Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Asai, Shiho*; Horita, Takuma
Bunseki Kagaku, 73(10-11), p.569 - 578, 2024/10
The accurate estimation of the quantities and composition of long-lived radionuclides in radioactive waste is crucial for assessing the long-term safety of its disposal. Traditionally, theoretical predictions of the quantities of long-lived radionuclides obtained from burn-up calculation codes with evaluated nuclear data have been used especially for the safety assessment of high-level radioactive waste. However, such nuclear data used in theoretical predictions have not been sufficiently validated due to the scarcity of the reported measurement data. In this study, we aim to contribute to the improvement of the reliability of theoretical predictions by confirming them with the measured quantities of long-lived radionuclides per unit mass of uranium in spent nuclear fuel, which are output data obtained from the burnup calculation code. This involves measuring the long-lived radionuclides present in nuclear fuel pellets used in commercial nuclear reactors. Specifically, we focused on  Zr,
Zr,  Pd, and
Pd, and  Cs, which can be effectively measured using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). Besides the purpose of validating the nuclear data, this article also highlights viable measurement techniques for these radionuclides, along with examples demonstrating their applicability to long-lived radionuclides, including the preparation procedures for their measurement.
Cs, which can be effectively measured using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). Besides the purpose of validating the nuclear data, this article also highlights viable measurement techniques for these radionuclides, along with examples demonstrating their applicability to long-lived radionuclides, including the preparation procedures for their measurement.
 Sr analysis
Sr analysisHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho*; Konda, Miki; Matsueda, Makoto; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 69(10-11), p.619 - 626, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a Sr adsorption fiber for rapid analysis of  Sr. The prepared Sr adsorption fiber has a Sr-extraction layer that densely retains a Sr-selective extractant, an 18-crown-6 ether derivative, on the fiber surface. Hydrophobic group-containing polymer chains embedded onto the surface of the fiber allow to form a hydrophobic phase, incorporating Sr-selective extractants. This unique surface structure provides high adsorption capacity, leading to rapid and highly efficient adsorption of Sr
Sr. The prepared Sr adsorption fiber has a Sr-extraction layer that densely retains a Sr-selective extractant, an 18-crown-6 ether derivative, on the fiber surface. Hydrophobic group-containing polymer chains embedded onto the surface of the fiber allow to form a hydrophobic phase, incorporating Sr-selective extractants. This unique surface structure provides high adsorption capacity, leading to rapid and highly efficient adsorption of Sr . The adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was 3 times higher than commercially available 18-crown-6 ether derivative-impregnated resin (Sr Resin). The equilibrium adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was comparable to the Sr Resin. The retained
. The adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was 3 times higher than commercially available 18-crown-6 ether derivative-impregnated resin (Sr Resin). The equilibrium adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was comparable to the Sr Resin. The retained  Sr was finally determined by a GM counter. The total analysis time including the Sr adsorption and measurement was about 1 hour.
Sr was finally determined by a GM counter. The total analysis time including the Sr adsorption and measurement was about 1 hour.
 Cs in spent Cs adsorbent used for the decontamination of radiocesium-containing water by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Cs in spent Cs adsorbent used for the decontamination of radiocesium-containing water by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryAsai, Shiho*; Ohata, Masaki*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Yomogida, Takumi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Chemistry, 92(4), p.3276 - 3284, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.64(Chemistry, Analytical)The long-term safety assessment of spent Cs adsorbents produced during the decontamination of radiocesium-containing water at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant requires one to estimate their  Cs content prior to final disposal.
Cs content prior to final disposal.  Cs is usually quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), which necessitates the elution of Cs from Cs adsorbents. However, this approach suffers from the high radiation dose from
Cs is usually quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), which necessitates the elution of Cs from Cs adsorbents. However, this approach suffers from the high radiation dose from  Cs. To address this challenge, we herein employed laser ablation ICP-MS for direct quantitation of
Cs. To address this challenge, we herein employed laser ablation ICP-MS for direct quantitation of  Cs in Cs adsorbents and used a model Cs adsorbent prepared by immersion of a commercially available Cs adsorbent into radiocesium-containing liquid waste to verify the developed technique. The use of the
Cs in Cs adsorbents and used a model Cs adsorbent prepared by immersion of a commercially available Cs adsorbent into radiocesium-containing liquid waste to verify the developed technique. The use of the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio and
Cs ratio and  Cs radioactivity obtained by gamma spectrometry achieved simple and precise quantitation of
Cs radioactivity obtained by gamma spectrometry achieved simple and precise quantitation of  Cs and the resulting
Cs and the resulting  Cs activity of 0.36 Bq agreed well with that in the original radiocesium-containing liquid waste.
Cs activity of 0.36 Bq agreed well with that in the original radiocesium-containing liquid waste.
 Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MS
Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Ohata, Masaki*; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), p.973 - 983, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:58.05(Biochemical Research Methods)Determination of radiopalladium  Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of
Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of  Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study,
Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study, 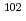 Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of
Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of  Pd/
Pd/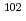 Pd. The amount of
Pd. The amount of  Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
 Pd by ICP-MS; The Relation between separation conditions and Pd recovery
Pd by ICP-MS; The Relation between separation conditions and Pd recoveryYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(9), p.647 - 652, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.96(Chemistry, Analytical)Palladium-107 is a long-lived fission product, which can be found in high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW). Determination of the  Pd contents in HLLW is essential to evaluate the long-term safety of HLLW repositories. However, the
Pd contents in HLLW is essential to evaluate the long-term safety of HLLW repositories. However, the  Pd content in HLLW has not been reported because of difficulties in pretreatment for the measurement. In this study, we investigated applicability of laser-induced photoreduction to HLLW solution: it enables a simple and non-contact separation of Pd. The results showed the recovery of 60% was achieved at the conditions: 40% ethanol, 20 min irradiation, 100 mJ of pulse energy. Additionally, major radionuclides and potentially interfering components in ICP-MS were removed from the simulated HLLW over a wide concentration range of Pd from 0.24 to 24 mg L
Pd content in HLLW has not been reported because of difficulties in pretreatment for the measurement. In this study, we investigated applicability of laser-induced photoreduction to HLLW solution: it enables a simple and non-contact separation of Pd. The results showed the recovery of 60% was achieved at the conditions: 40% ethanol, 20 min irradiation, 100 mJ of pulse energy. Additionally, major radionuclides and potentially interfering components in ICP-MS were removed from the simulated HLLW over a wide concentration range of Pd from 0.24 to 24 mg L , showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
 Sr measurement
Sr measurementHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Konda, Miki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(3), p.189 - 193, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.92(Chemistry, Analytical)A Sr-selective adsorption fiber was prepared for rapid analysis of  Sr content by using radiation-induced emulsion graft polymerization and subsequent chemical modification. A polyethylene fiber with a diameter of 13
Sr content by using radiation-induced emulsion graft polymerization and subsequent chemical modification. A polyethylene fiber with a diameter of 13  m was first immersed in a methanol solution of an epoxy-group-containing vinyl monomer, glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), and polyoxyethylene sorbitol ester (Tween20) as a surfactant for graft-polymerization of GMA. Octadecylamine was then bound to a polymer chain extending from the fiber surface providing hydrophobicity to the polymer chain. Dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6) was finally impregnated onto the polymer chain via a hydrophobic interaction between the octadecyl moiety of the polymer chain and the cyclohexyl moiety of DCH18C6. The fiber surface structure, characterized by DCH18C6 molecules loosely entangled with polymer chains, afforded realizes the rapid and selective adsorption of Sr ions with an adsorption rate approximately 100 times higher than that of a commercially available Sr-selective resin (Sr Resin).
m was first immersed in a methanol solution of an epoxy-group-containing vinyl monomer, glycidyl methacrylate (GMA), and polyoxyethylene sorbitol ester (Tween20) as a surfactant for graft-polymerization of GMA. Octadecylamine was then bound to a polymer chain extending from the fiber surface providing hydrophobicity to the polymer chain. Dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6) was finally impregnated onto the polymer chain via a hydrophobic interaction between the octadecyl moiety of the polymer chain and the cyclohexyl moiety of DCH18C6. The fiber surface structure, characterized by DCH18C6 molecules loosely entangled with polymer chains, afforded realizes the rapid and selective adsorption of Sr ions with an adsorption rate approximately 100 times higher than that of a commercially available Sr-selective resin (Sr Resin).
 Pd in Pd recovered by laser-induced photoreduction with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Pd in Pd recovered by laser-induced photoreduction with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryAsai, Shiho; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Chemistry, 88(24), p.12227 - 12233, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:56.29(Chemistry, Analytical)Safety evaluation of a radioactive waste repository requires credible activity estimates confirmed by actual measurements. A long-lived radionuclide,  Pd, which can be found in radioactive wastes, is one of the difficult-to-measure nuclides and results in a deficit in experimentally determined contents. In this study, a precipitation-based separation method has been developed for the determination of
Pd, which can be found in radioactive wastes, is one of the difficult-to-measure nuclides and results in a deficit in experimentally determined contents. In this study, a precipitation-based separation method has been developed for the determination of  Pd with ICP-MS. The photoreduction induced by laser irradiation at 355 nm provides short-time and one-step recovery of Pd. The proposed method was verified by applying it to a spent nuclear fuel sample. In order to efficiently recover Pd, a natural Pd standard was employed as the Pd carrier. The chemical yield of Pd was about 90% with virtually no impurities, allowing accurate quantification of
Pd with ICP-MS. The photoreduction induced by laser irradiation at 355 nm provides short-time and one-step recovery of Pd. The proposed method was verified by applying it to a spent nuclear fuel sample. In order to efficiently recover Pd, a natural Pd standard was employed as the Pd carrier. The chemical yield of Pd was about 90% with virtually no impurities, allowing accurate quantification of  Pd.
Pd.
Saigusa, Mikio*; Oyama, Gaku*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Takii, Keita*; Sai, Takuma*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.577 - 582, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:40.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A wideband polarizer has been developed for an ECCD system in JT-60SA. The groove depth of the mirrors installed in miter bends were optimized for two frequencies (110 GHz and 138 GHz) by numerical simulations. All surfaces of Poincare spheres were covered at both of the frequencies in low power test. The thermal stress of polarizer were estimated by the numerical simulations. The twister polarizer has been tested up to 0.24 MW during 3 s at 110 GHz.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:197 Percentile:99.37Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:50.67(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:188 Percentile:98.29(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 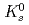 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Asai, Shiho; Ohata, Masaki*; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
Safe and cost-effective disposal of radioactive wastes requires reliable evaluation of the amount of the radionuclides found in such wastes. Measurement of  Pd, one of the radionuclides that are necessary to be evaluated, is associated with highly radioactive sample (e.g., spent nuclear fuel sample), resulting in only a few data in published forms. We separated Pd as a precipitate from a spent nuclear fuel sample and then determined the precise amount of
Pd, one of the radionuclides that are necessary to be evaluated, is associated with highly radioactive sample (e.g., spent nuclear fuel sample), resulting in only a few data in published forms. We separated Pd as a precipitate from a spent nuclear fuel sample and then determined the precise amount of  Pd. However, the method needed dissolution of the Pd precipitate to carry it to the sample introduction system of ICP-MS. In this study, we tried direct measurement of the Pd precipitate with laser-ablation (LA)-ICP-MS that enables solid sample measurement. The diameters of the recovered Pd precipitates were less than 500 nm, which is much smaller than the ablation spot. This allowed Pd to be uniformly vaporized, leading to sufficiently stable signals with high precisions equivalent to those of conventional ICP-MS.
Pd. However, the method needed dissolution of the Pd precipitate to carry it to the sample introduction system of ICP-MS. In this study, we tried direct measurement of the Pd precipitate with laser-ablation (LA)-ICP-MS that enables solid sample measurement. The diameters of the recovered Pd precipitates were less than 500 nm, which is much smaller than the ablation spot. This allowed Pd to be uniformly vaporized, leading to sufficiently stable signals with high precisions equivalent to those of conventional ICP-MS.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Asai, Shiho; Yomogida, Takumi; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
Platinum-group metals (PGMs), such as Pd, Ru, and Rh are generated by nuclear fission of U and can be found in spent nuclear fuel (SNF) and high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Separation techniques for PGMs from HLW have been investigated for the safety assessment of HLW and the reuse of PGMs as resources. Among such PGMs, only Pd has a long-lived radionuclide  Pd. Accordingly, the precise measurement of the amount of
Pd. Accordingly, the precise measurement of the amount of  Pd in HLW is essential for the long-term safety management of HLW. The determination of
Pd in HLW is essential for the long-term safety management of HLW. The determination of  Pd requires a reliable separation technique that allows selective Pd recovery with high purity. We developed a new separation technique specialized for PGMs. The technique involves UV-laser irradiation that induces selective reduction of ions of PGMs. The reduced PGMs can be readily recovered as precipitates. At the conference, the separation performances of PGMs and some applications of our technique will be discussed.
Pd requires a reliable separation technique that allows selective Pd recovery with high purity. We developed a new separation technique specialized for PGMs. The technique involves UV-laser irradiation that induces selective reduction of ions of PGMs. The reduced PGMs can be readily recovered as precipitates. At the conference, the separation performances of PGMs and some applications of our technique will be discussed.
 Cs
CsTajima, Taiyo*; Asai, Shiho*; Saito, Kyoichi*; Seko, Noriaki*; Hoshina, Hiroyuki*; Horita, Takuma; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Takaku, Yuichi*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Sakaguchi, Aya*
no journal, ,
 Cs is a radionuclide introduced into the environment by human nuclear activities. The use of
Cs is a radionuclide introduced into the environment by human nuclear activities. The use of  Cs as an oceanic circulation tracer and the need for monitoring around nuclear facilities require the establishment of a measurement method for this nuclide. In this study, the appropriate adsorption and desorption conditions of Cs in seawater using the insoluble cobalt ferrocyanide-impregnated adsorbent synthesized by graft polymerisation were investigated. A chemical separation method of Cs for mass spectrometry was also investigated.
Cs as an oceanic circulation tracer and the need for monitoring around nuclear facilities require the establishment of a measurement method for this nuclide. In this study, the appropriate adsorption and desorption conditions of Cs in seawater using the insoluble cobalt ferrocyanide-impregnated adsorbent synthesized by graft polymerisation were investigated. A chemical separation method of Cs for mass spectrometry was also investigated.
Sai, Takuma*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Takii, Keita*; Oyama, Gaku*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Horie, Naoyuki*; Sai, Takuma*; Omori, Kohei*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Arata, Hiroshi*; Uno, Tsuyoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Horita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
There has been an increasing demand for rapid analysis of  Sr to ensure a prompt action against the contaminated water in the Fukushima Daiichi NPP. Precedent works demonstrated that Cs adsorption fibers prepared by utilizing graft polymerization technology achieved high-speed removal of
Sr to ensure a prompt action against the contaminated water in the Fukushima Daiichi NPP. Precedent works demonstrated that Cs adsorption fibers prepared by utilizing graft polymerization technology achieved high-speed removal of  Cs in the contaminated water. In this study, we have investigated the applicability of such proven technology to the preparation of a Sr adsorption fiber specialized for the selective extraction of Sr. In the prepared fiber, an extractant for Sr
Cs in the contaminated water. In this study, we have investigated the applicability of such proven technology to the preparation of a Sr adsorption fiber specialized for the selective extraction of Sr. In the prepared fiber, an extractant for Sr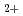 ,dicyclohexano-18-crown-6-ether (DCH18C6) was impregnated via hydrophobic interaction between DCH18C6 and the hydrophobic polymer chains attached onto the surface of the fiber. To increase the adsorption capacity, emulsion graft polymerization which promotes the polymer chains to grow longer was applied. The densely-packed DCH18C6 inside the interfacial phase formed by the polymer chains facilitates the efficient adsorption. The amounts of Sr adsorbed is comparable to those of conventional adsorbents, indicating that the prepared fiber has a feasible performance for Sr adsorption.
,dicyclohexano-18-crown-6-ether (DCH18C6) was impregnated via hydrophobic interaction between DCH18C6 and the hydrophobic polymer chains attached onto the surface of the fiber. To increase the adsorption capacity, emulsion graft polymerization which promotes the polymer chains to grow longer was applied. The densely-packed DCH18C6 inside the interfacial phase formed by the polymer chains facilitates the efficient adsorption. The amounts of Sr adsorbed is comparable to those of conventional adsorbents, indicating that the prepared fiber has a feasible performance for Sr adsorption.
 Sr adsorbed on fiber surface; Preparation of 18-crown 6-ether derivative-impregnated Sr adsorption fiber based on the radiation-induced graft polymerization
Sr adsorbed on fiber surface; Preparation of 18-crown 6-ether derivative-impregnated Sr adsorption fiber based on the radiation-induced graft polymerizationHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Konda, Miki; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
There has been an increasing importance of the development of rapid separation techniques for  Sr analysis, responding to needs in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. However, conventional
Sr analysis, responding to needs in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. However, conventional  Sr analytical methods require two different separation steps for Sr and Y, respectively, resulting in a long processing time of about one month. In this study, we prepared a Sr adsorptive fiber (Sr fiber) that has a high density Sr adsorption phase on its surface, allowing to highly efficient
Sr analytical methods require two different separation steps for Sr and Y, respectively, resulting in a long processing time of about one month. In this study, we prepared a Sr adsorptive fiber (Sr fiber) that has a high density Sr adsorption phase on its surface, allowing to highly efficient  -ray counting by minimizing the self-attenuation effects. The adsorption capacity of the prepared Sr fiber was about 14 g/mol, which is equivalent to that of a commercially available Sr adsorptive resin (Sr Resin). The selectivity of the Sr fiber was nearly the same as that of the Sr resin. Considering that the Sr fiber has a specific surface area 1000 times smaller than that of the Sr Resin, the Sr ions can be concentrated to 1000 times on its surface, capable of achieving highly-efficient
-ray counting by minimizing the self-attenuation effects. The adsorption capacity of the prepared Sr fiber was about 14 g/mol, which is equivalent to that of a commercially available Sr adsorptive resin (Sr Resin). The selectivity of the Sr fiber was nearly the same as that of the Sr resin. Considering that the Sr fiber has a specific surface area 1000 times smaller than that of the Sr Resin, the Sr ions can be concentrated to 1000 times on its surface, capable of achieving highly-efficient  -ray counting. From these result, we confirmed that Sr fiber has adsorption capacity and selectivity necessary for highly efficient
-ray counting. From these result, we confirmed that Sr fiber has adsorption capacity and selectivity necessary for highly efficient  -ray counting of
-ray counting of  Sr.
Sr.
Horita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Saito, Kyoichi*; Sugo, Takanobu*; Fujiwara, Kunio*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
There has been an increasing importance of the development of rapid  Sr analysis technique, responding to needs in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. We have been trying to achieve a rapid analysis using a fibrous Sr adsorbent which has high selectivity for Sr
Sr analysis technique, responding to needs in Fukushima Daiichi NPP. We have been trying to achieve a rapid analysis using a fibrous Sr adsorbent which has high selectivity for Sr . The fiber we prepared that has a high-density Sr adsorption phase on its surface, and so it can adsorb Sr
. The fiber we prepared that has a high-density Sr adsorption phase on its surface, and so it can adsorb Sr on the fiber surface. On the other hand, base material of a conventional Sr adsorptive resin for
on the fiber surface. On the other hand, base material of a conventional Sr adsorptive resin for  Sr analysis (Sr Resin) is bead-shaped resin, and
Sr analysis (Sr Resin) is bead-shaped resin, and  Sr is adsorbed inside pores. The fiber allows highly efficient
Sr is adsorbed inside pores. The fiber allows highly efficient  counting by minimizing the self-attenuation effects. The adsorption capacity and selectivity of the fiber was nearly the same as those of the Sr Resin. From these results, we confirmed that the fiber has performance for efficient
counting by minimizing the self-attenuation effects. The adsorption capacity and selectivity of the fiber was nearly the same as those of the Sr Resin. From these results, we confirmed that the fiber has performance for efficient  counting of
counting of  Sr.
Sr.
Yomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
Recently, we developed a precipitation-based separation method for the determination of  Pd with ICP-MS. However, a pulsed-laser light source is indispensable to form Pd precipitation in the separation method. There were difficulties in handling of a pulsed-laser light source. Simplified irradiation procedure is desirable to facilitate a Pd separation procedure. In this study, we developed a simple Pd separation technique based on photoreduction with Xe lamp irradiation and applied the technique to a simulated HLW solution. The Pd recovery from a simulated HLW solution reached 50%, while 99% of the other 13 elements were removed. These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the simplified irradiation procedure.
Pd with ICP-MS. However, a pulsed-laser light source is indispensable to form Pd precipitation in the separation method. There were difficulties in handling of a pulsed-laser light source. Simplified irradiation procedure is desirable to facilitate a Pd separation procedure. In this study, we developed a simple Pd separation technique based on photoreduction with Xe lamp irradiation and applied the technique to a simulated HLW solution. The Pd recovery from a simulated HLW solution reached 50%, while 99% of the other 13 elements were removed. These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the simplified irradiation procedure.