Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
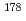 Hg
HgM ller-Gatermann, C.*; Dewald, A.*; Fransen, C.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Beckers, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Braunroth, T.*; Cullen, D. M.*; Fruet, G.*; et al.
ller-Gatermann, C.*; Dewald, A.*; Fransen, C.*; Auranen, K.*; Badran, H.*; Beckers, M.*; Blazhev, A.*; Braunroth, T.*; Cullen, D. M.*; Fruet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054325_1 - 054325_7, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.85(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
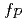 shell; Lifetime measurements in
shell; Lifetime measurements in  Zn
ZnQueiser, M.*; Vogt, A.*; Seidlitz, M.*; Reiter, P.*; Togashi, Tomoaki*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Homma, Michio*; Petkov, P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044313_1 - 044313_13, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.71(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Giroud, C.*; Jachmich, S.*; Jacquet, P.*; J rvinen, A.*; Lerche, E.*; Rimini, F.*; Aho-Mantila, L.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Balboa, I.*; Belo, P.*; et al.
rvinen, A.*; Lerche, E.*; Rimini, F.*; Aho-Mantila, L.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Balboa, I.*; Belo, P.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 57(3), p.035004_1 - 035004_20, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:95.82(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reports the progress made at JET-ILW on integrating the requirements of the reference ITER baseline scenario with normalized confinement factor of 1, at a normalized pressure of 1.8 together with partially detached divertor whilst maintaining these conditions over many energy confinement times. The 2.5 MA high triangularity ELMy H-modes are studied with two different divertor configurations with D-gas injection and nitrogen seeding. The power load reduction with N seeding is reported. The relationship between an increase in energy confinement and pedestal pressure with triangularity is investigated. The operational space of both plasma configurations is studied together with the ELM energy losses and stability of the pedestal of unseeded and seeded plasmas.
Bolton, P.; Borghesi, M.*; Brenner, C.*; Carroll, D. C.*; De Martinis, C.*; Fiorini, F.*; Flacco, A.*; Floquet, V.*; Fuchs, J.*; Gallegos, P.*; et al.
Physica Medica; European Journal of Medical Physics, 30(3), p.255 - 270, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:91 Percentile:89.30(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Urano, Hajime; Saibene, G.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Parail, V.*; de Vries, P.*; Sartori, R.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113004_1 - 113004_10, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:42.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of TF ripple on the edge pedestal characteristics are examined in JET and JT-60U. By the installation of ferritic inserts, TF ripple was reduced from 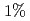 to
to 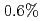 in JT-60U. In JET, TF ripple was varied from
in JT-60U. In JET, TF ripple was varied from 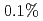 to
to 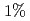 by feeding different currents to TF coils. The pedestal pressure was similar with reduced ripple in JT-60U. In JET, no clear difference of the pedestal characteristics was also observed. The edge toroidal rotation clearly decreased in counter direction by increased TF ripple. However, in JT-60U, the ELM frequency decreased by
by feeding different currents to TF coils. The pedestal pressure was similar with reduced ripple in JT-60U. In JET, no clear difference of the pedestal characteristics was also observed. The edge toroidal rotation clearly decreased in counter direction by increased TF ripple. However, in JT-60U, the ELM frequency decreased by 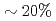 and the increased ELM loss power by
and the increased ELM loss power by 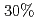 with reduced ripple. In JET, ELM frequency increases only slightly with increased TF ripple. From this inter-machine experiment, TF ripple less than
with reduced ripple. In JET, ELM frequency increases only slightly with increased TF ripple. From this inter-machine experiment, TF ripple less than 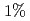 does not strongly affect the pedestal pressure. The effect of TF ripple on pedestal characteristics at lower collisionality close to ITER should be investigated as a next step study.
does not strongly affect the pedestal pressure. The effect of TF ripple on pedestal characteristics at lower collisionality close to ITER should be investigated as a next step study.
Alimov, V.; Shu, Wataru*; Roth, J.*; Lindig, S.*; Balden, M.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.572 - 575, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:98.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Blistering and deuterium retention in re-crystallized tungsten exposed to a low energy (38 eV/D) and high deuterium ion flux (10 D/m
D/m s) D plasma at ion fluences of 10
s) D plasma at ion fluences of 10 and 10
and 10 D/m
D/m at temperatures in the range from 320 to 800 K have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the nuclear reaction. During exposure to the D plasma blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are formed on the W surface. At the temperatures above 700 K the blisters disappear. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching its maximum value of about 7
at temperatures in the range from 320 to 800 K have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the nuclear reaction. During exposure to the D plasma blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are formed on the W surface. At the temperatures above 700 K the blisters disappear. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching its maximum value of about 7 10
10 D/m
D/m at 530 K and about 1
at 530 K and about 1 10
10 D m
D m at 480 K for ion fluences of 10
at 480 K for ion fluences of 10 and 10
and 10 D/m
D/m , respectively. As the temperature grows further, the D retention decreases to about 10
, respectively. As the temperature grows further, the D retention decreases to about 10 D/m
D/m at 800 K.
at 800 K.
Alimov, V.; Tyburska, B.*; Ogorodnikova, O. V.*; Roth, J.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 415(Suppl.1), p.S628 - S631, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:71.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Deuterium retention in porous vacuum plasma spraying tungsten coating exposed at various temperatures to a low-energy, high flux (10 D/m
D/m s) pure D and helium-seeded D plasmas was examined by thermal desorption spectroscopy and the nuclear reaction. Under exposure to pure D plasma (76 eV D
s) pure D and helium-seeded D plasmas was examined by thermal desorption spectroscopy and the nuclear reaction. Under exposure to pure D plasma (76 eV D
 ) at 340-560 K, the D concentration reaches 1
) at 340-560 K, the D concentration reaches 1 2 at.% at depths of several micrometers, while at temperatures above 700 K the D concentration is below 10
2 at.% at depths of several micrometers, while at temperatures above 700 K the D concentration is below 10 at.% and deuterium is retained over the whole thickness of the coating. Seeding of 76 eV He
at.% and deuterium is retained over the whole thickness of the coating. Seeding of 76 eV He into the D plasma reduces the D retention at temperatures of 400-600 K. However, at temperature above 700 K, the D retention becomes comparable to that for pure D plasma exposure.
into the D plasma reduces the D retention at temperatures of 400-600 K. However, at temperature above 700 K, the D retention becomes comparable to that for pure D plasma exposure.
Imbeaux, F.*; Citrin, J.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; K chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083026_1 - 083026_11, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:80.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas) O
O nanoparticles on radiolytic H
nanoparticles on radiolytic H O
O production in water
production in waterRoth, O.*; Hiroki, Akihiro; LaVerne, J. A.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115(16), p.8144 - 8149, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:40.56(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrogen peroxide, H O
O , is the major stable oxidizing species produced in the radiolysis of water and understanding the mechanisms involved in its production is important both from a fundamental science perspective and for engineering purposes, in particular within the nuclear power industry. In this work, the yields of H
, is the major stable oxidizing species produced in the radiolysis of water and understanding the mechanisms involved in its production is important both from a fundamental science perspective and for engineering purposes, in particular within the nuclear power industry. In this work, the yields of H O
O were determined in aqueous slurries in the pH range of 1-13 with various amounts of added Al
were determined in aqueous slurries in the pH range of 1-13 with various amounts of added Al O
O nanoparticles. The addition of Al
nanoparticles. The addition of Al O
O generally decreased H
generally decreased H O
O yields at all pH values within this range in the
yields at all pH values within this range in the  radiolysis of both deaerated and aerated slurries, except at very high pH. Very little effect of pH was observed in the
radiolysis of both deaerated and aerated slurries, except at very high pH. Very little effect of pH was observed in the  radiolysis of deaerated systems in the pH range of 3-8, whereas a large increase in H
radiolysis of deaerated systems in the pH range of 3-8, whereas a large increase in H O
O yields was observed in aerated Al
yields was observed in aerated Al O
O slurries at the extreme pH values. Scavenger capacity studies using methanol as an OH radical scavenger show that the decrease in H
slurries at the extreme pH values. Scavenger capacity studies using methanol as an OH radical scavenger show that the decrease in H O
O yields with added Al
yields with added Al O
O occurs at relatively long time scales and is probably due to reaction of the solid nanoparticles with OH radicals.
occurs at relatively long time scales and is probably due to reaction of the solid nanoparticles with OH radicals.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from several tokamaks have been analyzed by means of integrated modeling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. The results of these studies are presented and projections to ITER current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios are done, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of 15 MA). Various transport models have been tested by means of integrated modeling against experimental data from ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod, DIII-D, JET and Tore Supra, including both Ohmic plasmas and discharges with additional heating/current drive. With using the most successful models, projections to the ITER current ramp-up and ramp-down phases are carried out. Though significant differences between models appear on the electron temperature prediction, the final q-profiles reached in the simulation are rather close.
Alimov, V.; Roth, J.*; Shu, Wataru*; Komarov, D. A.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 399(2-3), p.225 - 230, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:91.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A study of the influence of the deposition conditions on the surface morphology and deuterium concentration in tungsten deposition layers formed by magnetron sputtering and in the linear plasma generator has been carried out. Adhesion of the W layer to substrate is shown to depend on the coefficients of thermal expansion for tungsten and substrate material, thickness of the W layer, and the substrate temperature during layer deposition. A decreased D concentration for increased substrate temperatures and deposition rate are observed.
Harres, K.*; Alber, I.*; Tauschwitz, A.*; Bagnoud, V.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; G nther, M.*; N
nther, M.*; N rnberg, F.*; Otten, A.*; Schollmeier, M.*; Sch
rnberg, F.*; Otten, A.*; Schollmeier, M.*; Sch trumpf, J.*; et al.
trumpf, J.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 17(2), p.023107_1 - 023107_7, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:85.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Alimov, V.; Shu, Wataru*; Roth, J.*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Lindig, S.*; Balden, M.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Physica Scripta, T138, p.014048_1 - 014048_5, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:130 Percentile:95.26(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Blistering and deuterium retention in re-crystallized tungsten exposed to low-energy, high flux (10 D/m
D/m s) pure and helium-seeded D plasmas to a fluence of 10
s) pure and helium-seeded D plasmas to a fluence of 10 D/m
D/m have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the D(
have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the D( He,p)
He,p) He nuclear reaction at a
He nuclear reaction at a  He energy varied from 0.69 to 4.0 MeV. In the case of exposure to pure D plasma (38 eV/D), blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are found on the W surface. No blisters appear at temperatures above 700 K. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching a maximum value of about 10
He energy varied from 0.69 to 4.0 MeV. In the case of exposure to pure D plasma (38 eV/D), blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are found on the W surface. No blisters appear at temperatures above 700 K. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching a maximum value of about 10 D/m
D/m at 480 K, and then decreases as the temperature rises further. Seeding of helium into the D plasma to the He ion concentration of 0.2 and 5% significantly reduces the D retention at elevated temperatures and prevents formation of the blisters.
at 480 K, and then decreases as the temperature rises further. Seeding of helium into the D plasma to the He ion concentration of 0.2 and 5% significantly reduces the D retention at elevated temperatures and prevents formation of the blisters.
Roth, M.*; Alber, I.*; Bagnoud, V.*; Brown, C. R. D.*; Clarke, R.*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fernandez, J.*; Flippo, K.*; Gaillard, S.*; Gauthier, C.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 51(12), p.124039_1 - 124039_7, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:73.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Snyder, P. B.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085035_1 - 085035_8, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:196 Percentile:98.75(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The pressure at the top of the edge transport barrier impacts fusion performance, while large ELMs can constrain material lifetimes. Investigation of intermediate wavelength MHD mode has led to improved understanding of the pedestal height and the mechanism for ELMs. The combination of high resolution diagnostics and a suite of stability codes has made edge stability analysis routine, and contribute both to understanding, and to experimental planning and performance optimization. Here we present extensive comparisons of observations to predicted edge stability boundaries on several tokamaks, both for the standard (Type I) ELM regime, and for small ELM and ELM-free regimes. We further discuss a new predictive model for the pedestal height and width (EPED1), developed by self-consistently combining a simple width model with peeling-ballooning stability calculations. This model is tested against experimental measurements, and used in initial predictions of the pedestal height for ITER.
Shinohara, Koji; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; L nnroth, J.*; Saibene, G.*; Parail, V.*; Kamada, Yutaka
nnroth, J.*; Saibene, G.*; Parail, V.*; Kamada, Yutaka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(1), p.24 - 32, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:83.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Alimov, V.; Shu, Wataru; Roth, J.*; Komarov, D. A.*; Lindig, S.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Advanced Materials Research, 59, p.42 - 45, 2009/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Snyder, P. B.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Beurskens, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Investigation of intermediate wavelength MHD modes has led to improved understanding of important constraints on the pedestal height and the mechanism for ELMs. The combination of high resolution pedestal diagnostics and a suite of highly efficient stability codes, has made edge stability analysis routine on several major tokamaks, contributing both to understanding, and to experimental planning and performance optimization. Here we present extensive comparisons of observations to predicted edge stability boundaries on several tokamaks, both for the standard ELM regime, and for small ELM and ELM-free regimes. We further use the stability constraint on pedestal height to test models of the pedestal width, and self-consistently combine a simple width model with MHD stability calculations to develop a new predictive model (EPED1) for the pedestal height and width. This model is tested against experimental measurements, and used in initial predictions of the pedestal height for ITER.
de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Parail, V.*; Giroud, C.*; Andrew, Y.*; Biewer, T. M.*; Cromb , K.*; Jenkins, I.*; Johnson, T.*; Kiptily, V.*; et al.
, K.*; Jenkins, I.*; Johnson, T.*; Kiptily, V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(3), p.035007_1 - 035007_6, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:85.47(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dedicated experiments on TF ripple effects on the performance of tokamak plasmas have been carried out at JET. The TF ripple was found to have a profound effect on the plasma rotation. The central Mach number, M, defined as the ratio of the rotation velocity and the thermal velocity, was found to drop as a function of TF ripple amplitude from an average value of M = 0.40-0.55 for operations at the standard JET ripple of 0.08% to M = 0.25-0.40 for 0.5% ripple and M = 0.1-0.3 for 1% ripple. With standard co-current injection of neutral beam injection (NBI), plasmas were found to rotate in the co-current direction. However, for higher TF ripple amplitudes (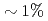 ) an area of counter rotation developed at the edge of the plasma, while the core kept its co-rotation.
) an area of counter rotation developed at the edge of the plasma, while the core kept its co-rotation.