Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Kudo, Takuto*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Sentoku, Sawako*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.1797_1 - 1797_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0The amount of C in steel, which is critical in determining its properties, is strongly influenced by steel production technology. We propose a novel method of quantifying the bulk C content in steel non-destructively using muons. This revolutionary method may be used not only in the quality control of steel in production, but also in analyzing precious steel archaeological artifacts. A negatively charged muon forms an atomic system owing to its negative charge, and is finally absorbed into the nucleus or decays to an electron. The lifetimes of muons differ significantly, depending on whether they are trapped by Fe or C atoms, and identifying the elemental content at the muon stoppage position is possible via muon lifetime measurements. The relationship between the muon capture probabilities of C/Fe and the elemental content of C exhibits a good linearity, and the C content in the steel may be quantitatively determined via muon lifetime measurements. Furthermore, by controlling the incident energies of the muons, they may be stopped in each layer of a stacked sample consisting of three types of steel plates with thicknesses of 0.5 mm, and we successfully determined the C contents in the range 0.20 - 1.03 wt% depth-selectively, without sample destruction.
Nagao, Michihiro*; Kelley, E. G.*; Faraone, A.*; Saito, Makina*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Kurokuzu, Masayuki*; Takata, Shinichi; Seto, Makoto*; Butler, P. D.*
Physical Review Letters, 127(7), p.078102_1 - 078102_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:88.38(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Onuki, Yusuke*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Sato, Shigeo*; Xu, P. G.; Ishigaki, Toru*; Saito, Yoichi*; Todoroki, Hidekazu*; Hayashi, Makoto*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(5), p.1579 - 1584, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:88.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) Ni synchrotron radiation-based M
Ni synchrotron radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of nickel-based nanoparticles with hexagonal structure
ssbauer spectroscopy of nickel-based nanoparticles with hexagonal structureMasuda, Ryo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Kitao, Shinji*; Kurokuzu, Masayuki*; Saito, Makina*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Mitsui, Takaya; Hosoi, Kohei*; Kobayashi, Hirokazu*; Kitagawa, Hiroshi*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.20861_1 - 20861_8, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.77(Multidisciplinary Sciences)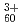 impacts
impactsKitayama, Takumi*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Suzuki, Motofumi*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Sataka, Masao*; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Isoda, Shoji*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 354, p.183 - 186, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)Saito, Tatsuo; Sakai, Akihiro; Sato, Kazuhiko; Yagi, Naoto; Hata, Haruhi; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Kawagoshi, Hiroshi; Hasegawa, Makoto
JAEA-Review 2014-021, 30 Pages, 2014/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency surveyed the reference cases for the disposal of uranium bearing waste in low activity concentration as the contents of their own category 2 waste disposal facility for the Research and Development Activities. We reviewed the concepts mentioned in IAEA and ICRP documents, reference cases of uranium bearing waste disposal in selected countries (USA, Canada, UK, France and Sweden), and the disposal styles of long-lived radioactive waste were summarized, and the action items for application to the disposal system of our country was arranged. The disposal facilities in selected countries can be classified into 2 types with the length of performance assessment period for intruder scenario. They are long term assessment type and short term assessment type. It seems that the disposal system construction in category 2 waste disposal is the most realistic since there are many precedence examples of each country. Correspondence of 2 types of these disposal facilities is useful as a reference case.
 Te synchrotron-radiation-based M
Te synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy
ssbauer spectroscopyKurokuzu, Masayuki*; Kitao, Shinji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Saito, Makina*; Masuda, Ryo*; Mitsui, Takaya; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Seto, Makoto*
Hyperfine Interactions, 226(1), p.687 - 691, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:69.82(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical) Te synchrotron-radiation-based M
Te synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Fe
ssbauer spectroscopy of Fe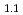 Te and FeTe
Te and FeTe Se
SeKurokuzu, Masayuki*; Kitao, Shinji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Saito, Makina*; Masuda, Ryo*; Mitsui, Takaya; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Seto, Makoto*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(4), p.044708_1 - 044708_4, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Kazuhiko; Sakai, Akihiro; Hata, Haruhi; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Kawagoshi, Hiroshi; Saito, Tatsuo; Hasegawa, Makoto
JAEA-Review 2014-006, 78 Pages, 2014/03
In this paper, we report the result of survey for basic principle of safety assessment for long-lived low-level (LL-LL) waste disposal and experience of the industrial waste disposal sites for uranium bearing waste in France, UK and Sweden, following the report of survey for U.S.A. and Canada published in December 2013.
 ssbauer spectra of
ssbauer spectra of 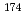 Yb measured with internal conversion electrons
Yb measured with internal conversion electronsMasuda, Ryo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; Kitao, Shinji*; Kurokuzu, Masayuki*; Saito, Makina*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Mitsui, Takaya; Iga, Fumitoshi*; Seto, Makoto
Applied Physics Letters, 104(8), p.082411_1 - 082411_5, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:65.2(Physics, Applied)A detection system for synchrotron-radiation (SR)-based M ssbauer spectroscopy was developed to enhance the nuclear resonant scattering counting rate and thus increase the available nuclides. In the system, a windowless avalanche photodiode (APD) detector was combined with a vacuum cryostat to detect the internal conversion (IC) electrons and fluorescent X-rays accompanied by nuclear de-excitation. As a feasibility study, the SR-based M
ssbauer spectroscopy was developed to enhance the nuclear resonant scattering counting rate and thus increase the available nuclides. In the system, a windowless avalanche photodiode (APD) detector was combined with a vacuum cryostat to detect the internal conversion (IC) electrons and fluorescent X-rays accompanied by nuclear de-excitation. As a feasibility study, the SR-based M ssbauer spectrum using the 76.5 keV level of
ssbauer spectrum using the 76.5 keV level of 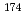 Yb was observed without
Yb was observed without 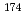 Yb enrichment of the samples. The counting rate was five times higher than that of our previous system, and the spectrum was obtained within 10 h. This result shows that nuclear resonance events can be more efficiently detected by counting IC electrons for nuclides with high IC coefficients. Furthermore, the windowless detection system enables us to place the sample closer to the APD elements and is advantageous for nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements. Therefore, this detection system can not only increase the number of nuclides accessible in SR-based M
Yb enrichment of the samples. The counting rate was five times higher than that of our previous system, and the spectrum was obtained within 10 h. This result shows that nuclear resonance events can be more efficiently detected by counting IC electrons for nuclides with high IC coefficients. Furthermore, the windowless detection system enables us to place the sample closer to the APD elements and is advantageous for nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements. Therefore, this detection system can not only increase the number of nuclides accessible in SR-based M ssbauer spectroscopy but also allows the nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements of small single crystals or enzymes with dilute probe nuclides that are difficult to measure with the previous detection system.
ssbauer spectroscopy but also allows the nuclear resonant inelastic scattering measurements of small single crystals or enzymes with dilute probe nuclides that are difficult to measure with the previous detection system.
Hasegawa, Makoto; Saito, Tatsuo; Zaitsu, Tomohisa; Sato, Kazuhiko; Sakai, Akihiro; Fumoto, Hiromichi*
JAEA-Review 2013-043, 42 Pages, 2013/12
Uranium bearing waste in Japan is not included in Category-2 radioactive waste disposal in NSCRG: F-RW-I.02 (published in August 2010, NSC Japan). Therefore, disposal of uranium bearing waste should be considered in institutionalization. In charge of the consideration, it is thought effective to refer to the proven tactics of the uranium waste disposal in overseas and the information on a safe regulatory system. Since the view of regulations and enterprises in this field are progressing day by day, renewal of the existing information of disposal of the uranium waste in each country is required. Furthermore, amendment of the U.S. federal rule aiming at safety disposal of depleted uranium is in progress. It is important to collect and arrange the latest information on the two above-mentioned points. Therefore, it visited the disposal responsible organization and regulatory agency of the disposal site of the uranium waste in the U.S. and Canada, and held institution investigations and interviews paying attention to the following four items: (1) "amendment of the U.S. 10CFR61", (2) "Safety evaluation of uranium bearing waste", (3) "Disposal site design", (4) "Stakeholder involvement".
Niwa, Hideharu*; Saito, Makoto*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Moriya, Shogo*; Matsubayashi, Katsuyuki*; Nabae, Yuta*; Kuroki, Shigeki*; Ikeda, Takashi; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 223, p.30 - 35, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:50.94(Chemistry, Physical)To design non-platinum, inexpensive, but high performance carbon-based cathode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells, it is important to elucidate the active site for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). However, it is difficult to directly identify the active site by applying conventional structural or electronic probes to such complex systems. Here, we used C 1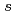 X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to observe electronic structure of carbon in iron phthalocyanine-based catalysts, and found a signature of edge exposure below the
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to observe electronic structure of carbon in iron phthalocyanine-based catalysts, and found a signature of edge exposure below the 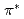 edge, whose intensity is well correlated with the ORR activity. These results demonstrate that C 1
edge, whose intensity is well correlated with the ORR activity. These results demonstrate that C 1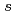 XAS can be used to characterize the ORR activity of carbon-based cathode catalysts in terms of the edge exposure.
XAS can be used to characterize the ORR activity of carbon-based cathode catalysts in terms of the edge exposure.
Ueda, Yoshio*; Oya, Kaoru*; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Ito, Atsushi*; Ono, Tadayoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kawashima, Hisato; Kawamura, Gakushi*; Kenmotsu, Takahiro*; Saito, Seiki*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(9), p.484 - 502, 2012/09
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Saito, Makoto*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ofuchi, Hironori*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ikeda, Takashi; Koshigoe, Yuka*; Ozaki, Junichi*; et al.
Electrochimica Acta, 74, p.254 - 259, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:80.98(Electrochemistry)The electronic structure of the residual metal atoms in FePc-based carbon catalysts, prepared by pyrolyzing a mixture of FePc and phenolic resin polymer at 800 C, before and after acid washing have been investigated using XAFS spectroscopy to clarify the role of Fe in the ORR activity. The decomposition analyses for the XAFS spectra reveal that the composition ratio of each Fe component is unaltered by the acid washing, indicating that the residual Fe components were removed by the acid washing irrespective of their chemical states. Because the oxygen reduction potential was approximately unchanged by the acid washing, the residual Fe itself does not seem to contribute directly to the ORR activity. The residual Fe can act as a catalyst to accelerate the growth of the sp
C, before and after acid washing have been investigated using XAFS spectroscopy to clarify the role of Fe in the ORR activity. The decomposition analyses for the XAFS spectra reveal that the composition ratio of each Fe component is unaltered by the acid washing, indicating that the residual Fe components were removed by the acid washing irrespective of their chemical states. Because the oxygen reduction potential was approximately unchanged by the acid washing, the residual Fe itself does not seem to contribute directly to the ORR activity. The residual Fe can act as a catalyst to accelerate the growth of the sp carbon network during pyrolysis. The results imply that light elements are components of the ORR active sites in the FePc-based carbon catalysts.
carbon network during pyrolysis. The results imply that light elements are components of the ORR active sites in the FePc-based carbon catalysts.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Kita, Makoto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 85(2), p.228 - 230, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:61.4(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Elemental analysis of bulk materials can be performed by detecting the high-energy X-rays emitted from muonic atoms. Muon irradiation of standard bronze samples was performed to determine the muon capture probabilities for the elemental components from muonic X-ray spectra. Nondestructive elemental analysis of an ancient Chinese coin was also performed.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Uchiyama, Takashi*; Miyajima, Tsukasa*; Honda, Yosuke*; Sato, Kotaro*; Matsuba, Shunya*; Saito, Yoshio*; Kobayashi, Masanori*; Kurisu, Hiriki*; Hajima, Ryoichi; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.717 - 720, 2010/08
A 500-kV photocathode DC electron gun which can supply the beam of a low emittance and a high average current has been developed in collaboration with KEK, JAEA, Hiroshima Univ., Nagoya Univ. and Yamaguchi Univ. The vacuum of the gun chamber has to be lower Extreme High Vacuum for maintain cathode-life time. A titanium chamber and new material of ceramic were employed to reduce outgassing rate. The result of outgassing rate of the gun chamber is described in this report.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Honda, Yosuke*; Miyajima, Tsukasa*; Uchiyama, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Masanori*; Muto, Toshiya*; Matsuba, Shunya*; Sakanaka, Shogo*; Sato, Kotaro*; Saito, Yoshio*; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.860 - 862, 2009/08
A newly 500 kV electron gun (2nd - 500 kV gun) for an ERL light source is designed at KEK. A new concept and state of-the-art technologies of vacuum system, ceramic insulators, high voltage power supply, photocathode and preparation system will be employed. The details are described in this report.
Saito, Kenji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Kawamata, Takanori; Nemoto, Masumi; Motegi, Toshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-015, 52 Pages, 2009/05
As In-core temperature monitoring system, Type N thermocouples arranged at hot plenum block measures the primary coolant temperature at each hot plenum block in order to monitor the condition of the reactor core during the reactor operation. Type N thermocouples should have a long lifetime with high reliability under the high temperature environment of about 1000 C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
Ueda, Kiyoshi*; Fukuzawa, Hironobu*; Liu, X.*; Sakai, Katsunori*; Pr mper, G.*; Morishita, Yuichiro*; Saito, Norio*; Suzuki, Isao*; Nagaya, Kiyonobu*; Iwayama, Hiroshi*; et al.
mper, G.*; Morishita, Yuichiro*; Saito, Norio*; Suzuki, Isao*; Nagaya, Kiyonobu*; Iwayama, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 166-167, p.3 - 10, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:72.33(Spectroscopy)Interatomic Coulombic decay (ICD) in Ar , ArKr and Kr
, ArKr and Kr following Ar 2p or Kr 3d Auger decay has been investigated by means of momentum-resolved electron-ion-ion-coincidence spectroscopy. This sequential decay leads to Coulombic dissociation into dication and monocation. Simultaneously determining the kinetic energy of the ICD electron and the kinetic energy release between the two atomic ions, we could unambiguously identify the ICD channels. We find that, in general, spin conserved ICD, in which the singlet (triplet) dicationic state produced via the atomic Auger decay preferentially decays to the singlet (triplet) state, transferring the energy to the other atom, is faster than the spin-flip ICD, in which the Auger final singlet (triplet) dicationic state decays to the triplet (singlet) state.
following Ar 2p or Kr 3d Auger decay has been investigated by means of momentum-resolved electron-ion-ion-coincidence spectroscopy. This sequential decay leads to Coulombic dissociation into dication and monocation. Simultaneously determining the kinetic energy of the ICD electron and the kinetic energy release between the two atomic ions, we could unambiguously identify the ICD channels. We find that, in general, spin conserved ICD, in which the singlet (triplet) dicationic state produced via the atomic Auger decay preferentially decays to the singlet (triplet) state, transferring the energy to the other atom, is faster than the spin-flip ICD, in which the Auger final singlet (triplet) dicationic state decays to the triplet (singlet) state.
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Kikuchi, Kenji; Kurata, Yuji; Mizumoto, Motoharu; Sasa, Toshinobu; Saito, Shigeru; Nishihara, Kenji; Umeno, Makoto*; Takei, Hayanori
Nuclear Technology, 161(3), p.315 - 328, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)Feasibility was discussed for lead-bismuth cooled accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides partitioned from high-level radioactive waste. Since lead-bismuth will cause considerable corrosion and erosion effects at high temperature, the fuel clad temperature must be kept as low as possible. Moreover, the most critical issue of ADS design is engineering viability of the high-power spallation target and the beam window. Thermal-hydraulic and structural analysis was carried out for both the fuel assembly and the beam window. In addition to the analysis in steady state, transient behaviors were also studied during typical transient and unprotected accidents. The results showed that engineering viability is reasonably achievable in nominal operation. For beam trip which will be the most frequent transient, the number of events to cause the failure of the beam window is estimated as more than 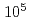 . For safety aspects of ADS during unprotected accidents, estimated results showed that ULOF would cause the most significant problem, if beam operation was kept. Therefore, high reliability of the beam shutdown is required for the ADS safety.
. For safety aspects of ADS during unprotected accidents, estimated results showed that ULOF would cause the most significant problem, if beam operation was kept. Therefore, high reliability of the beam shutdown is required for the ADS safety.