Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Yb for producing
Yb for producing  Lu with high radionuclide purity by
Lu with high radionuclide purity by  Yb(
Yb(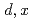 )
) Lu
LuNagai, Yasuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Saeki, Hideya*; Motomura, Arata*; Minato, Futoshi; Ito, Masatoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(4), p.044201_1 - 044201_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:47.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recently,  Lu is considered as one of the most important medical RIs for treating neuroendocrine tumors. A plan to produce
Lu is considered as one of the most important medical RIs for treating neuroendocrine tumors. A plan to produce  Lu with high purity by using enriched
Lu with high purity by using enriched  Yb samples with irradiation of deuteron beams in accelerators has been discussed. However, since the other Yb isotopes contained in the Yb sample interacts with deuterons, Lu isotopes other than
Yb samples with irradiation of deuteron beams in accelerators has been discussed. However, since the other Yb isotopes contained in the Yb sample interacts with deuterons, Lu isotopes other than  Lu are produced as impurities. Since the purity of
Lu are produced as impurities. Since the purity of  Lu is important for medical use, a method to evaluate the impurity of Lu has been required. In this study, we proposed a new method to estimate production yields of each Lu isotopes in Yb samples with arbitrary isotopic compositions by using excitation functions of Yb(
Lu is important for medical use, a method to evaluate the impurity of Lu has been required. In this study, we proposed a new method to estimate production yields of each Lu isotopes in Yb samples with arbitrary isotopic compositions by using excitation functions of Yb(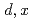 )Lu reactions and the particle transport calculation code PHITS. The method plays an important role in discussing the isotopic composition of enriched samples to produce high-purity
)Lu reactions and the particle transport calculation code PHITS. The method plays an important role in discussing the isotopic composition of enriched samples to produce high-purity  Lu using accelerators.
Lu using accelerators.
 Cu and
Cu and  Cu via the
Cu via the  Zn(n, p)
Zn(n, p) Cu and
Cu and  Zn(n, np/d)
Zn(n, np/d) Cu reactions using accelerator neutrons
Cu reactions using accelerator neutronsKawabata, Masako*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ota, Akio*; Motomura, Arata*; Saeki, Hideya*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 330(3), p.913 - 922, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:67.14(Chemistry, Analytical)Both  Cu and
Cu and  Cu are promising radionuclides in nuclear medicine. Production yields of these radionuclides were quantified by irradiating 55.4 g of natural zinc with accelerator neutrons. Clinically suitable
Cu are promising radionuclides in nuclear medicine. Production yields of these radionuclides were quantified by irradiating 55.4 g of natural zinc with accelerator neutrons. Clinically suitable  Cu and
Cu and  Cu yields were estimated by experimental based numerical simulations using 100 g of enriched
Cu yields were estimated by experimental based numerical simulations using 100 g of enriched  Zn and
Zn and  Zn, respectively, and elevated neutron fluxes from 40 MeV, 2 mA deuterons. A combined thermal- and resin-separation method was developed to isolate
Zn, respectively, and elevated neutron fluxes from 40 MeV, 2 mA deuterons. A combined thermal- and resin-separation method was developed to isolate  Cu and
Cu and  Cu from zinc, resulting in 73% separation efficiency and 97% zinc recovery. Such methods can provide large scale production of
Cu from zinc, resulting in 73% separation efficiency and 97% zinc recovery. Such methods can provide large scale production of  Cu and
Cu and  Cu for clinical applications.
Cu for clinical applications.
 ZnO using polyethylene by accelerator neutrons
ZnO using polyethylene by accelerator neutronsTsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Minato, Futoshi; Kawabata, Masako*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Saeki, Hideya*; Motoishi, Shoji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(3), p.034201_1 - 034201_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We found anomalously large yields of  Ga,
Ga, 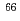 Ga,
Ga, 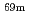 Zn and
Zn and  Cu by neutron irradiation on a
Cu by neutron irradiation on a  ZnO sample in a polyethylene shield. Neutron beams are generated from the
ZnO sample in a polyethylene shield. Neutron beams are generated from the  Be(
Be(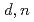 ) reaction for 50 MeV deuterons. The yields obtained were more than 20 times larger than those in the unshielded sample. On the other hand, the yields of
) reaction for 50 MeV deuterons. The yields obtained were more than 20 times larger than those in the unshielded sample. On the other hand, the yields of  Ga,
Ga, 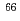 Ga,
Ga, 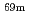 Zn and
Zn and  Cu from a metallic
Cu from a metallic  Zn sample and the yields of
Zn sample and the yields of  Cu,
Cu,  Ni and
Ni and  Zn from the
Zn from the  ZnO and
ZnO and  Zn samples were almost insensitive to the shield conditions. This finding would provide us a unique capability of accelerator neutrons to simultaneously produce a large amount of several radioisotopes, including proton induced reaction products, by using a single sample. The experimental data were compared with the yields estimated by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System and the result was discussed.
Zn samples were almost insensitive to the shield conditions. This finding would provide us a unique capability of accelerator neutrons to simultaneously produce a large amount of several radioisotopes, including proton induced reaction products, by using a single sample. The experimental data were compared with the yields estimated by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System and the result was discussed.
 Mo yield using large sample mass of MoO
Mo yield using large sample mass of MoO for sustainable production of
for sustainable production of  Mo
MoTsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Minato, Futoshi; Saeki, Hideya*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ito, Masatoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(4), p.043201_1 - 043201_5, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Mo production yield by
Mo production yield by  Mo(
Mo(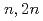 )
) Mo
MoMinato, Futoshi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Saeki, Hideya*; Kawabata, Masako*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Nagai, Yasuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(11), p.114803_1 - 114803_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have measured the yield of  Mo, the mother nuclide of
Mo, the mother nuclide of  Tc used in nuclear diagnostic procedure.
Tc used in nuclear diagnostic procedure.  Mo was produced by
Mo was produced by  Mo(
Mo( ,
,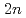 )
) Mo using neutrons with thermal energy up to about 40 MeV, provided by C(
Mo using neutrons with thermal energy up to about 40 MeV, provided by C( ,
, ). The
). The  Mo yield agrees with an estimated yield with the use of the latest data of C(
Mo yield agrees with an estimated yield with the use of the latest data of C( ,
, ) and the evaluated cross section given in the JENDL. Based on this, a new calculation was carried out to produce
) and the evaluated cross section given in the JENDL. Based on this, a new calculation was carried out to produce  Mo to seek for a good economical condition. Various conditions such as the
Mo to seek for a good economical condition. Various conditions such as the  MoO
MoO sample mass, the distance between the carbon target and the sample, the radius of the deuteron beam, and the neutron irradiation time were considered. The calculated
sample mass, the distance between the carbon target and the sample, the radius of the deuteron beam, and the neutron irradiation time were considered. The calculated  Mo yield indicates that about 30% of the
Mo yield indicates that about 30% of the  Mo demand in Japan can be fulfilled with a single accelerator. The elusion of
Mo demand in Japan can be fulfilled with a single accelerator. The elusion of  Tc from the
Tc from the  Mo twice per day would meet about 50% of the
Mo twice per day would meet about 50% of the  Mo demand.
Mo demand.
 Cu produced by
Cu produced by  Zn(
Zn(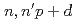 )
) Cu to biodistribution study in tumor-bearing mice
Cu to biodistribution study in tumor-bearing miceSugo, Yumi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Saeki, Hideya*; Sato, Shunichi*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_3, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:66.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cu produced by the
Cu produced by the  Zn(
Zn(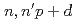 )
) Cu reaction was used for the first time to determine the biodistribution of
Cu reaction was used for the first time to determine the biodistribution of  CuCl
CuCl in colorectal tumor-bearing mice. High uptake of
in colorectal tumor-bearing mice. High uptake of  Cu was observed in the tumor as well as in the liver and kidney which are the major organs for copper metabolism. The result showing
Cu was observed in the tumor as well as in the liver and kidney which are the major organs for copper metabolism. The result showing  Cu accumulation in the tumor suggests that
Cu accumulation in the tumor suggests that  CuCl
CuCl can be a potential radionuclide agent for cancer radiotherapy. It would also encourage further studies on the therapeutic effect in small animals using an increased dose of
can be a potential radionuclide agent for cancer radiotherapy. It would also encourage further studies on the therapeutic effect in small animals using an increased dose of  Cu produced by the
Cu produced by the  Zn(
Zn(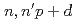 )
) Cu reaction using intense neutrons available at present.
Cu reaction using intense neutrons available at present.
 Tc-radiopharmaceuticals obtained from
Tc-radiopharmaceuticals obtained from  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo and fission of
Mo and fission of  U
UHashimoto, Kazuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Ota, Masayuki; Konno, Chikara; Ochiai, Kentaro; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(4), p.043202_1 - 043202_4, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Tc from molten
Tc from molten  MoO
MoO
Kawabata, Masako; Nagai, Yasuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Sato, Nozomi*; Ota, Akio*; Shiina, Takayuki*; Kawauchi, Yukimasa*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_4, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Tc for medical use can be separated by thermochromatography from a molten
Tc for medical use can be separated by thermochromatography from a molten  MoO
MoO sample. Effect of moist oxygen gas on the
sample. Effect of moist oxygen gas on the  Tc release from molten
Tc release from molten  MoO
MoO samples was investigated using a
samples was investigated using a  Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator.
Tc generator.  Mo was produced with
Mo was produced with  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo. A new phenomenon has been observed: release rate, separation- and recovery-efficiencies of
Mo. A new phenomenon has been observed: release rate, separation- and recovery-efficiencies of  Tc were higher in the moist oxygen gas than those in the dry oxygen gas. The present result is a significant progress towards the stable production of a high quality
Tc were higher in the moist oxygen gas than those in the dry oxygen gas. The present result is a significant progress towards the stable production of a high quality  Tc from a molten MoO
Tc from a molten MoO sample with high separation efficiency. The result would also give us a new insight into the interaction between the moist oxygen gas and the molten MoO
sample with high separation efficiency. The result would also give us a new insight into the interaction between the moist oxygen gas and the molten MoO .
.
 Cu produced by
Cu produced by  Z(
Z( ,
, ) reaction using
) reaction using  C(
C( ,
, ) neutrons
) neutronsSato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Kawabata, Masako; Saeki, Hideya; Nagai, Yasuki; Kin, Tadahiro*; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(7), p.073201_1 - 073201_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.40(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have for the first time demonstrated that the therapeutic nuclide of  Cu produced by
Cu produced by  Zn(
Zn( ,
, )
) Cu has highest radionuclide purity compared to previous ones. We measured a
Cu has highest radionuclide purity compared to previous ones. We measured a  -ray spectrum of the reaction product produced by bombarding an enriched
-ray spectrum of the reaction product produced by bombarding an enriched  Zn sample with neutrons with a HPGe detector. The neutrons were obtained by
Zn sample with neutrons with a HPGe detector. The neutrons were obtained by  C(
C( ,
, ) using 41 MeV deuterons provided from Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Relative production yields of impurity radionuclides such as
) using 41 MeV deuterons provided from Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Relative production yields of impurity radionuclides such as  Zn to
Zn to  Cu are extremely low, which allow us to chemically separate
Cu are extremely low, which allow us to chemically separate  Cu from an irradiated
Cu from an irradiated  Zn sample with a few steps and to reuse high cost an enriched
Zn sample with a few steps and to reuse high cost an enriched  Zn sample. The present result strongly suggest that the
Zn sample. The present result strongly suggest that the  Zn(
Zn( ,
, )
) Cu reaction is the most promising route to produce high quality
Cu reaction is the most promising route to produce high quality  Cu and could solve a longstanding problem of establishing an appropriate production method of
Cu and could solve a longstanding problem of establishing an appropriate production method of  Cu.
Cu.
 Tc from molten
Tc from molten  MoO
MoO samples by repeated milking tests
samples by repeated milking testsNagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(8), p.083201_1 - 083201_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.43(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nagai, Yasuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji; Sonoda, Nozomi; Kawabata, Masako; Harada, Hideo; Kin, Tadahiro*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_7, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:85.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Motoishi, Shoji; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Saeki, Hideya*
JAERI-Tech 2000-070, 34 Pages, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Ishioka, Noriko*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Sugo, Yumi*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Kawabata, Masako*; Saeki, Hideya*; et al.
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64. Enriched Mo-100, Zr-90, Zn-68 and Zn-64 oxide samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 12 - 50 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron and the JAEA tandem accelerator. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the
C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 12 - 50 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron and the JAEA tandem accelerator. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the  -rays. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
-rays. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kawabata, Masako*; Saeki, Hideya*; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Sugo, Yumi*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Re solutions by a multi column system for cancer therapeutic experiments
Re solutions by a multi column system for cancer therapeutic experimentsHashimoto, Kazuyuki; Motoishi, Shoji*; Saeki, Hideya*; Sorita, Takami; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu
no journal, ,
Rhenium-188 is a useful generator-produced radioisotope for therapeutic applications because of their energetic beta particles and  rays suitable for imaging. Because the
rays suitable for imaging. Because the  W parent is obtained in a relatively low specific activity from the irradiation of enriched
W parent is obtained in a relatively low specific activity from the irradiation of enriched  W in a reactor, relatively large volumes of normal saline are required to elute the
W in a reactor, relatively large volumes of normal saline are required to elute the  Re from alumina based
Re from alumina based  W/
W/ Re generators. In this study, a simple apparatus for effective concentrations of 188Re solutions from alumina-based
Re generators. In this study, a simple apparatus for effective concentrations of 188Re solutions from alumina-based  W/
W/ Re generators was developed by a tandem cation-anion column system. Concentration ratios greater than 50:1 can be achieved with this apparatus.
Re generators was developed by a tandem cation-anion column system. Concentration ratios greater than 50:1 can be achieved with this apparatus.
 Tc obtained from
Tc obtained from  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n) using accelerator neutrons
Mo(n,2n) using accelerator neutronsNagai, Yasuki; Kawabata, Masako; Sato, Nozomi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Ota, Akio; Shiina, Takayuki; Kawauchi, Yukimasa
no journal, ,
 Tc, the daughter nuclide of
Tc, the daughter nuclide of  Mo, is widely used for medical diagnosis. In Japan, about 0.9 million diagnostic procedures are carried out using
Mo, is widely used for medical diagnosis. In Japan, about 0.9 million diagnostic procedures are carried out using  Tc.
Tc.  Mo has been mostly produced using
Mo has been mostly produced using  U in research reactors. Because of recent shortages of
U in research reactors. Because of recent shortages of  Mo, a variety of alternative production methods of
Mo, a variety of alternative production methods of  Mo or
Mo or  Tc were proposed. We proposed to produce
Tc were proposed. We proposed to produce  Mo by
Mo by  Mo(n,2n) using neutrons from an accelerator. The route is characterized to produce a large quantity of high-quality
Mo(n,2n) using neutrons from an accelerator. The route is characterized to produce a large quantity of high-quality  Mo with a minimum level of radioactive wastes, since the cross section of the
Mo with a minimum level of radioactive wastes, since the cross section of the  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo reaction at 11
Mo reaction at 11  En
En  18 MeV is large, and the cross sections of the (n,He), (n,n'p), and (n,p) reactions on
18 MeV is large, and the cross sections of the (n,He), (n,n'p), and (n,p) reactions on  Mo are quite small. Intense neutrons are available because of recent progresses of accelerator and target technologies. In the talk, we show our recent experimental results to obtain
Mo are quite small. Intense neutrons are available because of recent progresses of accelerator and target technologies. In the talk, we show our recent experimental results to obtain  Tc with high-quality using
Tc with high-quality using  Mo produced by
Mo produced by  Mo(n,2n).
Mo(n,2n).
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Nagai, Yasuki; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Takeda, Shinsaku*
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of  Y (T
Y (T = 64 h), which has been used for the nuclear medicine. Enriched
= 64 h), which has been used for the nuclear medicine. Enriched  Zr nitrate samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the
Zr nitrate samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron.
C(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron.  Y was successfully produced via the (n, p) reaction, and separated from the Zr nitrate target by three columns method with a hydrochloric acid. After the purification, a labelling of DTPA with
Y was successfully produced via the (n, p) reaction, and separated from the Zr nitrate target by three columns method with a hydrochloric acid. After the purification, a labelling of DTPA with  Y had been performed. In this result, the yield was about 90% under
Y had been performed. In this result, the yield was about 90% under  2.5
2.5  M of DTPA, although the yields were decreased at the DTPA concentration below 2.5
M of DTPA, although the yields were decreased at the DTPA concentration below 2.5  M.
M.
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi*; Watanabe, Satoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kin, Tadahiro*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Kawabata, Masako; Saeki, Hideya; et al.
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64. Enriched Mo-100, Zr-90, Zn-68 and Zn-64 oxide samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the
C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 40 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the  -rays. Particularly, yields of impurity radionuclides were much smaller than that of Mo-99 and Cu-67, and therefore radioactive waste produced during chemical processing would be reduced compared with other proposed reaction systems. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
-rays. Particularly, yields of impurity radionuclides were much smaller than that of Mo-99 and Cu-67, and therefore radioactive waste produced during chemical processing would be reduced compared with other proposed reaction systems. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
 Mo production yield by the acceleration neutron
Mo production yield by the acceleration neutronTsukada, Kazuaki; Nagai, Yasuki*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Minato, Futoshi; Saeki, Hideya*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Ito, Masatoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujino, Shunsuke; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Saeki, Hideya*; Kawauchi, Yukimasa*; Kawabata, Masako*; Chiba, Yusuke
no journal, ,
Lutetium-177 (Lu-177)is a medical radioisotope used in approved radiopharmaceutical "Lutathera" to treat neuroendocrine tumours. And it is one of the promising radionuclides for new therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals. However, Lu-177 is dependent on imports from overseas, and there are concerns that transportation problems etc. may affect domestic distribution and development of new pharmaceuticals. In order to confirm whether JAEA can produce a portion of the Lu-177 for research, we conducted a production test of Lu-177 using JRR-3.