Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 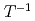 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
 studied by means of NMR/NQR techniques
studied by means of NMR/NQR techniquesSakai, Hironori; Kurita, Nobuyuki*; Miclea, C. F.*; Movshovich, R.*; Lee, H.-O.*; Ronning, F.*; Bauer, E. D.*; Thompson, J. D.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA059_1 - SA059_3, 2011/07
The effect of dilute La substitution in Ce La
La RhIn
RhIn (0
(0 x
x 0.07) has been investigated microscopically by nuclear magnetic/quadrupole resonance (NMR/NQR). By the dilute La substitutions, the 4
0.07) has been investigated microscopically by nuclear magnetic/quadrupole resonance (NMR/NQR). By the dilute La substitutions, the 4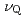 lines for In(1) sites are found to be undisturbed and to have a reasonably narrow width, even in the ordered AF state. These 4
lines for In(1) sites are found to be undisturbed and to have a reasonably narrow width, even in the ordered AF state. These 4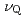 positions in the La-substituted CeRhIn
positions in the La-substituted CeRhIn indicate a decrease of the internal field on In(1) sites, due to the reduction of hyperfine couplings by La substitutions. The spin-lattice relaxation rates (
indicate a decrease of the internal field on In(1) sites, due to the reduction of hyperfine couplings by La substitutions. The spin-lattice relaxation rates (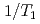 ) using these 4
) using these 4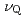 lines at high temperatures can be understood by the reduction of exchange energy and effective moments. On the other hand,
lines at high temperatures can be understood by the reduction of exchange energy and effective moments. On the other hand, 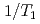 in the AF ordered state can be explained by a gapped Fermi surface and spin fluctuations of uncompensated localized Ce moments near the La ions.
in the AF ordered state can be explained by a gapped Fermi surface and spin fluctuations of uncompensated localized Ce moments near the La ions.
Bauer, E. D.*; Yang, Y.-F.*; Capan, C.*; Urbano, R. R.*; Miclea, C. F.*; Sakai, Hironori; Ronning, F.*; Graf, M. J.*; Balatsky, A. V.*; Movshovich, R.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(17), p.6857 - 6861, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.15(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here, we report a manifestation of electronic inhomogeneity in a strongly correlated  -electron system, using CeCoIn
-electron system, using CeCoIn as an example. A thermodynamic analysis of its superconductivity, combined with nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements, shows that nonmagnetic impurities (Y, La, Yb, Th, Hg, and Sn) locally suppress unconventional superconductivity, generating an inhomogeneous electronic "Swiss cheese" due to disrupted periodicity of the Kondo lattice. Our analysis may be generalized to include related systems, suggesting that electronic inhomogeneity should be considered broadly in Kondo lattice materials.
as an example. A thermodynamic analysis of its superconductivity, combined with nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements, shows that nonmagnetic impurities (Y, La, Yb, Th, Hg, and Sn) locally suppress unconventional superconductivity, generating an inhomogeneous electronic "Swiss cheese" due to disrupted periodicity of the Kondo lattice. Our analysis may be generalized to include related systems, suggesting that electronic inhomogeneity should be considered broadly in Kondo lattice materials.
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Zhang, K.*; Rotter, F.*; Schwen, D.*; Ronning, C.*; Hofs ss, H.*; Krauser, J.*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; et al.
ss, H.*; Krauser, J.*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to study the allotropic effect on ripple formation on carbon surfaces induced by sputter erosion, three types of carbon materials, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), single crystalline diamond and tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) films, were irradiated with 5 keV Xe at an incident angle of 30 degree. The irradiation fluence was 2
at an incident angle of 30 degree. The irradiation fluence was 2 10
10 cm
cm for all irradiations. No ripples were formed on diamond and ta-C surfaces, while ripples with a wavelength of
for all irradiations. No ripples were formed on diamond and ta-C surfaces, while ripples with a wavelength of  100 nm occurred on HOPG. Electron energy loss spectroscopy revealed that the surfaces of all carbon materials became amorphous with similar densities upon irradiation. Therefore, the presented results clearly show that rippling depends on the nature of the underlying carbon materials. The mechanism for rippling of carbon materials will be discussed.
100 nm occurred on HOPG. Electron energy loss spectroscopy revealed that the surfaces of all carbon materials became amorphous with similar densities upon irradiation. Therefore, the presented results clearly show that rippling depends on the nature of the underlying carbon materials. The mechanism for rippling of carbon materials will be discussed.