacific Ocean.
Cs levels in surface waters and in the water column are in reasonable agreement with predictions obtained from the Ocean General Circulation Model, which indicates that the radionuclides have been transported from the Fukushima coast eastward. Due to a suitable residence time in the ocean, Fukushima-derived radionuclides will provide useful tracers for isotope oceanography studies on the transport of water masses in the NW Pacific Ocean.
Takeshita, Hidefumi; Pham, T. L. H.*; Yoshii, Fumio; Kume, Tamikazu
Shokuhin Shosha, 35(1-2), p.59 - 63, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
 He,
He,  B,
B,  Y,
Y, 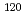 In and
In and  Tl observed in the (
Tl observed in the ( Li,
Li,  Be) charge-exchange reaction
Be) charge-exchange reactionAnnakkage, T.*; J necke, J.*; Winfield, J. S.*; Berg, G. P. A.*; Brown, J. A.*; Gawley, G. A.*; Danczyk, S.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Mercer, D. J.*; Pham, K.*; et al.
necke, J.*; Winfield, J. S.*; Berg, G. P. A.*; Brown, J. A.*; Gawley, G. A.*; Danczyk, S.*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Mercer, D. J.*; Pham, K.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 648(1-2), p.3 - 44, 1999/03
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:44.59(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Yagi, Toshiaki; Tamada, Masao; Pham, T. L. H.*
no journal, ,
Recently, we have reported the synthesis of hydrogels of polysaccharide derivatives such as carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), carboxymethylchitin, etc., by radiation-induced crosslinking methods. Control of gelation of polysaccharide derivatives by radiation is very important factor for various applications. It was investigated that control temperature during irradiation affects on crosslinking behavior of CMC. The gel fraction and swelling of CMC gel after irradiation at temperature of -78 to 70  C were determined. The more pronounced gelation was occurred in lower temperature region of -78 to 0
C were determined. The more pronounced gelation was occurred in lower temperature region of -78 to 0  C when compared to the other region of 0 to 70
C when compared to the other region of 0 to 70  C. It found that gelation could be controlled by changing temperature at the time of the irradiation when it was made to put a polysaccharide derivative such as CMCT and CMS on the crosslinking with the radiation and gel was formed.
C. It found that gelation could be controlled by changing temperature at the time of the irradiation when it was made to put a polysaccharide derivative such as CMCT and CMS on the crosslinking with the radiation and gel was formed.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Pham, T. L. H.*; Yagi, Toshiaki; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiroki, Akihiro; Pham, T. T. H.*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Pham, H. T. T.*; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sugiyama, Koichi*; Go, Shintaro*; Tomimatsu, Taro*; Kai, Tamito*; Nagae, Daisuke*; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Matsunaga, Sotaro*; Nagata, Yuto*; Nishibata, Hiroki*; Washiyama, Kohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have successfully performed in-beam gamma-ray spectroscopy using the isomer-scope technique to study excited-state structure of neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei. The neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei were produced in the multinucleon-transfer reactions with a  Cm target and
Cm target and  O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E-
O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E- E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
 Cf by Coulomb excitation gamma-ray spectroscopy
Cf by Coulomb excitation gamma-ray spectroscopyPham, T. T.*; Yanagihara, Rikuto*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Orlandi, R.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Hirose, Kentaro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; et al.
no journal, ,
 -irradiation technique
-irradiation techniqueHiroki, Akihiro; Pham, H. T. T.*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Cf by Coulomb excitation gamma-ray spectroscopy
Cf by Coulomb excitation gamma-ray spectroscopyPham, T. T.; Yanagihara, Rikuto*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Orlandi, R.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki
no journal, ,