Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okumura, Masahiko; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Lammers, L. N.*; Ikeda, Takashi*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 189, p.135 - 145, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:87.37(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
 (am) solubility at 25
(am) solubility at 25 C in the Ca
C in the Ca -Na
-Na -H
-H -Cl
-Cl -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; A Critical review
O system; A Critical reviewRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Altmaier, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 47(5), p.855 - 891, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:10.04(Chemistry, Physical)We have critically reviewed experimental data for Zr hydrolysis constant values for formation of several mononuclear and polynuclear species and a solubility product value for ZrO (am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
(am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH) (aq), Zr(OH)
(aq), Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH)
 and Ca
and Ca Zr(OH)
Zr(OH)
 , and the solubility product for ZrO
, and the solubility product for ZrO (am) after the critical review.
(am) after the critical review.
Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 65(5), p.371 - 375, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:77.31(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sassi, M.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 19(39), p.27007 - 27014, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.97(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 (am) in the aqueous K
(am) in the aqueous K - HCO
- HCO
 - CO
- CO
 - OH
- OH - H
- H O system
O systemRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K.*
Radiochimica Acta, 105(8), p.637 - 647, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.88(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility of HfO (am) was determined as a function of KHCO
(am) was determined as a function of KHCO concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg
concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg to 0.1 mol.kg
to 0.1 mol.kg . The solubility of HfO
. The solubility of HfO (am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO
(am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO
concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-)
concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-) (CO
(CO )
)
 and Hf(CO
and Hf(CO )
)
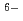 . The log
. The log K
K values for the reactions [Hf
values for the reactions [Hf + 2 CO
+ 2 CO
 +2 OH
+2 OH
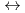 Hf(OH)
Hf(OH) (CO
(CO )
)
 ] and [Hf
] and [Hf + 5 CO
+ 5 CO

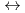 Hf(CO
Hf(CO )
)
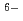 ], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53
], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53  0.46 and 41.53
0.46 and 41.53  0.46, respectively.
0.46, respectively.
Okumura, Masahiko; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
AIP Advances (Internet), 7(5), p.055211_1 - 055211_9, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.42(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)no abstracts in English
Kerisit, S.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(4), p.389 - 400, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:74.98(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 (cr)
(cr)Rai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Radiochimica Acta, 104(8), p.583 - 592, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.30(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility studies were conducted with HfO (cr) solid as a function of acid concentrations. These studies involved (1) using two different amounts of the solid phase, (2) acid washing the bulk solid phase, (3) preheating the solid phase to 1400
(cr) solid as a function of acid concentrations. These studies involved (1) using two different amounts of the solid phase, (2) acid washing the bulk solid phase, (3) preheating the solid phase to 1400  C, and (4) heating amorphous HfO
C, and (4) heating amorphous HfO (am) suspensions to 90
(am) suspensions to 90  C to ascertain whether the HfO
C to ascertain whether the HfO (am) converts to HfO
(am) converts to HfO (cr) and to determine the solubility from the oversaturation direction. Based on the results of these treatments it is concluded that the HfO
(cr) and to determine the solubility from the oversaturation direction. Based on the results of these treatments it is concluded that the HfO (cr) contains a small fraction of less crystalline, but not amorphous, material [HfO
(cr) contains a small fraction of less crystalline, but not amorphous, material [HfO (lcr)] and this, rather than the HfO
(lcr)] and this, rather than the HfO (cr), is the solubility-controlling phase in the range of experimental variables investigated in this study. The solubility data are interpreted using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The log
(cr), is the solubility-controlling phase in the range of experimental variables investigated in this study. The solubility data are interpreted using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The log of the solubility product of HfO
of the solubility product of HfO (cr) is estimated. The observation of a small fraction of less crystalline higher solubility material is consistent with the general picture that mineral surfaces are often structurally and/or imperfect leading to a higher solubility than the bulk crystalline solid. This study stresses the urgent need, during interpretation of solubility data, of taking precautions to make certain that the observed solubility behavior for sparingly-soluble solids is assigned to the proper solid phase.
(cr) is estimated. The observation of a small fraction of less crystalline higher solubility material is consistent with the general picture that mineral surfaces are often structurally and/or imperfect leading to a higher solubility than the bulk crystalline solid. This study stresses the urgent need, during interpretation of solubility data, of taking precautions to make certain that the observed solubility behavior for sparingly-soluble solids is assigned to the proper solid phase.
Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.108 - 114, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.47(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 =40;
=40;  Cu
CuSahin, E.*; Doncel, M.*; Sieja, K.*; De Angelis, G.*; Gadea, A.*; Quintana, B.*; G rgen, A.*; Modamio, V.*; Mengoni, D.*; Valiente-Dob
rgen, A.*; Modamio, V.*; Mengoni, D.*; Valiente-Dob n, J. J.*; et al.
n, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(3), p.034302_1 - 034302_9, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:82.31(Physics, Nuclear)Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Zheng, X.*; Underwood, T. R.*; Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Understanding the radionuclide diffusion phenomena is crucial for the safe geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The diffusion in clay-water systems is particularly important for the performance of the artificial barrier made of bentonite. Numerical simulation is one of the best research methods for understanding the phenomenon at the microscopic level. Recently, large-scale molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the systems with clay particles and water molecules were realized. In this presentation, we will show numerical simulation results of diffusion of cesium in the large system with MD. Our recent results suggest that cesium is less diffuse than sodium.
Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Zheng, X.*; Underwood, T. R.*; Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
In order to evaluate the long-term safety of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, it is necessary to clarify and model the migration behavior of radionuclides in clay minerals used as buffer material on a molecular scale. In this study, we perform classical molecular dynamics simulations in clay minerals-water systems and evaluate free-energy profiles of clay minerals to clarify and model the diffusion behavior of cesium on a molecular scale.
Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okumura, Masahiko; Kerisit, S.*; Bourg, I.*; Lammers, L.*; Ikeda, Takashi*; Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K.*; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Zheng, X.*; Underwood, T. R.*; Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
The migration behavior of radionuclides in clay minerals used as buffer material must be clarified for the long-term safety of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The recent development of supercomputers enables us to perform large-scale classical molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to evaluate the adsorption properties of cation to clay minerals. We evaluated the free-energy profiles of cesium adsorption from mesopore to the interlayer of Na-montmorillonite by classical MD on a supercomputer. We found that the free-energy profiles of cesium adsorption depend on the interlayer distance of the Na-montmorillonite and mesopore salinity in the water system. In the presentation, we also discuss the distribution and diffusion coefficients of cesium ions.
Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Zheng, X.*; Underwood, T. R.*; Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
The migration behavior of radionuclides in clay minerals used as buffer material must be clarified for the long-term safety of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. We can investigate diffusion/adsorption behavior of cesium ion and sodium ion in clay minerals and water systems at molecular scale using molecular dynamics simulation on a supercomputing system. In this study, we evaluated the free energy profiles of cesium and sodium ions adsorption to the interlayer of Na-montmorillonite from bulk water in mesopore. As a result, we found that the minimum of free energy profiles of these cations locates in the interlayer of Na-montmorillonite, and the minimum of free energy profile of cesium is lower than that of sodium. This result shows that the affinity of cesium ion to Na-montmorillonite is stronger than that of sodium ion. Moreover, we confirmed that the affinities of both cations to Na-montmorillonite decrease with salinity increase, and these cations maintain their adsorption mechanism. In the presentation, we discuss layer charge and layer size dependence on the free energy profiles of these cations.
Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Zheng, X.*; Underwood, T. R.*; Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Bourg, I. C.*; Okumura, Masahiko
no journal, ,
In order to evaluate the long-term safety of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, it is necessary to understand the migration behavior of radionuclides in clay minerals used as buffer materials. In this study, the difference in the diffusion behavior of cesium and sodium ions in Na-montmorillonite is analyzed by evaluating the free energy using classical molecular dynamics simulations.