Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
G tz, M.*; G
tz, M.*; G tz, S.*; Kratz, J.-V.*; Ballof, J.*; D
tz, S.*; Kratz, J.-V.*; Ballof, J.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Mokry, C.*; Renisch, D.*; Runke, J.*; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Mokry, C.*; Renisch, D.*; Runke, J.*; Sato, Tetsuya; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 109(3), p.153 - 165, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We report on a novel two-chamber approach for the synthesis of volatile complexes that allows spatial decoupling of thermalization and gas-phase carbonyl complex synthesis. Neutron induced fission on  U and spontaneous fission of
U and spontaneous fission of  Cm were employed for the production of the fission products. These were stopped inside a gas volume behind the target and flushed with an inert-gas flow into a second chamber. This was flushed with carbon monoxide to allow the gas-phase synthesis of carbonyl complexes. Parameter studies of the transfer from the first into the second chamber as well as on the carbonyl complex formation and transport processes have been performed. High overall efficiencies of more than 50% were reached rendering this approach interesting for studies of superheavy elements. Our results show that carbonyl complex formation of thermalized fission products is a single-atom reaction, and not a hot-atom reaction.
Cm were employed for the production of the fission products. These were stopped inside a gas volume behind the target and flushed with an inert-gas flow into a second chamber. This was flushed with carbon monoxide to allow the gas-phase synthesis of carbonyl complexes. Parameter studies of the transfer from the first into the second chamber as well as on the carbonyl complex formation and transport processes have been performed. High overall efficiencies of more than 50% were reached rendering this approach interesting for studies of superheavy elements. Our results show that carbonyl complex formation of thermalized fission products is a single-atom reaction, and not a hot-atom reaction.
Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064602_1 - 064602_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:98.01(Physics, Nuclear)A search for production of the superheavy elements with atomic numbers 119 and 120 was performed in the  Ti+
Ti+ Bk and
Bk and  Ti+
Ti+ Cf fusion-evaporation reactions, respectively, at the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA. Over four months of irradiation, neither was detected at cross-section sensitivity levels of 65 and 200 fb, respectively. The non-observation of elements 119 and 120 is discussed within the concept of fusion-evaporation reactions including various theoretical predictions on the fission-barrier heights of superheavy nuclei in the region of the island of stability.
Cf fusion-evaporation reactions, respectively, at the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA. Over four months of irradiation, neither was detected at cross-section sensitivity levels of 65 and 200 fb, respectively. The non-observation of elements 119 and 120 is discussed within the concept of fusion-evaporation reactions including various theoretical predictions on the fission-barrier heights of superheavy nuclei in the region of the island of stability.
 Ca+
Ca+ Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)
Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054306_1 - 054306_16, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:90.91(Physics, Nuclear)We have performed an experiment to synthesize the element 117 (Ts) with the  Ca+
Ca+ Bk fusion reaction. Four
Bk fusion reaction. Four  -decay chains attributed to the element 117 were observed. Two of them were long decay chains which can be assigned to the one originating from the
-decay chains attributed to the element 117 were observed. Two of them were long decay chains which can be assigned to the one originating from the  decay of
decay of 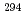 Ts. The other two were short decay chains which are consistent with the one originating from the
Ts. The other two were short decay chains which are consistent with the one originating from the  decay of
decay of 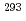 Ts. We have compared the present results with the literature data, and found that our present results mostly confirmed the literature data, leading to the firm confirmation of the synthesis of the element 117.
Ts. We have compared the present results with the literature data, and found that our present results mostly confirmed the literature data, leading to the firm confirmation of the synthesis of the element 117.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Beerwerth, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(44), p.14609 - 14613, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:69.46(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.05001_1 - 05001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.9(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We measured ionization efficiencies of fermium, einsteinium, mendelevium, and lawrencium by using a newly developed gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of the elements have not been determined so far due to their low production rates and/or their short half-lives. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potentials of these actinide elements have been successfully determined.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
Nature, 520(7546), p.209 - 211, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:97.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We successfully measured ionization efficiencies of lawrencium (Lr,  =103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
=103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
 Ca +
Ca +  Bk fusion reaction leading to element Z = 117; Long-lived
Bk fusion reaction leading to element Z = 117; Long-lived  -decaying
-decaying 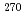 Db and discovery of
Db and discovery of  Lr
LrKhuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_5, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:208 Percentile:98.43(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The superheavy element with atomic number 117 was produced in the  Ca +
Ca +  Bk fusion reaction using the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI in Germany. This result verified the previous result of the discovery of new element 117 reported by Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Russia, which makes certain the synthesis and discovery of element 117 in human history. On the other hand, the last nucleus in the
Bk fusion reaction using the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI in Germany. This result verified the previous result of the discovery of new element 117 reported by Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Russia, which makes certain the synthesis and discovery of element 117 in human history. On the other hand, the last nucleus in the  decay chain from the element 117 was assigned to be the unknown nucleus
decay chain from the element 117 was assigned to be the unknown nucleus  Lr instead of the previously reported
Lr instead of the previously reported 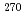 Db, and
Db, and 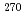 Db was found to be the
Db was found to be the  -decaying nucleus with very long half-life.
-decaying nucleus with very long half-life.
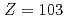 )
)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential of the heaviest actinide elements have not been measured until today owing to short half-lives and low production rate of the isotopes. Based on the surface ionization technique, we performed a measurement of the ionization potential of the heaviest actinide element, lawrencium (Lr, 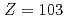 ), by using a newly developed surface ion-source installed to the JAEA-ISOL (Isotope Separator On-Line) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. We report on an evaluation of the IP value of Lr based on comparison of ionization behavior of short-lived lanthanide isotopes and
), by using a newly developed surface ion-source installed to the JAEA-ISOL (Isotope Separator On-Line) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. We report on an evaluation of the IP value of Lr based on comparison of ionization behavior of short-lived lanthanide isotopes and  Lr on Ta surface at several temperature in the ion-source.
Lr on Ta surface at several temperature in the ion-source.
 = 103)
= 103)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potentials of the heaviest actinide elements have not been measured until today owing to short half-lives and low production rates of the isotopes. Based on the surface ionization technique, we performed a measurement of the ionization potential of the heaviest actinide element, lawrencium (Lr,  = 103), by using a newly developed surface ion-source installed to the JAEA-ISOL (Isotope Separator On-Line) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. We report on an evaluation of the IP value of Lr based on comparison of ionization behavior of
= 103), by using a newly developed surface ion-source installed to the JAEA-ISOL (Isotope Separator On-Line) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. We report on an evaluation of the IP value of Lr based on comparison of ionization behavior of  Lr with that of short-lived lanthanide isotopes on Ta surface at several temperature.
Lr with that of short-lived lanthanide isotopes on Ta surface at several temperature.
Sato, Tetsuya; Stora, T.*; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eliav, E.*; Kaldor, U.*; Kratz, J. V.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eliav, E.*; Kaldor, U.*; Kratz, J. V.*; et al.
no journal, ,
It is known that an ionization efficiency of an element in surface ionization process depends on temperature, work function of the surface, and the first ionization energy of the atom of the element to be ionized. We determined the first ionization energy of lawrencium (Lr), the last member of the actinide series, using the relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization energy. The ionization energy of Lr had not been measured owing to its low production rate and short half-lives so far. The experimental value of the ionization energy is in good agreement of the theoretical one which was calculated using the state-of-the-art relativistic calculation.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Vascon, A.*; Sakama, Minoru*; Sato, Daisuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
Nagame, Yuichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
del, M.*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Vascon, A.*; Sakama, Minoru*; Sato, Daisuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.