Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rapp, L.*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Firestein, K. L.*; Sagae, Daisuke*; Habara, Hideaki*; Mukai, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Kazuo*; Gamaly, E. G.*; Kodama, Ryosuke*; Seto, Yusuke*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023101_1 - 023101_18, 2024/04
It is generally known that irradiating a solid surface with a laser pulse of ultra-relativistic intensity generates a plasma on the surface, which in turn creates an ultrahigh pressure inside. In this study, the crystal structure analysis of high-pressure phases generated inside silicon single-crystals irradiated by this laser was performed using the diffraction system at the Stress and Imaging apparatus of BL22XU, which is a JAEA-BL. The results obtained confirm the existence of high-pressure phases that silicon is said to possess: body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal, and tetragonal phases in the interior. We can get the results that the crystal structure of silicon polymorphs of being include body-centered, rhombohedral, hexagonal-diamond, tetragonal exists. In the future, we will accumulate data and apply them to control the internal structure, strength, and functionality of materials.
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.78(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 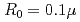 m.
m.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko*; Sakaki, Hironao*; Esirkepov, T. Zh.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Pirozhkov, A. S.*; Sagisaka, Akito*; et al.
Plasma Physics Reports, 42(4), p.327 - 337, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:54.81(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A combination of a petawatt laser and nuclear physics techniques can crucially facilitate the measurement of exotic nuclei properties. With numerical simulations and laser-driven experiments we show prospects for the Laser-driven Exotic Nuclei extraction-acceleration method proposed in [M. Nishiuchi et al., Phys. Plasmas 22, 033107 (2015)]: a femtosecond petawatt laser, irradiating a target bombarded by an external ion beam, extracts from the target and accelerates to few GeV highly charged short-lived heavy exotic nuclei created in the target via nuclear reactions.
Oks, E.*; Dalimier, E.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Andreev, A.*; Koga, J. K.; Sakaki, Hironao; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 23(25), p.31991 - 32005, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.80(Optics)We present experiments dealing with a femtosecond laser-driven cluster-based plasma, where by analyzing the nonlinear phenomenon of satellites of spectral lines of Ar XVII, we revealed the nonlinear phenomenon of the generation of the second harmonic of the laser frequency. For performing this analysis we developed new results in the theory of satellites of spectral lines. From such lineshape analysis we found, in particular, that the efficiency of converting the short (40 fs) intense (3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm ) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
Pikuz, T.*; Faenov, A.*; Matsuoka, Takeshi*; Matsuyama, Satoshi*; Yamauchi, Kazuto*; Ozaki, Narimasa*; Albertazzi, B.*; Inubushi, Yuichi*; Yabashi, Makina*; Tono, Kensuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 5, p.17713_1 - 17713_10, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:87.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Faenov, A.*; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Yasuda, Ryo; Iikura, Hiroshi; Nojima, Takehiro; Sakai, Takuro; Shiozawa, Masahiro*; et al.
High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 3, p.e27_1 - e27_9, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:46.81(Optics)Ishino, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Pikuz, T.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Faenov, A.*; Inogamov, N.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
X-Ray Lasers and Coherent X-Ray Sources; Development and Applications XI (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9589), p.958904_1 - 958904_6, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.38(Optics)To study the ablation process induced by the soft X-ray laser pulse, we investigated the electron temperature of the ablating material. Focused soft X-ray laser pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm and duration of 7 ps were irradiated onto target surfaces, and we observed the optical emission from surfaces by use of an optical camera. On target surfaces, we could confirm damage structures, but no emission signal in the visible spectral range during ablation could be observed. Then, we estimated the electron temperature in the ablating matter, and we estimated the electron temperature to be lower than 1 eV and the process duration was shorter than 1000 ps. This result is in good accordance with the theoretical prediction. Our investigation implies that the spallative ablation occurs in the low electron temperature region of a non-equilibrium state of warm dense matter. We will present the current state of our eperimental results.
Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Ishino, Masahiko; Agranat, M. B.*; Ashitkov, S. I.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Khokhlov, V. A.*; et al.
Applied Physics B, 119(3), p.413 - 419, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.23(Optics)Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Kanasaki, Masato; et al.
Research Using Extreme Light; Entering New Frontiers with Petawatt-Class Lasers II (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9515), p.95151D_1 - 95151D_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Experimental demonstration of multi-charged heavy ion acceleration from the interaction between the ultra-intense short pulse laser system and the metal target is presented. The laser pulse of  10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of
10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of  10
10 from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of
from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of  10
10 Wcm
Wcm interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T.*; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 22(3), p.033107_1 - 033107_8, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:96.14(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic low-emittance high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a compact radio isotope source in combination with conventional technology.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Y.; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science XI; Springer Series in Chemical Physics, Vol.109, p.215 - 233, 2015/00
Clusters formed in supersonic gas expansion through a three-staged conical nozzle have been verified by measuring the angular distribution of the light scattered from cluster target. The size distirbutions of the clusters are calculated based on the Mie theory. The reliability of the size measurement is verified to be an experimental error of 10% using standard particles. The mean sizes of CO clusters for the cases of CO
clusters for the cases of CO /H
/H and CO
and CO /He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26
/He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26  m and 0.22
m and 0.22  m, respectively. For the CO
m, respectively. For the CO /H
/H , the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5
, the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5 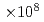 clusters/cm
clusters/cm by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Koga, J. K.; Mori, Michiaki; Kawase, Keigo*; et al.
RAL-TR-2015-025, P. 22, 2015/00
Ishino, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Y.*; Faenov, A.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
Journal of Applied Physics, 116(18), p.183302_1 - 183302_6, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.97(Physics, Applied)We investigated the optical emission from the ablating surfaces induced by the irradiations of soft X-ray laser (SXRL) pulses with the aim of estimation of the maximum electron temperature. No emission signal in the spectral range of 400-800 nm could be observed despite the formation of damage structures on the target surfaces. Hence, we estimated an upper limit for the electron temperature of 0.4-0.7 eV for the process duration of 100-1000 ps. Our results imply that the ablation and/or surface modification by the SXRL is not accompanied by plasma formation but is induced by thermo-mechanical pressure, which is so called a spallative ablation. This spallative ablation process occurs in the low electron temperature region of a non-equilibrium state of warm dense matter.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 16(9), p.093003_1 - 093003_30, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:80.06(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Ashitkov, S. I.*; Emirov, Y. N.*; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Ishino, Masahiko; Kando, Masaki; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 500(11), p.112070_1 - 112070_6, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:98.41(Physics, Applied)The mechanism of formation and geometry of surface structures are discussed for the case of single pulse acting on a well-polished metal surface. We demonstrate that the complex surface nano-structures are formed after laser irradiation due to the thermomechanical spallation of ultrathin surface layer of melt. Spallation is accompanied by a strong foaming of melt followed by breaking of the foam. After several nanoseconds the foam remnants freeze up with formation of complex nano-structures on a target surface.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Maeda, Shota; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukami, Tomoyo; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A705_1 - 02A705_4, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)High intensity laser-plasma interaction has attracted considerable interest for a number of years. The laser-plasma interaction is accompanied by generation of various charged particle beams. Results of simultaneous novel measurements of electron-induced photonuclear neutrons (photoneutron), which are a diagnostic of the laser-plasma interaction, are proposed to use for optimization of the laser-plasma ion generation. The proposed method is demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity os 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Pikuz, T.; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G.*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2012; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.147, p.121 - 124, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) clusters formed in a supersonic expansion of a gas mixture
clusters formed in a supersonic expansion of a gas mixtureJinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 21(18), p.20656 - 20674, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:72.45(Optics)A detailed mathematical model is presented for a submicron-sized cluster formation in a binary gas mixture flowing through a three-staged conical nozzle. In order to experimentally confirm this model, the cluster sizes have been evaluated using the Mie scattering method, which is to measure the angular distribution of light scattered from targets. The mean sizes of CO clusters produced in the gas mixtures of CO
clusters produced in the gas mixtures of CO (30%)/H
(30%)/H (70%) and CO
(70%) and CO (10%)/He(90%) are estimated to be 0.28
(10%)/He(90%) are estimated to be 0.28 0.03
0.03  m and 0.26
m and 0.26 0.04
0.04  m, respectively. In addition, total gas density profiles measured with an interferometer were found to be agreed with the numerical modeling within a factor of two. The dryness (
m, respectively. In addition, total gas density profiles measured with an interferometer were found to be agreed with the numerical modeling within a factor of two. The dryness (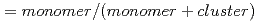 ratio) in the targets was found to support the numerical modeling. Thus, our mathematical model of cluster formation was proved to be reliable enough for the binary gas mixture by the experimental results.
ratio) in the targets was found to support the numerical modeling. Thus, our mathematical model of cluster formation was proved to be reliable enough for the binary gas mixture by the experimental results.
Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, T.; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Inogamov, N.*; Skobelev, I.*; Fortov, V.*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8849, p.88490F_1 - 88490F_8, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:71.63(Optics)Magnitskiy, S.*; Nagorskiy, N.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; Tanaka, Momoko; Ishino, Masahiko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 4, p.1936_1 - 1936_7, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.82(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Advent of plasma-based transient collisional excitation X-ray lasers allowed us to realize compact coherent X-ray sources, thus opening the way to a wide range of applications. Here we report the observation of unexpected concentric rings in the far-field beam profile at the output of a two-stage plasma-based X-ray laser developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, which can be considered as the first manifestation of a mirage phenomenon in X-rays. We have developed a method of solving the Maxwell-Bloch equations, which has allowed to find that the observed phenomenon is due to the emergence in the plasma-amplifier of X-ray mirage in the form of the phase matched coherent virtual point source. The obtained results bring a new insight into physical nature of amplification of X-ray radiation in laser-induced plasma amplifiers and open new opportunities for X-ray plasma diagnostics and extreme UV lithography.