Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kobayashi, Naoki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Furukawa, Hazuki*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Terada, Noriki*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Manuel, P.*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The frustrated antiferromagnet CuFeO exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (
exhibits pressure-induced complex magnetic phase transitions from the commensurate collinear (CM1) phase to several incommensurate noncollinear phases. To study the effect of high pressure on magnetic interactions, we performed neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering experiments under high-pressure conditions. With increasing pressure, the CM1 ground state becomes less stable against application of a magnetic field even below the critical pressure (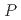
 3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from
3 GPa), as proved by the significant reduction in the critical magnetic field from 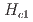 =7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of
=7.5 T to 4.5 T at 2.1 GPa. Additionally, the energy gap in the spin-wave dispersion relation is reduced from 1.0 to 0.88 meV by the application of a pressure of 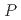 = 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
= 2.1 GPa. Comparing the experimental results with spin-wave calculations revealed that the change in the spin-wave excitation can be explained by the reduction in either the uniaxial anisotropy term or the degree of separation in the nearest-neighbor exchange interactions.
 Si
Si
Kon, Fusako*; Tabata, Chihiro; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044701_1 - 044701_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:48.53(Chemistry, Physical)Takagi, Hirotaka*; Takagi, Rina*; Minami, Susumu*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Michito*; Yanagi, Yuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Khanh, N.*; Karube, Kosuke*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:99.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takagi, Rina*; Matsuyama, Naofumi*; Ukleev, V.*; Yu, L.*; White, J. S.*; Francoual, S.*; Mardegan, J. R. L.*; Hayami, Satoru*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.1472_1 - 1472_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:111 Percentile:99.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences) investigated by time-of-flight neutron diffraction in long-pulse magnetic fields
investigated by time-of-flight neutron diffraction in long-pulse magnetic fieldsWatanabe, Masao; Nakajima, Taro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Matsui, Kazuki*; Kanda, Tomoki*; Nomoto, Tetsuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Saito, Hiraku*; Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, due to advances in precision measurement technology in pulsed magnetic fields, a novel magnetic state was discovered in a strong magnetic field. We constructed a measurement environment that can comprehensively explore the reciprocal lattice space under magnetic fields up to 14 Tesla by combining the long-pulse magnetic field generated by the supercapacitor and pulsed neutrons at J-PARC. This equipment can generate a magnetic field that is sufficiently longer than the time width (about 10 milliseconds) of the multi-wavelength neutron pulse passing through the sample. This method was used to investigate the magnetic phase transition in the frustrated magnet CuFeO .
.
 MgGe
MgGe with the Shastry-Sutherland lattice
with the Shastry-Sutherland latticeHirose, Yusuke; Honda, Fuminori*; Settai, Rikio*; Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*
no journal, ,
Ozeki, Kazuhide*; Yonemura, Masao*; Masuzawa, Toru*; Saito, Hidetoshi*; Ogoe, Yasuharu*; Hirakuri, Kenji*; Takeda, Masayasu
no journal, ,
Hydrogen content in the DLC film is very important factor because it greatly influences on its mechanical properties and microstructure such as hardness, wear resistance, surface roughness, and sp3/sp2 ratio. In the present study, we prepared the DLC film using plasma CVD technique varying H /CH
/CH ratio from 0 to 9. Cross-sectional hydrogen content and mass density profiles of the films were defined by neutron and X-ray reflectivity measurements, and the results were compared with that from ERDA analysis. And O/C atomic ratio of the oxide layer of the film surface was also analyzed using XPS. From the neutron and X-ray reflectivity analysis, hydrogen content and mass density in the DLC film increased with film depth from the surface, and average hydrogen content showed more than 30 % in all films. By combining with XPS results, it is clarified that hydrogen content in the surface layer was lower than that in bulk layer.
ratio from 0 to 9. Cross-sectional hydrogen content and mass density profiles of the films were defined by neutron and X-ray reflectivity measurements, and the results were compared with that from ERDA analysis. And O/C atomic ratio of the oxide layer of the film surface was also analyzed using XPS. From the neutron and X-ray reflectivity analysis, hydrogen content and mass density in the DLC film increased with film depth from the surface, and average hydrogen content showed more than 30 % in all films. By combining with XPS results, it is clarified that hydrogen content in the surface layer was lower than that in bulk layer.