Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horibe, Sohei*; Shimizu, Hiroki*; Hoshi, Kojiro*; Makiuchi, Takahiko*; Hioki, Tomosato*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Express, 16(7), p.073001_1 - 073001_4, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Umeda, Maki; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Imai, Masaki; Sato, Nana; Saito, Eiji
Review of Scientific Instruments, 94(6), p.063906_1 - 063906_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation)Meer, H.*; Wust, S.*; Schmitt, C.*; Herrgen, P.*; Fuhrmann, F.*; Hirtle, S.*; Bednarz, B.*; Rajan, A.*; Ramos, R.*; Ni o, M. A.*; et al.
o, M. A.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 33(21), p.2213536_1 - 2213536_6, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:54.89(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Zhou, Z.*; Frost, W.*; Lloyd, D. C.*; Seki, Takeshi*; Kubota, Takahide*; Ramos, R.*; Saito, Eiji; Takanashi, Koki; Hirohata, Atsufumi*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 571, p.170575_1 - 170575_5, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Adachi, Hiroto*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 107(15), p.155142_1 - 155142_10, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kikkawa, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji
Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics, 14, p.129 - 151, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:85.47(Physics, Condensed Matter)Hirata, Sakiko*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Meiji, Shogo*; Tamekuni, Seita*; Okudera, Kosuke*; Hamada, Shoken*; Sakamoto, Chihiro*; Honda, Takumi*; Matsushita, Kosuke*; Muramatsu, Satoru*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(1), p.474 - 486, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Maekawa, Sadamichi; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 133(2), p.020902_1 - 020902_24, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:96.84(Physics, Applied)Oyanagi, Koichi*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 107(1), p.014423_1 - 014423_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Lee, O.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Umeda, Maki; Zollitsch, C. W.*; Elyasi, M.*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Kurebayashi, Hidekazu*
Physical Review Letters, 130(4), p.046703_1 - 046703_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:80.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hoshi, Kojiro*; Hioki, Tomosato*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 121(21), p.212404_1 - 212404_6, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.67(Physics, Applied) Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructuresIeda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The combination of spin-driven thermoelectric (STE) devices based on spin Seebeck effect (SSE), and radioactive isotopes as heat sources, has potential as a next-generation method of power generation in applications such as power supplies for space probes. However, there has been very limited knowledge available indicating the irradiation tolerance of spin thermoelectric devices. Through analysis using a heavy ion-beam accelerator and the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements, we show that a prototypical STE device based on Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to
/Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to 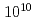 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 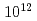 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y
/Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
/Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
 Cs activity concentration in the aquatic insect
Cs activity concentration in the aquatic insect 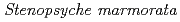 (Tricoptera: Stenopsychidae) in the Ota River, Fukushima, Japan
(Tricoptera: Stenopsychidae) in the Ota River, Fukushima, JapanIshii, Yumiko*; Miura, Hikaru*; Jo, J.*; Tsuji, Hideki*; Saito, Rie; Koarai, Kazuma; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Urushidate, Tadayuki*; Nishikiori, Tatsuhiro*; Wada, Toshihiro*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 17(5), p.e0268629_1 - e0268629_17, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.07(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We investigated the variability in  Cs activity concentration in individual aquatic insects in detritivorous caddisfly (
Cs activity concentration in individual aquatic insects in detritivorous caddisfly (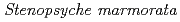 ) and carnivorous dobsonfly (
) and carnivorous dobsonfly ( ) larvae from the Ota River, Fukushima. Caddisfly larvae showed sporadically higher radioactivity, whereas no such outliers were observed in dobsonfly larvae. Autoradiography and scanning electron microscopy analyses confirmed that these caddisfly larvae samples contained radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which are insoluble Cs-bearing silicate glass particles. CsMPs were also found in potential food sources of caddisfly larvae, such as periphyton and drifting particulate organic matter, indicating that larvae may ingest CsMPs along with food particles of similar size. Although CsMPs distribution and uptake by organisms in freshwater ecosystems is relatively unknown, our study demonstrates that CsMPs can be taken up by aquatic insects.
) larvae from the Ota River, Fukushima. Caddisfly larvae showed sporadically higher radioactivity, whereas no such outliers were observed in dobsonfly larvae. Autoradiography and scanning electron microscopy analyses confirmed that these caddisfly larvae samples contained radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which are insoluble Cs-bearing silicate glass particles. CsMPs were also found in potential food sources of caddisfly larvae, such as periphyton and drifting particulate organic matter, indicating that larvae may ingest CsMPs along with food particles of similar size. Although CsMPs distribution and uptake by organisms in freshwater ecosystems is relatively unknown, our study demonstrates that CsMPs can be taken up by aquatic insects.
Yokoi, Naoto*; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 545, p.168673_1 - 168673_12, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Elyasi, M.*; Saito, Eiji; Bauer, G. E. W.*
Physical Review B, 105(5), p.054403_1 - 054403_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:77.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.19(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Schreiber, F.*; Meer, H.*; Schmitt, C.*; Ramos, R.*; Saito, Eiji; Baldrati, L.*; Kl ui, M.*
ui, M.*
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 16(6), p.064023_1 - 064023_9, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.71(Physics, Applied)Oyanagi, Koichi*; Gomez-Perez, J. M.*; Zhang, X.-P.*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Chen, Y.*; Sagasta, E.*; Chuvilin, A.*; Hueso, L. E.*; Golovach, V. N.*; Sebastian Bergeret, F.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(13), p.134428_1 - 134428_14, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:77.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
O /YIG structure
/YIG structureQi, J.*; Hou, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Saito, Eiji; Jin, X.*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 534, p.167980_1 - 167980_6, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nishimura, Hayato*; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Ajita, Saya*; Shibayama, Yuki*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Yasuda, Ryo*; Shobu, Takahisa; Akiyama, Eiji*
Tetsu To Hagane, 107(9), p.760 - 768, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English