Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tominaga, Taiki*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Sahara, Masae*; Oda, Takashi*; Inoue, Rintaro*; Sugiyama, Masaaki*
Life (Internet), 12(5), p.675_1 - 675_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.29(Biology)The background scattering of sample cells suitable for aqueous protein solution samples, conducted with a neutron backscattering spectrometer, was evaluated. It was found that the scattering intensity of an aluminum sample cell coated with boehmite using D O was lower than that of a sample cell coated with regular water (H
O was lower than that of a sample cell coated with regular water (H O). In addition, meticulous attention to cells with small individual weight differences and the positional reproducibility of the sample cell relative to the spectrometer neutron beam position enabled the accurate subtraction of the scattering profiles of the D
O). In addition, meticulous attention to cells with small individual weight differences and the positional reproducibility of the sample cell relative to the spectrometer neutron beam position enabled the accurate subtraction of the scattering profiles of the D O buffer and the sample container. Consequently, high quality information on protein dynamics could be extracted from dilute protein solutions.
O buffer and the sample container. Consequently, high quality information on protein dynamics could be extracted from dilute protein solutions.
Tominaga, Taiki*; Sahara, Masae*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 54(6), p.1631 - 1640, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:57.51(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Tominaga, Taiki*; Sahara, Masae*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Shimamoto, Naonobu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011094_1 - 011094_5, 2021/03
In quasielastic neutron scattering studies, aluminum or aluminum alloys are frequently employed as sample cells. With the increasing incident-neutron flux, the research area currently continues to expand; thus, obtaining data has become quicker than ever for dilute conditions. One such area is the water-containing systems. In this study, we investigated the effect of temperature on Al and found that even in a low temperature atmosphere, Al corrosion can occur. This was attributed to the different thermal expansion coefficients of Al as a base substrate and Al oxide as a passivating film.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Miura, Daisuke*; Torikai, Naoya*
J-PARC 20-02; J-PARC MLF Annual Report 2019, p.38 - 40, 2021/00
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 52(5), p.1054 - 1060, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:35.60(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We developed a technique of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectometry (SCV-NR). Polarized-neutron reflectivity curves of film samples vary as a function of their proton-polarization P. The P-dependent reflectivity curves of a polystyrene film was precisely reproduced using a common set of structure parameters and the P-dependent neutron scattering length. The reflectivity curve of poly (styrene-block-isoprene) (PSPI) presented a shoulder attributed to holes with the depth corresponding to one period of periodic lamellae on the free surface only at a specific P. In this way, structural information about specific surfaces or interfaces can be obtained by controlling the P.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
no journal, ,
We have developed a technique of spin contrast variation neutron reflectometry (SCV-NR). The reflectivity curve of the polarized neutrons nonsimilarly varies as a function of proton polarization PH of a polymer thin film on silicon substrate. The PH-dependent reflectivity curve determines the roughnesses of the surface and interface of the polymer thin film, whereas single reflection curve of non-polarized neutrons cannot determine uniquely. We consider that the SCV-NR would be a promising technique to determine surface and interface structure of thin films of soft materials.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
no journal, ,
Scattering power of neutron against proton remarkably depends on relative direction of these spins. Spin contrast variation (SCV) is a technique to determine structure of composite materials from their polarized neutron scattering profiles that vary as a function of proton polarization. Very recently, we succeeded in the first SCV neutron reflectometry measurement. We determined roughness of two surfaces of a thin-film polymer from the SCV neutron reflection curves. We will use this technique to study structures of multilayered films such as coupling agents (glues) between organic and inorganic materials.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
no journal, ,
Scattering power of neutron against proton remarkably depends on relative direction of these spins. Spin contrast variation (SCV) is a technique to determine structure of composite materials from their polarized neutron scattering profiles that vary as a function of proton polarization. Very recently, we succeeded in the first SCV neutron reflectometry measurement. We determined roughness of two surfaces of a thin-film polymer from the SCV neutron reflection curves. We will use this technique to study structures of multilayered films such as coupling agents (glues) between organic and inorganic materials.
Hiroi, Kosuke; Takata, Shinichi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*
no journal, ,
Kumada, Takayuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Sahara, Masae*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Torikai, Naoya*
no journal, ,
We developed a technique of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectometry (SCV-NR). Polarized-neutron reflectivity curves of a styrene homopolymer film vary as a function of their proton-polarization, P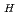 , coherently with what expected when the films are homogeneously polarized. This result ensures that the SCV-NR curves are not deformed by inhomogeneous P
, coherently with what expected when the films are homogeneously polarized. This result ensures that the SCV-NR curves are not deformed by inhomogeneous P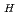 in the film, but determine the structures of surfaces and interfaces properly. Conventional unpolarized neutron reflectivity UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves of poly(styrene-block-isoprene) (PSPI) films are reproduced by the model that the film has a flat free surface, but positively-polarized SCV-NR curves are not. We found from the global fit that the holes with the depth corresponding to one period of periodic lamellae are produced on the free surface of the PSPI films, whose reflection is hidden by strong one from the PSPI-Si interface in the UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves.
in the film, but determine the structures of surfaces and interfaces properly. Conventional unpolarized neutron reflectivity UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves of poly(styrene-block-isoprene) (PSPI) films are reproduced by the model that the film has a flat free surface, but positively-polarized SCV-NR curves are not. We found from the global fit that the holes with the depth corresponding to one period of periodic lamellae are produced on the free surface of the PSPI films, whose reflection is hidden by strong one from the PSPI-Si interface in the UNR and negatively-polarized SCV-NR curves.