Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 No
NoLopez-Martens, A.*; Henning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.03001_1 - 03001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.81(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Fission barrier height and its angular-momentum dependence have been measured for the first time in the nucleus with the atomic number greater than 100. The entry distribution method, which can determine the excitation energy at which fission starts to dominate the decay process, was applied to  No. The fission barrier of
No. The fission barrier of  No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the
No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the  No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
 No and
No and 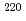 Th
ThHenning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(26), p.262505_1 - 262505_6, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:81.70(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fission barrier heights of a shell-stabilized superheavy nucleus  No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19
No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19 through the measured distribution of entry points of
through the measured distribution of entry points of  deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of
deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of  No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15
No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15 , and 6.6 MeV at spin 0
, and 6.6 MeV at spin 0 by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
 No
NoHenning, G.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 66, p.02046_1 - 02046_8, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.16(Physics, Nuclear)Fission barrier heights of  No have been determined through the entry distribution method. The entry distribution is the initial distribution of excitation energy and spin from which the
No have been determined through the entry distribution method. The entry distribution is the initial distribution of excitation energy and spin from which the  deexcitation starts in the fusion-evaporation reaction. The initial distribution is extracted from measured
deexcitation starts in the fusion-evaporation reaction. The initial distribution is extracted from measured  -ray multiplicity and total
-ray multiplicity and total  -ray energy. This paper describes the details of the entry distribution method, and reports the first determination of the fission barrier heights of
-ray energy. This paper describes the details of the entry distribution method, and reports the first determination of the fission barrier heights of  No, which is the heaviest nucleus whose fission barrier has been measured.
No, which is the heaviest nucleus whose fission barrier has been measured.
 -ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element; The
-ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element; The  Rf
RfRubert, J.*; Dorvaux, O.*; Gall, B. J. P.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Asfari, Z.*; Piot, J.*; Andersson, L. L.*; Asai, Masato; Cox, D. M.*; Dechery, F.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 420, p.012010_1 - 012010_10, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)The first prompt in-beam  -ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element,
-ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element,  Rf, has been performed successfully. A development of an intense isotopically enriched
Rf, has been performed successfully. A development of an intense isotopically enriched  Ti beam using the MIVOC method enabled us to perform this experiment. A rotational band up to a spin of 20
Ti beam using the MIVOC method enabled us to perform this experiment. A rotational band up to a spin of 20  has been discovered in
has been discovered in  Rf, and its moment of inertia has been extracted. These data suggest that there is no evidence of a significant deformed shell gap at
Rf, and its moment of inertia has been extracted. These data suggest that there is no evidence of a significant deformed shell gap at  = 104.
= 104.
 =104 nucleus
=104 nucleus  Rf
RfGreenlees, P. T.*; Rubert, J.*; Piot, J.*; Gall, B. J. P.*; Andersson, L. L.*; Asai, Masato; Asfari, Z.*; Cox, D. M.*; Dechery, F.*; Dorvaux, O.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 109(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_5, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:88.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Rotational band structure of the  =104 nucleus
=104 nucleus  Rf has been observed for the first time using an in-beam
Rf has been observed for the first time using an in-beam  -ray spectroscopic technique. This nucleus is the heaviest among the nuclei whose rotational band structure has ever been observed. Thus, the present result provides valuable information on the single-particle shell structure and pairing interaction in the heaviest extreme of nuclei. The deduced moment of inertia indicates that there is no deformed shell gap at
-ray spectroscopic technique. This nucleus is the heaviest among the nuclei whose rotational band structure has ever been observed. Thus, the present result provides valuable information on the single-particle shell structure and pairing interaction in the heaviest extreme of nuclei. The deduced moment of inertia indicates that there is no deformed shell gap at  =104, which is predicted in a number of current self-consistent mean-field models.
=104, which is predicted in a number of current self-consistent mean-field models.