Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
坂本 雅洋; 奥村 啓介; 神野 郁夫; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; Riyana E. S.; 溝上 暢人*; 溝上 伸也*
JAEA-Research 2024-017, 14 Pages, 2025/03
東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所では、2号機から燃料デブリの試験的取り出しを行い、回収物を構外輸送し茨城地区で分析することが計画されている。取り出された燃料デブリの分析結果は、将来的な燃料デブリ管理の各工程(取り出し、収納、移送、保管等)の検討にフィードバックされ、必要な技術開発に活用することが期待されている。試験的取り出しでサンプリングされる燃料デブリは数グラム程度が予定されており、その後、段階的に取り出し規模を拡大させていくことになる。試験的取り出しにおいては、構外輸送に係る関係法令に則って事前に合理的な輸送容器を検討することが必要になる。本報では物質組成や性状が不明瞭な燃料デブリ回収物の安全評価に資するため、少量燃料デブリの構外輸送に向けたA型輸送容器の適用性評価を行った。
松村 太伊知; 奥村 啓介; 坂本 雅洋; 寺島 顕一; Riyana E. S.; 近藤 千博*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113791_1 - 113791_9, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Retrieving objects with a small amount of fuel debris, such as a few grams, will begin soon at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) at the start of decommissioning. Objects retrieved from the primary containment vessel are not necessarily fuel debris; fuel debris is an object from which neutrons are emitted because it contains nuclear-fuel material. However, the characteristics of the neutrons emitted by fuel debris are unknown. Fuel debris was categorized into five types according to the elapsed time from the accident, burnup, and fuel type (UO or mixed oxide). The number and energy spectra of (
or mixed oxide). The number and energy spectra of ( ,
,  ) and spontaneous fission neutrons emitted from 1 g of each fuel debris type were estimated using the SOURCES 4C code to obtain the neutron characteristics. The results showed that the average neutron energy is approximately 2.1 MeV, regardless of the type of fuel debris. However, the intensities of neutrons emitted from the fuel debris in 1F Units 2 and 3 varied by four orders of magnitude according to the fuel debris type.
) and spontaneous fission neutrons emitted from 1 g of each fuel debris type were estimated using the SOURCES 4C code to obtain the neutron characteristics. The results showed that the average neutron energy is approximately 2.1 MeV, regardless of the type of fuel debris. However, the intensities of neutrons emitted from the fuel debris in 1F Units 2 and 3 varied by four orders of magnitude according to the fuel debris type.
坂本 雅洋; 奥村 啓介; 神野 郁夫; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; Riyana E. S.; 金子 純一*; 溝上 暢人*; 溝上 伸也*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this paper, we propose a new nuclide inventory estimation method based on computational methods, called a "theoretical scaling factor method" for difficult-to-measure (DTM) nuclides in fuel debris and radioactive wastes. The theoretical scaling factor method provides a method similar to a conventional scaling factor method. The theoretical scaling factor method, however, does not require performing many measurements to obtain correlations between a key nuclide which is easy-to-measure and a DTM nuclide. Instead of actual analytical measurements, the results of theoretical calculations are used. A correlation equation between the key nuclide and the DTM nuclide is created based on the results of theoretical calculations, and the DTM nuclide is deterministically estimated using the measurement value of the key nuclide only. In this paper, we selected Cs-135 as the DTM nuclide and Cs-137 as the key nuclide. Cs-135 has a long half-life of 2.3 10
10 years and is one of the important fission products in the safety evaluation for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, because it dissolves and migrates in groundwater easily. We confirmed the validity of the proposed method using measured data of Cs-137 and Cs-135 on radioactive wastes from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) accident obtained by many researchers. It can be used as a rational and efficient technology to reduce the analysis costs of various types of fuel debris and radioactive waste present at 1F.
years and is one of the important fission products in the safety evaluation for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, because it dissolves and migrates in groundwater easily. We confirmed the validity of the proposed method using measured data of Cs-137 and Cs-135 on radioactive wastes from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) accident obtained by many researchers. It can be used as a rational and efficient technology to reduce the analysis costs of various types of fuel debris and radioactive waste present at 1F.
Riyana, E. S.; 奥村 啓介; 坂本 雅洋; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; 神野 郁夫
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.269 - 276, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We investigated the possibility of estimating the effective neutron multiplication factor (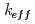 ) of the fuel debris inside the canister and primary containment vessel (PCV) of Unit 2 of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) using remote gas-radioactivity measurement via simulation-based calculations. Our results demonstrate an almost linear correlation between
) of the fuel debris inside the canister and primary containment vessel (PCV) of Unit 2 of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) using remote gas-radioactivity measurement via simulation-based calculations. Our results demonstrate an almost linear correlation between 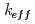 and the
and the  Kr-to-
Kr-to- Xe activity ratio with respect to various fuel debris compositions. This correlation is maintained regardless of geometries such as the fuel debris canister and the PCV.
Xe activity ratio with respect to various fuel debris compositions. This correlation is maintained regardless of geometries such as the fuel debris canister and the PCV.
 -rays of fuel debris
-rays of fuel debris松村 太伊知; 奥村 啓介; 藤田 学*; 坂本 雅洋; 寺島 顕一; Riyana, E. S.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110298_1 - 110298_8, 2022/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:41.50(Chemistry, Physical)The characterization of bremsstrahlung and  -rays from fuel debris differs from that of spent fuels evaluated to date, due to factors such as material composition and release of volatile fission products. In this work, in order to clarify the conditions under which the effect of bremsstrahlung compared to the total photons (bremsstrahlung and
-rays from fuel debris differs from that of spent fuels evaluated to date, due to factors such as material composition and release of volatile fission products. In this work, in order to clarify the conditions under which the effect of bremsstrahlung compared to the total photons (bremsstrahlung and  -rays) in fuel debris is maximized, the average energies and dose rates from the energy spectra of bremsstrahlung and
-rays) in fuel debris is maximized, the average energies and dose rates from the energy spectra of bremsstrahlung and  -rays on the fuel debris surface were obtained using a Monte Carlo simulation. In the simulation, the average energies and dose rates were evaluated with consideration of the composition, size, fission product release, and retrieval time of the fuel debris. The simulation showed that the composition with the largest amount of change to the average total photons energy caused by bremsstrahlung was the molten fuel debris, and the composition with the maximum fraction of bremsstrahlung in the dose rate was the UO
-rays on the fuel debris surface were obtained using a Monte Carlo simulation. In the simulation, the average energies and dose rates were evaluated with consideration of the composition, size, fission product release, and retrieval time of the fuel debris. The simulation showed that the composition with the largest amount of change to the average total photons energy caused by bremsstrahlung was the molten fuel debris, and the composition with the maximum fraction of bremsstrahlung in the dose rate was the UO . The maximum value of the fraction of bremsstrahlung in the dose rate was evaluated to be about 17%. This work is expected to contribute to the prediction of the radiation characteristics of the fuel debris that will be retrieved from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in the near future.
. The maximum value of the fraction of bremsstrahlung in the dose rate was evaluated to be about 17%. This work is expected to contribute to the prediction of the radiation characteristics of the fuel debris that will be retrieved from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in the near future.
Riyana, E. S.; 奥村 啓介; 坂本 雅洋; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.424 - 430, 2022/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Modification of the Monte Carlo depletion calculation code OpenMC was performed to enable the depletion calculation of the subcritical neutron multiplying system. With the modified code, it became possible to evaluate the quantity of short half-life fission products from spontaneous and induced fissions in the subcritical system. As a preliminary study, it was applied to the fuel debris storage canister filled with nuclear materials and spontaneous fission nuclides. It was confirmed that the code could successfully provide a quantity of short half-life FPs over time and provide the relationship between the activity ratio of Kr-88 to Xe-135 and effective neutron multiplication factor of the canister.
Riyana, E. S.; 奥村 啓介; 寺島 顕一; 松村 太伊知; 坂本 雅洋
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00543_1 - 19-00543_8, 2020/06
Prediction of the fuel debris location and distribution inside the primary containment vessel (PCV) of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is important to decide further decommissioning step and strategy. The radiation measurements in the past internal investigations have not yet provided enough information to predict fuel debris location and its distribution inside PCV. To support further measurement efforts, we simulate the detector response inside the PCV. The calculation result could provide a base on deciding suitable detector systems to assist the efforts on searching, localizing and defining distributions of the fuel debris.
Riyana, E. S.; 奥村 啓介; 寺島 顕一
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.922 - 931, 2019/09
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:53.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Determination of fuel debris location and distribution inside primary containment vessel of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station is important to decide further decommissioning step and strategy. We calculate neutron flux produced from fuel debris and secondary particles photon resulted from neutron reaction with nuclides inside fuel debris, including direct photon emission from FPs in fuel debris. Neutron and gamma characteristics resulted from calculation could be use as basis for determination suitable spectrometer system or detector for searching, localizing and treatment of fuel debris.
Riyana, E. S.*; 須田 翔哉*; 石橋 健二*; 松浦 秀明*; 片倉 純一*; Sun, G. M.*; 片野 好章
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(5), p.369 - 375, 2019/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)原子炉は主に核分裂片のベータ崩壊チェインから多数の反電子ニュートリノを生成し、それらのニュートリノは主にMeV程度のエネルギーを有することが知られている。一方、エネルギーkeV程度の低エネルギーニュートリノは燃料の燃焼の情報を含むと考えられ、その低エネルギーニュートリノは計測技術の進歩により将来的に測定可能になる可能性がある。そこで、著者らはkeV領域の低エネルギーニュートリノの生成に注目した。本研究では、典型的なPWRとその他の型の原子炉について低エネルギーニュートリノスペクトルを示し、それらは燃料の燃焼に従って低Q値をもつ核種が蓄積されるにつれて生成が増えることを示した。
Riyana, E. S.; 奥村 啓介; 寺島 顕一
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/05
Determination of fuel debris location and distribution inside primary containment vessel (PCV) of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station is important to decide further decommissioning step and strategy. Past measurements not yet provide enough information to determine fuel debris location and its distribution inside PCV. To support further measurements effort, we simulate detector response inside PCV based on calculated photon and neutron emission spectrum produced from fuel debris. The Calculation result could be use as basis for determination of suitable spectrometer system or detector for search, localized, define fuel debris distributions and treatment of fuel debris.
奥村 啓介; Riyana, E. S.; 佐藤 若英*; 前田 裕文*; 片倉 純一*; 鎌田 創*; Joyce, M. J.*; Lennox, B.*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.108 - 112, 2019/01
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の原子炉格納容器(PCV)内における線量率分布の予測手法を確立するため、以下の一連の計算を行った。(1)事故時の燃料組成を得るための燃焼計算、(2)不純物を含む炉内構造物の放射化計算、(3) IRIDによる事故解析の結果に基づくPCV中のCs汚染分布の推定、(4) PCV内の放射性核種の崩壊計算、(5)線量率を得るための光子輸送計算。これらの計算の後、ドライウェル周辺のCs濃度を、IRIDによるPCV調査で測定された局所線量率の結果と一致するように修正した。
奥村 啓介; Riyana, E. S.
JAEA-Conf 2018-001, p.63 - 68, 2018/12
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の廃炉は未踏の分野である。IRIDによってロボットによる格納容器(PCV)の内部調査が進められているが、PCV内部の実際の状況や燃料デブリの特性はまだ十分に解明されていない。このような状況下で、信頼性の高いデータを使った計算シミュレーションは、1F廃炉の多くの問題を解決する有効な手段となる。ここでは、JENDL-4.0のような近年の核データを利用した研究開発への応用例として、(1)PCVにおける線量率分布の予測、(2)PCV内の水中燃料デブリ探査のためのROVシステム、(3)燃料デブリキャニスター内の核燃料物質の非破壊測定、について紹介する。
Riyana, E. S.; 坂本 雅洋; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
We investigated the possibility of estimating the effective neutron multiplication factor (keff) of the fuel-debris inside the primary containment vessel (PCV) of unit-2 of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) using remote gas-radioactivity measurement. Our calculation result demonstrates the correlation between keff and the activity ratio (AR) of  Kr-to-
Kr-to- Xe for various fuel debris compositions and geometry. We also show the time-dependent behavior of the AR of
Xe for various fuel debris compositions and geometry. We also show the time-dependent behavior of the AR of  Kr-to-
Kr-to- Xe when the keff changes suddenly in PCV.
Xe when the keff changes suddenly in PCV.
松村 太伊知; 坂本 雅洋; 寺島 顕一; Riyana, E. S.; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
これまでの原子炉格納容器(PCV)内部調査から、福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の1-3号機には、燃料と被覆管等が溶融した後に固化した燃料デブリが存在すると考えられている。2023年には、2号機(1F2)から数g程度の燃料デブリ試料の試験的取り出しが予定されている。燃料デブリの検知において中性子が検出されれば燃料デブリであると推定できるため、燃料デブリから放出される中性子の特性評価を行うことは重要である。そこで、UO 燃料のみで構成されていた1F2と本格取出し時期での対象とされMOX燃料を部分的に含んでいた3号機(1F3)からの取出し燃料デブリに対する検出器開発や中性子応答の物理的解釈に資するため、1F2(広範囲燃焼度UO
燃料のみで構成されていた1F2と本格取出し時期での対象とされMOX燃料を部分的に含んでいた3号機(1F3)からの取出し燃料デブリに対する検出器開発や中性子応答の物理的解釈に資するため、1F2(広範囲燃焼度UO )、1F3(低燃焼度MOX)、TMI-2(低燃焼度UO
)、1F3(低燃焼度MOX)、TMI-2(低燃焼度UO )の3種類の代表的な燃料デブリモデルに対し、それぞれの燃焼履歴に基づく核種インベントリデータとSOURCES 4Cコードを用いて、燃料デブリから放出される自発核分裂(遅発中性子を含む)と(
)の3種類の代表的な燃料デブリモデルに対し、それぞれの燃焼履歴に基づく核種インベントリデータとSOURCES 4Cコードを用いて、燃料デブリから放出される自発核分裂(遅発中性子を含む)と( , n)反応によって放出される中性子の特性評価を行った。
, n)反応によって放出される中性子の特性評価を行った。
寺島 顕一; 坂本 雅洋; 松村 太伊知; Riyana E. S.; 神野 郁夫; 奥村 啓介
no journal, ,
At the time of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, mixed oxide (MOX) fuels were partially loaded in the core of Unit-3 while not in Unit-1 and Unit-2. Since the MOX fuel contain larger amount of plutonium even if its burnup degree is relatively smaller than that of UO fuel, it is expected to distinguish whether fuel debris are originated from MOX or UO
fuel, it is expected to distinguish whether fuel debris are originated from MOX or UO . Therefore, we focused on
. Therefore, we focused on  Cm and
Cm and  Eu generated until the accident. From the burnup calculations, the possibility of a method for detecting the MOX-derived fuel debris was suggested.
Eu generated until the accident. From the burnup calculations, the possibility of a method for detecting the MOX-derived fuel debris was suggested.
松村 太伊知; 奥村 啓介; 神野 郁夫; Riyana E. S.; 寺島 顕一; 坂本 雅洋; 佐藤 若英*
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉において、回収物中の核燃料物質の有無また含有量を把握することは重要である。核燃料物質として中性子によって誘導核分裂を起こすU(MAを含む)を想定し、14MeV高速中性子の照射で発生する遅発中性子を用いてU量の評価が可能な手法を提案する。
 Xe,
Xe,  Kr) emitted by fuel debris for criticality estimation
Kr) emitted by fuel debris for criticality estimationRiyana, E. S.; 坂本 雅洋; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; 奥村 啓介; 神野 郁夫
no journal, ,
Our previous study showed a linear relationship between the activity ratio of  Kr to
Kr to  Xe and the effective multiplication factor,
Xe and the effective multiplication factor, 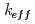 , in a primary containment vessel (PCV) and in a fuel debris canister. The accuracy of the activity ratio, which closely related to the accuracy of predicted
, in a primary containment vessel (PCV) and in a fuel debris canister. The accuracy of the activity ratio, which closely related to the accuracy of predicted 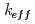 , is estimated based on an existing gamma ray energy spectrum. Practical measurement method for the gamma ray from nuclides in the PCV and the fuel debris canister gas is proposed.
, is estimated based on an existing gamma ray energy spectrum. Practical measurement method for the gamma ray from nuclides in the PCV and the fuel debris canister gas is proposed.
松村 太伊知; 奥村 啓介; 坂本 雅洋; 寺島 顕一; Riyana E. S.; 近藤 千博*
no journal, ,
Retrieving objects with a small amount, such as a few grams, will begin soon at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station as the start of decommissioning process. The retrieved objects will be sorted as fuel debris and others for reducing the amount of long-time storage. Since the fuel debris emits neutrons, the knowledge of emitted neutron features is necessary for the design of neutron detectors. For this purpose, we estimated the number and energy spectra of ( ,
,  ) and the spontaneous fission neutrons emitted from 1 g of fuel debris by calculation using the SOURCES 4C code. The calculations were performed for five types of fuel debris, according to the elapsed time from the accident, burnup, and fuel type. The results showed that the average neutron energy is
) and the spontaneous fission neutrons emitted from 1 g of fuel debris by calculation using the SOURCES 4C code. The calculations were performed for five types of fuel debris, according to the elapsed time from the accident, burnup, and fuel type. The results showed that the average neutron energy is  2 MeV regardless of the fuel debris type, however, the intensity changed four orders of magnitude according to the fuel debris type.
2 MeV regardless of the fuel debris type, however, the intensity changed four orders of magnitude according to the fuel debris type.
神野 郁夫; 奥村 啓介; 松村 太伊知; Riyana E. S.; 寺島 顕一; 坂本 雅洋
no journal, ,
東京電力福島第一原子力発電所2号機のシールドプラグ下部汚染分布を評価するため、ガンマ線ピンホールカメラを用いて一定厚さの遮蔽体背後にあるCs-137汚染分布を得る手法を計算により開発した。
Riyana E. S.; 坂本 雅洋; 松村 太伊知; 寺島 顕一; 奥村 啓介; 神野 郁夫
no journal, ,
The activity ratio of short half-life noble gas fission products,  Kr to
Kr to  Xe (A(
Xe (A( Kr/
Kr/ Xe)), has close relationship with the criticality (
Xe)), has close relationship with the criticality (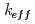 ) in the primary containment vessel (PCV) or fuel debris canister, in which fuel debris are accumulated. In this paper, we investigated the time-dependence of the A(
) in the primary containment vessel (PCV) or fuel debris canister, in which fuel debris are accumulated. In this paper, we investigated the time-dependence of the A( Kr/
Kr/ Xe) when the
Xe) when the 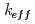 changes according to an incident such as the change of geometry in the PCV. Our calculation shows a slow change of the A(
changes according to an incident such as the change of geometry in the PCV. Our calculation shows a slow change of the A( Kr/
Kr/ Xe) value with the maximum or minimum values before settling in a new stable value after several hours from the
Xe) value with the maximum or minimum values before settling in a new stable value after several hours from the 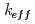 change. The applicability and the suitability of the A(
change. The applicability and the suitability of the A( Kr/
Kr/ Xe) time-dependent measurement is discussed for the monitoring of the
Xe) time-dependent measurement is discussed for the monitoring of the 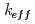 in PCV.
in PCV.