Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Batsaikhan, M.; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Saeki, Morihisa*; Karino, Takahiro; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 13 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 ion complex; Presence of a Rh
ion complex; Presence of a Rh Intermediate in Direct Photoreduction
Intermediate in Direct PhotoreductionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(12), p.5607 - 5616, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.66(Chemistry, Physical)The reaction mechanism of the direct photoreduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh
species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh
species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh . Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh
. Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh
species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh species. The Rh
species. The Rh species were assigned to Rh
species were assigned to Rh , Rh
, Rh , and Rh
, and Rh species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
 Rh
Rh
 Rh
Rh . A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh
. A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh
, photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , and photooxidation of Rh
, and photooxidation of Rh , well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh
, well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh species.
species.
Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Morii, Shiori; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 37(12), p.1843 - 1846, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we developed a simple and one-step Pd separation technique based on photoreduction with Xe lamp irradiation for the determination of  Pd in highly radioactive samples. A simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) solution, which consists of 14 major elements (Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) in a 3 mol L
Pd in highly radioactive samples. A simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) solution, which consists of 14 major elements (Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) in a 3 mol L HNO
HNO solution, was used to evaluate the separation performance. The Pd precipitate were formed by Xe lamp irradiation and recovered by centrifugation. The results showed that the recovery of Pd from a simulated HLLW solution depend on the irradiation time and concentration of ethanol. By optimizing the conditions at photo irradiation, the Pd recovery from the simulated HLLW solution reached up to 50 %, while 99.5 % of the other 13 elements were separated. The Pd precipitate could be separated from the elements that are the main source of radioactivity (Sr, Cs, and Ba) and the source of spectral interference for the determination of
solution, was used to evaluate the separation performance. The Pd precipitate were formed by Xe lamp irradiation and recovered by centrifugation. The results showed that the recovery of Pd from a simulated HLLW solution depend on the irradiation time and concentration of ethanol. By optimizing the conditions at photo irradiation, the Pd recovery from the simulated HLLW solution reached up to 50 %, while 99.5 % of the other 13 elements were separated. The Pd precipitate could be separated from the elements that are the main source of radioactivity (Sr, Cs, and Ba) and the source of spectral interference for the determination of  Pd (Zr, and Ru). These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the proposed method, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Pd (Zr, and Ru). These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the proposed method, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:84.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
Nakanishi, Ryuzo; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo; Tanabe, Rie*; Ito, Yoshiro*
Optics Express (Internet), 29(4), p.5205 - 5212, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:83.13(Optics)Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) combined with liquid jets was applied to the detection of trace sodium (Na) in aqueous solutions. The sensitivities of two types of liquid jets were compared: a liquid cylindrical jet with a diameter of 500  m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20
m and a liquid sheet jet with a thickness of 20  m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57
m. Compared with the cylindrical jet, the liquid sheet jet effectively reduced the splash from the laser-irradiated surface and produced long-lived luminous plasma. The limit of detection (LOD) of Na was determined to be 0.57  g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5
g/L for the sheet jet and 10.5  g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
g/L for the cylindrical jet. The LOD obtained for the sheet jet was comparable to those obtained for commercially available inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Tsuji, Takuya; Oba, Hironori*
Analytical Sciences, 36(11), p.1371 - 1378, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10(Chemistry, Analytical)We measured X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and Raman spectra of isopolymolybdates(VI) in HNO solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo
solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo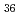 O
O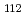 (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [Mo
[Mo O
O (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [HMoO
[HMoO (H
(H O)
O) ]
] in the highly concentrated HNO
in the highly concentrated HNO solution.
solution.
Sasaki, Yuji; Saeki, Morihisa*; Yoshizuka, Kazuharu*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 26(1), p.21 - 34, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.61(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Three tridentate extractants and three masking reagents including O, N, and S donors have been developed and their properties are compared and discussed. The extractants are termed as tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA), methylimino-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) and tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (TDGA(C8)) and masking agents have the same central frame but with short alkyl chain. The results of the present study indicate that TODGA can extract mainly hard acid metals belonging groups 2-4,13-15 in periodic table, MIDOA can extract soft acid metals and oxyanions (groups 5-10, 16), and TDGA can extract soft acid metals (groups 10-11). Some spectrophotometric studies (UV, IR, and NMR) indicate the stoichiometry and effect of donor atoms for metal-complexation. The Hf values, the heat generation during complex formation, obtained by chemical calculation by DFT theory show the reverse-correlation with their extraction ability.
 Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MS
Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Ohata, Masaki*; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), p.973 - 983, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.2(Biochemical Research Methods)Determination of radiopalladium  Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of
Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of  Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study,
Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study, 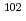 Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of
Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of  Pd/
Pd/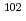 Pd. The amount of
Pd. The amount of  Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yomogida, Takumi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123(1), p.817 - 824, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:53.94(Chemistry, Physical)Reaction kinetics of laser-induced particle formation in an aqueous solution of PdCl
 was investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS). The Pd particle was generated by irradiation of nanosecond pulsed 266-nm laser. The TEM observation showed dependence of the particle size on the laser fluence and promotion of the particle growth by irradiation of high-fluence laser. The DXAFS data give us the Pd
was investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS). The Pd particle was generated by irradiation of nanosecond pulsed 266-nm laser. The TEM observation showed dependence of the particle size on the laser fluence and promotion of the particle growth by irradiation of high-fluence laser. The DXAFS data give us the Pd concentration. Temporal changes of the Pd
concentration. Temporal changes of the Pd concentration analyzed based on Finke-Watzky two step mechanism. The analysis elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the reduction of the PdCl
concentration analyzed based on Finke-Watzky two step mechanism. The analysis elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the reduction of the PdCl
 ion by the one-photon process and to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles by the multi-photon process.
ion by the one-photon process and to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles by the multi-photon process.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Asai, Shiho; Oba, Hironori*
Bunseki, 2018(4), p.138 - 143, 2018/04
Platinum group metal (PGM) has attracted much attention in light of increasing demands in the industrial sector. A wide variety of techniques specialized for PGM separation, such as, solvent extraction, solid phase extraction, and molten salt electrolysis have been developed so far. Among such techniques, a newly developed separation technique based on laser-induced particulate formation can be a promising alternative to conventional ones. It enables non-contact and highly-selective separation with a simple operation. In this review, the research history and the basic mechanism of laser-induced particulate formation were outlined. Several applications were also mentioned, focusing on our latest research progress which achieved a world first quantitation of radioactive palladium in a spent nuclear fuel sample.
Sasaki, Yuji; Morita, Keisuke; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hisamatsu, Shugo*; Yoshizuka, Kazuharu*
Proceedings of 21st International Solvent Extraction Conference (ISEC 2017) (Internet), p.131 - 134, 2017/11
Three tridentate extractants including soft and hard donor has been developed and examined. The extractants are termed as 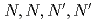 -tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA), methylimino-
-tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA), methylimino-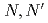 -dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) and
-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA) and 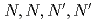 -tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (TDGA). The results of the present study show that TODGA can extract completely lanthanides and actinides, MIDOA can extract palladium, technetium, and rhenium, and TDGA can extract palladium, silver, and gold. We can compare the distribution ratios of these metals by TODGA, MIDOA, and TDGA. These results can be supported by some spectrometric studies, i.e., IR, NMR and UV, and calculations of metal complexes.
-tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (TDGA). The results of the present study show that TODGA can extract completely lanthanides and actinides, MIDOA can extract palladium, technetium, and rhenium, and TDGA can extract palladium, silver, and gold. We can compare the distribution ratios of these metals by TODGA, MIDOA, and TDGA. These results can be supported by some spectrometric studies, i.e., IR, NMR and UV, and calculations of metal complexes.
 Pd by ICP-MS; The Relation between separation conditions and Pd recovery
Pd by ICP-MS; The Relation between separation conditions and Pd recoveryYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(9), p.647 - 652, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.93(Chemistry, Analytical)Palladium-107 is a long-lived fission product, which can be found in high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW). Determination of the  Pd contents in HLLW is essential to evaluate the long-term safety of HLLW repositories. However, the
Pd contents in HLLW is essential to evaluate the long-term safety of HLLW repositories. However, the  Pd content in HLLW has not been reported because of difficulties in pretreatment for the measurement. In this study, we investigated applicability of laser-induced photoreduction to HLLW solution: it enables a simple and non-contact separation of Pd. The results showed the recovery of 60% was achieved at the conditions: 40% ethanol, 20 min irradiation, 100 mJ of pulse energy. Additionally, major radionuclides and potentially interfering components in ICP-MS were removed from the simulated HLLW over a wide concentration range of Pd from 0.24 to 24 mg L
Pd content in HLLW has not been reported because of difficulties in pretreatment for the measurement. In this study, we investigated applicability of laser-induced photoreduction to HLLW solution: it enables a simple and non-contact separation of Pd. The results showed the recovery of 60% was achieved at the conditions: 40% ethanol, 20 min irradiation, 100 mJ of pulse energy. Additionally, major radionuclides and potentially interfering components in ICP-MS were removed from the simulated HLLW over a wide concentration range of Pd from 0.24 to 24 mg L , showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Oba, Hironori*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Yomogida, Takumi
Denki Gakkai Kenkyukai Shiryo, Denshi Zairyo Kenkyukai (EFM-17-010 021), p.15 - 18, 2017/09
021), p.15 - 18, 2017/09
Irradiation of nanosecond pulsed UV laser into a solution of palladium ion leads to formation of palladium particles with sub-micron size particles by time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Sasaki, Yuji; Morita, Keisuke; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hisamatsu, Shugo; Yoshizuka, Kazuharu*
Hydrometallurgy, 169, p.576 - 584, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:56.4(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The novel tridentate extractant including soft donor has developed and examined. The extractant, tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (TDGA), is analogous structure to tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA) and methylimino-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA), but with sulfur donor instead of ether oxygen or nitrogen atoms of TODGA or MIDOA. From the present work, TDGA can extract silver, palladium, gold, and mercury from acidic solutions to n-dodecane. In addition to these results, the distribution ratios of hard and soft acid metals by using TDGA, TODGA, and MIDOA are compared, where the metal-complexations with each donor atom are investigated. 1H-NMR and IR studies for the metal-TDGA complexes indicate the role on donor atoms, S and N, of TDGA.
 Pd in Pd recovered by laser-induced photoreduction with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Pd in Pd recovered by laser-induced photoreduction with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryAsai, Shiho; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Chemistry, 88(24), p.12227 - 12233, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.58(Chemistry, Analytical)Safety evaluation of a radioactive waste repository requires credible activity estimates confirmed by actual measurements. A long-lived radionuclide,  Pd, which can be found in radioactive wastes, is one of the difficult-to-measure nuclides and results in a deficit in experimentally determined contents. In this study, a precipitation-based separation method has been developed for the determination of
Pd, which can be found in radioactive wastes, is one of the difficult-to-measure nuclides and results in a deficit in experimentally determined contents. In this study, a precipitation-based separation method has been developed for the determination of  Pd with ICP-MS. The photoreduction induced by laser irradiation at 355 nm provides short-time and one-step recovery of Pd. The proposed method was verified by applying it to a spent nuclear fuel sample. In order to efficiently recover Pd, a natural Pd standard was employed as the Pd carrier. The chemical yield of Pd was about 90% with virtually no impurities, allowing accurate quantification of
Pd with ICP-MS. The photoreduction induced by laser irradiation at 355 nm provides short-time and one-step recovery of Pd. The proposed method was verified by applying it to a spent nuclear fuel sample. In order to efficiently recover Pd, a natural Pd standard was employed as the Pd carrier. The chemical yield of Pd was about 90% with virtually no impurities, allowing accurate quantification of  Pd.
Pd.
Sasaki, Yuji; Saeki, Morihisa; Sugo, Yumi; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Suzuki, Tomoya*; Ohashi, Akira*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 22(1), p.37 - 45, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:42.85(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)An extractant, methylimino-bis-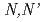 -dioctylacetamide (MIDOA), was used for the extraction of soft acid metals. It was found that MIDOA can extract not only Cr(VI), Mo(VI), W(VI), Tc(VII) and Re(VII), whose metals can form the oxonium anions due to their high oxidation states, but also other metal cations, like Nb(V), Ta(V) and Pd(II). Analogous compounds, imino-bis-
-dioctylacetamide (MIDOA), was used for the extraction of soft acid metals. It was found that MIDOA can extract not only Cr(VI), Mo(VI), W(VI), Tc(VII) and Re(VII), whose metals can form the oxonium anions due to their high oxidation states, but also other metal cations, like Nb(V), Ta(V) and Pd(II). Analogous compounds, imino-bis-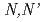 -dioctylacetamide (IDOA) and methylimino-bis-
-dioctylacetamide (IDOA) and methylimino-bis-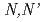 -di-2-ethylhexylacetamide (MIDEHA), are synthesized and compared for their extractability. It is clear that these extractants have almost same or lower
-di-2-ethylhexylacetamide (MIDEHA), are synthesized and compared for their extractability. It is clear that these extractants have almost same or lower  values than those for MIDOA. In order to examine the effect on extractability with different donor atoms, TODGA (
values than those for MIDOA. In order to examine the effect on extractability with different donor atoms, TODGA (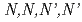 -tetraoctyl-diglycolamide) and TDGA (
-tetraoctyl-diglycolamide) and TDGA (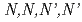 -tetraoctyl-tyiodiglycolamide) having oxygen and sulfur donor are employed. The comparison of their extractabilities suggests that the trend of Pd and Re extraction is N
-tetraoctyl-tyiodiglycolamide) having oxygen and sulfur donor are employed. The comparison of their extractabilities suggests that the trend of Pd and Re extraction is N  S
S  O and N
O and N  O
O  S, respectively.
S, respectively.
Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Nakashima, Nobuaki*; Oba, Hironori
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A; Chemistry, 299, p.189 - 193, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:35.41(Chemistry, Physical)Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo
Reza Kenkyu, 42(12), p.892 - 896, 2014/12
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is an attractive technique for determining elemental composition in real time, in-situ and remotely without any sample preparation. The LIBS analysis of metal ions in an aqueous solution is available in process control and environmental monitoring. In the present paper, we have reviewed the LIBS methods for a liquid phase that tried to improve the detection sensitivity. We have performed the LIBS measurement with the sheet flow for the simultaneous determination of elements in the simulated high-level radioactive waste liquid and have discussed on the application possibility as a tool for online process monitoring.
Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Wakaida, Ikuo; Tanabe, Rie*; Ito, Yoshiro*
Optics Express (Internet), 22(20), p.24478 - 24490, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:66.56(Optics)For aqueous-solution-based elemental analysis, we used a thin liquid sheet ( m-scale thickness) in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with nanosecond laser pulses. Laser-induced plasma is emitted by focusing a pulsed Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm) on a 5- to 80-
m-scale thickness) in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with nanosecond laser pulses. Laser-induced plasma is emitted by focusing a pulsed Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm) on a 5- to 80- m-thick liquid sheet in air. To optimize the conditions for detecting elements, we studied how the signal-to-background ratio (SBR) for H
m-thick liquid sheet in air. To optimize the conditions for detecting elements, we studied how the signal-to-background ratio (SBR) for H Balmer and Na-neutral emission lines depends on the liquid-sheet thickness. The SBR of the H
Balmer and Na-neutral emission lines depends on the liquid-sheet thickness. The SBR of the H Balmer and Na-neutral lines was maximized for a sheet thickness of
Balmer and Na-neutral lines was maximized for a sheet thickness of  20
20  m at the laser energy of 100 mJ. The hydrodynamics of liquid flow induced by the laser pulse was analyzed by laser flash shadowgraph imaging. Time-resolved observation of the hydrodynamics and plasma emission suggests that the dependence of the SBR on the liquid-sheet thickness is correlated with the volume of flowing liquid that interacts with the laser pulses.
m at the laser energy of 100 mJ. The hydrodynamics of liquid flow induced by the laser pulse was analyzed by laser flash shadowgraph imaging. Time-resolved observation of the hydrodynamics and plasma emission suggests that the dependence of the SBR on the liquid-sheet thickness is correlated with the volume of flowing liquid that interacts with the laser pulses.