Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhao, Y.; 吉田 実留*; 大島 竜也*; 小泉 智*; 陸川 政弘*; Szekely, N.*; Radulescu, A.*; Richter, D.*
Polymer, 86, p.157 - 167, 2016/03
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:40.53(Polymer Science)We investigated the structure and the swelling behavior of two synthesized hydrocarbon polymer electrolyte membranes, made of multiblock copolymer poly(sulphonate phenylene)-b-poly(arylene ether ketone) with different block ratios, by using small-angle neutron scattering technique. A scattering maximum (ionomer peak) at high-q range is shown commonly in both dry and wet states, with q being the magnitude of the scattering vector, while it shifts towards low-q region in the wet state due to the swelling of the ionomer domains with water. The swelling effect also results to a second scattering maximum in the middle-q range because of the water-induced microphase separation. The morphology in this q-range was elucidated in terms of Hard-Sphere model with Percus-Yervick interference approximation.
吉田 実留*; Zhao, Y.; 藤田 正博*; 大平 昭博*; 竹岡 裕子*; 小泉 智*; 陸川 政弘*
ECS Transactions, 50(2), p.1045 - 1053, 2012/10
We employed the pulsed field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFG-NMR) technique to investigate the self-diffusion coefficient of water, 
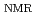 , in newly designed cation exchange membranes, made of sulfonated poly(
, in newly designed cation exchange membranes, made of sulfonated poly( -phenylene)-poly(ether ketone) multiblock copolymers, which are denoted by S-6H (
-phenylene)-poly(ether ketone) multiblock copolymers, which are denoted by S-6H ( )
)  :
: . The
. The 
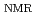 value was measured as a function of the gradient strength, g, from 0.1 to 11.0 T/m. S-6H (14) 1:1 showed the
value was measured as a function of the gradient strength, g, from 0.1 to 11.0 T/m. S-6H (14) 1:1 showed the 
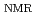 value about 10 times lower than the value in bulk liquid water. Small angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements showed two peaks in S-6H (14) 1:1. The low
value about 10 times lower than the value in bulk liquid water. Small angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements showed two peaks in S-6H (14) 1:1. The low  peak is attributed to the formation of microdomains and the high
peak is attributed to the formation of microdomains and the high  peak is due to the formation of ionic clusters in the swollen microdomains.
peak is due to the formation of ionic clusters in the swollen microdomains.
Zhao, Y.; 小泉 智; 陸川 政弘*; 吉田 実留*
no journal, ,
In this study, we employed Small-angle neutron scattering method to investigate the morphology and water distribution in a polymer electrolyte membrane, made by comb-shaped poly(sulphonate phenylene)-bpoly(arylene ether ketone) (PSP-PAEK) block copolymer. Two scattering maximums were found in both low q and high q regions, where q is the scattering vector. The low q maximum is attributed to the interaction among the self-assembly hydrophilic and hydrophobic micodomains, whereas the high q maximum is due to the water channels, namely, ion clusters. To understand the structure, a random sphere model is applied to fit the scattering data. This model reproduces experimental data well. From this model, we are able to estimate the size and volume fraction of water in hydrophilic microdomains. The analysis of front factor gives us the information of volume fraction of water in the interconnected regions. Thus the possible morphology of the membranes can be deduced.
Zhao, Y.; 小泉 智; 陸川 政弘*; 吉田 実留*
no journal, ,
We investigate the morphologies of a newly designed hydrocarbonate polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM), and commercial PEM Nafion. Two scattering maximums were observed for both materials at low q and high q regions for wet membranes, where q is a magnitude of scattering vector. The low q maximum is attributed to the formation of microdomain upon either swelling or crystallites, whereas the high q maximum is due to the formation of ionic clusters. The mesoscale and microscale structures could be elucidated by the contrast variation neutron scattering technique.
Zhao, Y.; 小泉 智; 陸川 政弘*; 吉田 実留*
no journal, ,
We employed contrast variation of small-angle neutron scattering method to investigate the morphologies of a newly designed polymer electrolyte membrane, made of multi-block copolymer poly(sulphonate phenylene)-b-poly(arylene ether ketone). Two scattering maximums were observed at low q and high q regions for wet membranes, where q is the scattering vector. The low q maximum is attributed to the formation of microdomains upon swelling, whereas the high q maximum is due to the swollen ion clusters. The morphology could be stressed by the contrast variation method. In this talk, we aim to understand the morphology and water distributions in the hydrophilic domains.
Zhao, Y.; 小泉 智; 陸川 政弘*; 吉田 実留*
no journal, ,
We employed contrast variation small-angle neutron scattering method to investigate the morphologies of a newly designed polymer electrolyte membrane, made of multi-block copolymer poly(sulphonate phenylene)-b-poly(arylene ether ketone), which is denoted by S-6H (n) x:y, where x:y means a ratio of the hydrophilic to the hydrophobic blocks. Two scattering maximums were observed at low q and high q regions for wet membranes, where q is a magnitude of scattering vector. The low q maximum is attributed to the formation of microdomains upon swelling, whereas the high q maximum is due to the formation of ionic clusters in the swollen microdomain. These morphologies could be clarified by the contrast variation method, which results in a matching in the scattering contrast either between water mixture (H O/D
O/D O) and the swollen microdomains, or between the water mixture and ionic clusters. The further analysis of the scattering profiles indicates that the microdomains are spherical and percolated with each other. Moreover, the ionic clusters distribute homogenously inside the hydrophilic domains.
O) and the swollen microdomains, or between the water mixture and ionic clusters. The further analysis of the scattering profiles indicates that the microdomains are spherical and percolated with each other. Moreover, the ionic clusters distribute homogenously inside the hydrophilic domains.
小泉 智; 陸川 政弘*; 吉田 実留*; 徳増 崇*; Zhao, Y.; 前川 康成
no journal, ,
固体高分子形燃料電池の本格普及に際して、電池システムのコスト削減は急務である。このためには高温低加湿条件で動作する高分子電荷質膜を開発することが必須な課題といえる。例えば標準膜として実績のあるナフィオン(フッ素系高分子)でも、低加湿のもと水の脱離に伴いプロトン伝導性が急激に低下する。このような事情のもと、環境調和性及び廃棄コストに優れる炭化水素系電解質膜で、低加湿のもとで動作する新材料を開発することができれば代替材料となる期待が大きい。炭化水素系電解質膜では、確立された連鎖重合や縮合重合を用いてブロック共重合体などの特殊構造高分子を合成し膜内のミクロ相分離構造を精密化することができる。高分子の1次構造に起因する分子集合体としての2次構造が高分子電解質特性を改善する可能性がある。一般にミクロ相分離等の2次構造は、膜形成のプロセスに強く依存する。特に結晶化が伴う高分子の場合は結晶構造によるミクロ構造の形成が大きく影響を受けるであろう。このため1次構造と膜形成プロセスの組合せを考えれば、これまでに予見されていない優れたプロトン伝導性を実現することが可能かも知れない。この目的のためには高分子合成化学と、構造評価を担当する高分子物性の連携が必須であろう。特にマルチスケールに渡る構造解析が求められる。そこで本研究では電解質膜の2次構造を評価する手法として中性子小角散乱を用いる。特に膜を膨潤させる水の一部を重水で置き換えることで中性子散乱のコントラストを変化させる溶媒置換コントラスト変調法を用いて2次構造の詳細を明らかにすることを目的とした。
Zhao, Y.; 小泉 智; 陸川 政弘*; 吉田 実留*
no journal, ,
Hydrocarbonic block copolymer electrolyte membranes are highly considered to be protential material for fuel cell applications. In this study, small-angle neutron scattering method is employed to observe structures of the polymer membranes. We found two scattering maximums, corresponding to the microphase separation of hydrophilic domains from hydrophobic matrix, and the ion clusters. We introduced a random sphere model to analyze the scattering profiles and estimated the possible morphologies of the membranes, and the water distributions.