Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibama, Yusuke; Okano, Fuminori; Yagyu, Junichi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Sagawa, Keiich*; Mochida, Tsutomu*; Morimoto, Tamotsu*; Hamada, Takashi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1614 - 1619, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JT-60SA vacuum vessel (150 tons) is a double wall torus structure and the maximum major radius of 5.0 m and height of 6.6 m. The manufacturing design concept is that the vessel is split in the 10 toroidal sectors manufactured at factory, and assembled on-site; seven of the 40-degree sectors, two of the 30-degree beside final one, and the final of the 20-degree. The final sector is assembled with the VV thermal shield and toroidal field magnets into the 340-degree as prepared in one sector. Sectors are temporally fitted on-site and adjusted one over the other before the assembly. After measurement of the dimensions and the reference, these sectors are transferred onto the cryostat base. First, three 80-degree sectors are manufactured with mating each 40-degree sector by direct joint welding. The rest sectors including the final sector are jointed with splice plates. Welding manipulator and its guide rails are used for these welding. In this paper, the detail of the VV sectors assembly including the final sector is explained. Welding technologies to joint the two of 40-degree sectors are reported with the present manufacturing status and the welding trial on the vertical stub with the partial mock-up of the final sector are discussed with the assembly process.
Ishihara, Yoshinao*; Matsuoka, Fushiki*; Sagawa, Hiroshi*; Kawahara, Kenichi*; Kataoka, Shinichi*; Shinohara, Yoshinori*; Muroi, Masayuki*; Tsuchiya, Makoto*; Tsujimoto, Keiichi*; Ohashi, Toyo*
JNC TJ8400 2001-011, 259 Pages, 2001/03
In this study, the basic design study on integrated computer system has been carried out in order to develop the integrated methodologies for future research and development activities of geological disposal system. The key conclusions are summarized as follows: (1) As the result of the investigation of work items and associated flow of information (data) between items in the second progress report by JNC, the interaction matrix and work flow chart have been identified in order to specify the basic configuration of the integrated computer system. In addition, the model chain and the structure of data relation between the repository design study and safety assessment study have been summarized. (2)We organized and examined the system factor and the information process flow in the design, safety analysis, and geological environment study based on the 2000 Report by JNC. Then we analyzed the workflow of geological disposal business when a specific site for a repository is fixed to obtain the system factor and the information process flow. We consider the fracture/porous media, site location (land/under the sea), and long-term stability of the crust (upheaval/sink) as the key factors in examining the workflow of geological disposal business. Then we organized the information change between the design and other study in geological disposal based on the 2000 Report by JNC. We examined the ideal workflow in which the design, safety analysis, and geologic environment study of geological disposal are closely coupled. We examined the scientific and technical base of the knowledge base (the system factor and the information process flow) which is derived from the above to construct the hierarchical structure of the knowledge base for geological disposal. (3)As the result of the interaction matrix and work flow chart for the R&D activities, the conceptual design and the function diagram on the integrated computer system has been proposed. (4)We examined the plan to ...
Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi; Sagawa, Masato*; Koyama, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
Sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets are the most promising materials for a driving motor of the hybrid electric vehicles(HV). In this application, a large value of coecivity 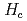 is required because of the high operating temperature beyond 450 K. As a symptomatic treatment, Nd has been replaced partly by Dy to enhance
is required because of the high operating temperature beyond 450 K. As a symptomatic treatment, Nd has been replaced partly by Dy to enhance 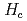 . But the problem is an estimated short supply of Dy in the HV mass-production stage due to its low natural abundance. We have recently shown that
. But the problem is an estimated short supply of Dy in the HV mass-production stage due to its low natural abundance. We have recently shown that 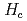 of Nd-Fe-B magnets can be enhanced by applying a high magnetic field during the annealing. In order to elucidate the reason for the
of Nd-Fe-B magnets can be enhanced by applying a high magnetic field during the annealing. In order to elucidate the reason for the 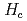 increase, we performed a small angle neutron scattering (SANS) study using SANS-J and PNO at JRR-3 of JAEA. We observed a marked deviation from the simple relation above for
increase, we performed a small angle neutron scattering (SANS) study using SANS-J and PNO at JRR-3 of JAEA. We observed a marked deviation from the simple relation above for 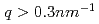 in the sample with Al and Cu additives. SANS results suggest that an existence of the Cu-containing liquid phases is strongly correlated with the
in the sample with Al and Cu additives. SANS results suggest that an existence of the Cu-containing liquid phases is strongly correlated with the 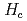 enhancement by the high field annealing.
enhancement by the high field annealing.
Shibama, Yusuke; Okano, Fuminori; Yagyu, Junichi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Sagawa, Keiich*; Mochida, Tsutomu*; Morimoto, Tamotsu*; Hamada, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 B sintered magnets
B sintered magnetsTakeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Sagawa, Masato*; Koyama, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
Nd-Fe-B magnets are now widely used because of the highest BH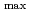 of them in the commercially available magnets. At the present, Dy, which is one of the rare metals, has to be added to maintain the coercivity especially in the operational temperatures higher than the room temperature. The key to achieve the Dy-free Nd-Fe-B magnets is how to control the grain size and the structure near the grain boundary. We have performed the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements of the sintered Nd-Fe-
of them in the commercially available magnets. At the present, Dy, which is one of the rare metals, has to be added to maintain the coercivity especially in the operational temperatures higher than the room temperature. The key to achieve the Dy-free Nd-Fe-B magnets is how to control the grain size and the structure near the grain boundary. We have performed the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements of the sintered Nd-Fe- B magnets using unpolarized and polarized neutrons to obtain the averaged internal structures of samples with the different coercivity introduced by applying different high magnetic fields during the annealing. We found that inhomogeneity was induced by the magnetic fields applied parallel to
B magnets using unpolarized and polarized neutrons to obtain the averaged internal structures of samples with the different coercivity introduced by applying different high magnetic fields during the annealing. We found that inhomogeneity was induced by the magnetic fields applied parallel to 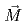 . The relation between the inhomogeneity and the coercivity force is unclear at the moment, but we will present possible interpretation.
. The relation between the inhomogeneity and the coercivity force is unclear at the moment, but we will present possible interpretation.
Asano, Shiro*; Okuyama, Toshihisa*; Ejiri, Mitsuru*; Mizumaki, Shoichi*; Mochida, Tsutomu*; Hamada, Takashi*; Araki, Takao*; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Sagawa, Keiich*; Kai, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi; Sagawa, Masato*; Koyama, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi; Sagawa, Masato*; Koyama, Keiichi*; Miyazaki, Terunobu*
no journal, ,
Sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets consist of Nd Fe
Fe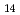 B main phase with about 5
B main phase with about 5 m diameter and Nd-rich grain boundary phase. It is well known that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets is highly dominated by this Nd-rich phase, which is reported to change from discontinuous to continuous arrangement by a low temperature annealing around 500
m diameter and Nd-rich grain boundary phase. It is well known that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets is highly dominated by this Nd-rich phase, which is reported to change from discontinuous to continuous arrangement by a low temperature annealing around 500 600
600 C. We have shown that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets can be further increased by applying a high magnetic field during the annealing. We found that such a coercivity enhancement phenomenon occurred only when a small amount of Cu is added, and when the annealing temperature is around 500
C. We have shown that the coercivity of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets can be further increased by applying a high magnetic field during the annealing. We found that such a coercivity enhancement phenomenon occurred only when a small amount of Cu is added, and when the annealing temperature is around 500 C or 550
C or 550 C. In this paper, we report on the results of interface nanostructure analysis by DSC and Small Angle Neutron Scattering experiments to investigate the reason magnetic field effect occurs only in Cu-containing samples at specific annealing temperatures.
C. In this paper, we report on the results of interface nanostructure analysis by DSC and Small Angle Neutron Scattering experiments to investigate the reason magnetic field effect occurs only in Cu-containing samples at specific annealing temperatures.