Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saigusa, Mikio*; Oyama, Gaku*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Takii, Keita*; Sai, Takuma*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.577 - 582, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.34(Nuclear Science & Technology)A wideband polarizer has been developed for an ECCD system in JT-60SA. The groove depth of the mirrors installed in miter bends were optimized for two frequencies (110 GHz and 138 GHz) by numerical simulations. All surfaces of Poincare spheres were covered at both of the frequencies in low power test. The thermal stress of polarizer were estimated by the numerical simulations. The twister polarizer has been tested up to 0.24 MW during 3 s at 110 GHz.
Saigusa, Mikio*; Atsumi, Kohei*; Yamaguchi, Tomoki*; Oda, Yasuhisa; Sakamoto, Keishi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.964 - 969, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)Atsumi, Kohei*; Yamaguchi, Tomoki*; Nagashima, Koji*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Fukunari, Masafumi*; Oda, Yasuhisa; Sakamoto, Keishi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8(Sp.1), p.2405077_1 - 2405077_4, 2013/06
Kashiwa, Yoshinori*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Takahashi, Koji; Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(19), p.2249 - 2256, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)High efficiency ECCD operations need an obliquely propagating electromagnetic wave with a specified elliptical polarization in magnetized plasma. The polarizer is necessary in order to excite the specified polarization. In the ITER design for ECCD system, the transmitted power per one waveguide is planned to be 1 MW as CW operation. The ohmic loss evaluation code for grooved mirror polarizers which calculates tangential magnetic field to the material at exterior to the groove and inside of that was developed. Calculation results were made sure of agreement with high power experiment qualitatively, and validity of the evaluation code has been confirmed.
Maebara, Sunao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Saigusa, Mikio*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Proceedings of 10th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC 2006) (CD-ROM), p.1990 - 1992, 2006/06
International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is an accelerator-based neutron irradiation facility employing the D-Li stripping reaction, to produce the neutron field similar to the D-T Fusion reactor (2 MW/m , 20 dpa/year for Fe). The required beam current of 250 mA is realized by two beam lines of 125 mA, and the output energies at injector, RFQ and DTL were designed to be 0.1, 5 and 40 MeV, respectively. The operation frequency of 175 MHz was selected to accelerate the large current of 125 mA. After an intensive beam simulation, the RFQ with a total length of 12 m was designed to keep the minimum emittance growth with the RF injection power of 2.3 MW CW. For such a 12 m-long RFQ, two coupling plates are indispensable in order to suppress higher modes in a longitudinal direction at least. From beam dynamics point views, the transmission co-efficient has been evaluated by TOUTATIS code, and it is found that the transmission decay within 0.5% can be achieved by employing a gap width of less than 4 mm for a coupling plate design.
, 20 dpa/year for Fe). The required beam current of 250 mA is realized by two beam lines of 125 mA, and the output energies at injector, RFQ and DTL were designed to be 0.1, 5 and 40 MeV, respectively. The operation frequency of 175 MHz was selected to accelerate the large current of 125 mA. After an intensive beam simulation, the RFQ with a total length of 12 m was designed to keep the minimum emittance growth with the RF injection power of 2.3 MW CW. For such a 12 m-long RFQ, two coupling plates are indispensable in order to suppress higher modes in a longitudinal direction at least. From beam dynamics point views, the transmission co-efficient has been evaluated by TOUTATIS code, and it is found that the transmission decay within 0.5% can be achieved by employing a gap width of less than 4 mm for a coupling plate design.
Maebara, Sunao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Saigusa, Mikio*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 75-79, p.823 - 827, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.10(Nuclear Science & Technology)An RF-Input coupler with a multi-loop antenna using co-axial waveguides has been developed for the RFQ linac on IFMIF. In case of using a loop antenna, the loop antenna structure will affected phase difference and power balance in each cavity. A mock-up loop antenna using the pipe diameter of 10mm was fabricated, phase differences and power balances were measured by a low power test. It is found that it is necessary to shorten the installed depth up to 3 cm to make the phase differences and power balance small. But, from a withstanding voltage, it is difficult to couple multi-MW with the single coupler. The coupling with multi-loop antennas using two or four loops is better than one loop antenna from the point views of both withstanding voltage and power balance. The phase difference and power balance were also measured in both cases. A good average phase-difference of 179 . and a good RF power balance within 8% error for each cavity were obtained. These results showed one of feasibility for an RF-Input coupler with a multi-loop antenna in the IFMIF 175 MHz RFQ.
. and a good RF power balance within 8% error for each cavity were obtained. These results showed one of feasibility for an RF-Input coupler with a multi-loop antenna in the IFMIF 175 MHz RFQ.
Saigusa, Mikio*; Takahashi, Koji; Kashiwa, Yoshinori*; Oishi, Shimpei*; Hoshi, Yuki*; Nakahata, Hiroyuki*; Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 74(1-4), p.473 - 478, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)The specification of an electron cyclotron current driving (ECCD) system in International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) demands severe operational conditions for transmission lines and polarizers. For evaluating Ohmic loss of a miter bend type polarizer, the six polarizers were made of chromium copper alloy, installed in miter bends and tested at a frequency of 170GHz, rf power of 441kW and pulse duration of 0.1-6 seconds. The increase in temperature on the back of the grooved mirrors has been measured with thermo couplers during high power rf pulses. The Ohmic loss of grooved mirrors strongly depends on the rotation angle of the polarization plane of the incident waves and the mirror rotation in high power experiments, for example the Ohmic loss distributed from 0.2% to1.6%. The thermal analysis of grooved mirror has been performed with the 3D FEM code: FEVA. The all strange behavior of Ohmic loss of polarizers could be explained, theoretically.
Maebara, Sunao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Saigusa, Mikio*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Fusion Science and Technology, 47(4), p.941 - 945, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For tuning the 175MHz RFQ used in the baseline design of IFMIF, the RF power-balance control by slug tuner is indispensable because the RF power-balance for quadrupole operation mode (TE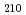 ) in each RFQ quadrant will be affected by the insertion of the loop antennas and pick-up coils. In this study, RF power-balance recovery by slug tuners have been measured by using a low power module of 175MHz RFQ mock-up. The optimal insertion depth of loop antenna was determined to be 3 cm for realizing the appropriate phase differences of TE
) in each RFQ quadrant will be affected by the insertion of the loop antennas and pick-up coils. In this study, RF power-balance recovery by slug tuners have been measured by using a low power module of 175MHz RFQ mock-up. The optimal insertion depth of loop antenna was determined to be 3 cm for realizing the appropriate phase differences of TE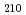 mode. Under this condition, cylindrical slug tuners were inserted, and S
mode. Under this condition, cylindrical slug tuners were inserted, and S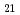 parameters in each cavity were measured. As a typical result, RF power-balance control less than 20% error can be achieved in case of
parameters in each cavity were measured. As a typical result, RF power-balance control less than 20% error can be achieved in case of  3cm tuner up to 3cm insertion.
3cm tuner up to 3cm insertion.
Maebara, Sunao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Saigusa, Mikio*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAERI-Research 2005-007, 11 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Maebara, Sunao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Saito, Yuichi*; Saigusa, Mikio*
Proceedings of 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC '05) (CD-ROM), p.904 - 906, 2005/00
The IFMIF is an accelerator-based neutron irradiation facility employing the D-Li stripping reaction. The required beam current of 250 mA is realized by two beam lines of 125mA, and the output energies at injector, RFQ and DTL were designed to be 0.1, 5 and 40 MeV, respectively. The operation frequency of 175MHz was selected to accelerate the large current of 125mA. After an intensive beam simulation, the RFQ with a total length of 12m was designed to keep the minimum emittance growth with the RF injection power of 2.3MW CW. For such a 175MHz RFQ, a design for RF input coupler with loop antenna and co-axial window, supplying RF power shared by 3  4 ports, was conducted by using MW-Studio code. In order to withstand the voltage exceeding 200kW CW per one loop antenna, the co-axial line of 4 1/16" diameter is necessary, and it is found that the electric field distortion factor less than 1% can be achieved in beam bore only by employing the 4-loop antenna configuration providing the same power for each quadrants.
4 ports, was conducted by using MW-Studio code. In order to withstand the voltage exceeding 200kW CW per one loop antenna, the co-axial line of 4 1/16" diameter is necessary, and it is found that the electric field distortion factor less than 1% can be achieved in beam bore only by employing the 4-loop antenna configuration providing the same power for each quadrants.
Kashiwa, Yoshinori*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Takahashi, Koji; Oishi, Shimpei*; Hoshi, Yuki*; Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Proceedings of 2004 International Symposium on Microwave Science and Its Application to Related Fields (Microwave 2004), p.527 - 530, 2004/07
An electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) system is, especially, necessary to suppress the neoclassical tearing mode instability in ITER. The polarizers are one of the important components in the ECCD system, to generate optimum polarization for an efficient ECCD. An ohmic loss of the polarizers is evaluated, when 170GHz, high power RF wave taransmits, in oreder to investigate its performance. The maximum temperature increase on the back plate of the deep grooved and the conventinal type were 65 C and 30
C and 30 C, respectively. RF power and pulse were 441kW and 6sec, respectively. The dependence of temperature increase on the plolarizer angle obtained in the experiment agrees with the calculation, qualitatively. It was also found that the significant reduction of ohmic loss on the polarizers was achievable with the optimized rotation angle of the linearly polarized incident wave.
C, respectively. RF power and pulse were 441kW and 6sec, respectively. The dependence of temperature increase on the plolarizer angle obtained in the experiment agrees with the calculation, qualitatively. It was also found that the significant reduction of ohmic loss on the polarizers was achievable with the optimized rotation angle of the linearly polarized incident wave.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Maebara, Sunao; Morishita, Takatoshi; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Takeuchi, Hiroshi; Sazawa, Shingo*; Saigusa, Mikio*
Proceedings of 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC 2003) (CD-ROM), p.2829 - 2831, 2003/00
It is indispensable to obtain the technical know-how of the IFMIF RFQ design in the development of RFQ system. It is very important to determine the mesh size in analysis code of the RFQ design. The design of 175MHz RFQ mock-up modules has been done by MAFIA code. Based on this design, the 175MHz RFQ mock-up which consists of two end-plate modules and RFQ modules are fabricated for low power tests. The resonant frequencies have been measured in RFQ length of 1.1m and 2.1m.The measured frequencies are in a good agreement with the calculated values within 1MHz when the mesh size is 1/350 of the longitudinal length.
Saigusa, Mikio*; Takahashi, Koji; Oishi, Shimpei*; Kashiwa, Yoshitada*; Hoshi, Yuki*; Kobayashi, Yuki*; Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Proceedings of IAEA TM on ECRH Physics and Technology for ITER (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2003/00
The specified elliptical polarization which is necessary to excite a pure ordinary or extraordinary mode, when rf waves obliquely propagate in plasma, for electron cyclotron current drive(ECCD) can be produced by a grooved mirror polarizer. The Joule loss of deeped groove mirrors has been experimentally investigated at a frequency of 170 GHz. The strange dependence of the Joule loss of groove mirror on the mirror rotation angle was obtained. In addition, maximum loss of 0.8% in regard to the injection rf power to the mirrors was estimated. The calculation code to estimate the Joule loss of grooved mirror is developed for the structure analysis. The dependence of the mirror on its rotation angle can be explained by the calculation results, clearly.
Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Nakayama, Koichi*; Suzuki, Shohei*; Saigusa, Mikio*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part2), p.1691 - 1695, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF) is an accelerator-based intense neutron source for fusion reactor materials development. Each one of the two accelerator modules needs to have a capability to provide the 40MeV/125mA deuteron beam continuously. Although the technology to produce the 7MeV/100mA proton beam is already verified using 350 MHz linac in the past, an engineering study using a prototype is necessary to verify the performance of IFMIF 175 MHz deuteron linac, and Engineering Validation Phase (EVP) is planned for this purpose. Some critical design parameters, like final and transition energies of linacs or RF source characteristics, are needed to be optimised for the prototype. As it is also important to verify the essential component technology, e.g. ion source, RFQ beam matching, rf system components, etc., the present status and expected results of such undergoing verification tests are described. An integrated concept of prototype accelerator is shown as a Japanese proposal for EVP to provide for the international discussion.
Moriyama, Shinichi; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Kimura, Haruyuki; Anno, Katsuto; Yokokura, Kenji; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Terakado, Masayuki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Saigusa, Mikio*
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.467 - 481, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Shinohara, Koji; Nishitani, Takeo; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kramer, G. J.*; Nemoto, Masahiro*; Kondoh, Takashi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.315 - 326, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:46.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)Energetic particle experiments in JT-60U are summarized, mainly covering ripple loss and Alfven eigenmodes (AE modes). Significant loss was observed for 85 keV NBI ions and fusion-produced tritons increased when toroidal field ripple at the plasma surface, especially in reversed shear plasma. Measurement of hot spots on the first wall due to ripple loss confirmed agreement with code predictions, validating the modeling incorporated in an orbit-following Monte Carlo code. A variety of AE modes were destabilized in ICRF minority heating and negative-ion-based NBI (N-NBI) heating. Most of the observed modes are gap modes identified to be TAE, EAE and NAE. Interesting finding is pulsating modes accompanying frequency sweep, which were destabilized by N-NBI and sometimes induced a beam ion loss of up to 25%. Also presented are energetic particle issues in auxiliary heating with ICRF and N-NBI.
Saigusa, Mikio*; Kanazawa, Sadayoshi*; Ogawa, Toshihide; Kawashima, Hisato; Kikuchi, Kazuo; Ido, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*
Nuclear Fusion, 42(4), p.412 - 417, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A new diagnostic method is proposed for direct measurements of electromagnetic field patterns of fast waves in toroidal plasmas. The fluctuation of ponderomotive potential at a beat wave frequency between the two frequency fast waves produces the actual potential fluctuation via electron and ion motions. A heavy ion beam probe (HIBP) detected the potential fluctuation patterns at a beat wave frequency during the fast wave pulse. The amplitude of potential fluctuations decreases with increasing an electron temperature in fast wave current drive (FWCD) experiments of JFT-2M, due to the improvement of wave absorption via electron Landau damping. The measured potential fluctuation does not contradict with the prediction using a full wave code calculations.