Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yildirim, A. C.*; Mei, H.*; Toda, Kanako*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Applied Clay Science, 274, p.107853_1 - 107853_9, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical) and Eu
and Eu onto coherent and melange-type pre-neogene sedimentary rocks
onto coherent and melange-type pre-neogene sedimentary rocksHou, L.*; Toda, Kanako*; Mei, H.; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1488 - 1498, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.80(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Saito, Takumi*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 258, p.107476_1 - 107476_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.91(Chemistry, Physical)Tanaka, Takuro*; Fukuoka, Masafumi*; Toda, Kanako*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Niwano, Yuma*; Kato, Hiroaki*; Kobayashi, Natsuko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; et al.
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 4(8), p.3579 - 3586, 2024/08
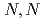 -dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid; Effect of S donor on metal extraction
-dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid; Effect of S donor on metal extractionShimojo, Kojiro; Fujiwara, Iori*; Saito, Takumi*; Oshima, Tatsuya*
Analytical Sciences, 40(8), p.1429 - 1436, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Extraction ability of 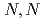 -dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (T-DODGAA), a soft-base sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxylic acid connected by a thioether chain, for 56 metal ions have been comprehensively investigated and compared with that of N,N-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) with an etheric oxygen atom, a hard-base donor. The p
-dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (T-DODGAA), a soft-base sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxylic acid connected by a thioether chain, for 56 metal ions have been comprehensively investigated and compared with that of N,N-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) with an etheric oxygen atom, a hard-base donor. The p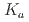 of the thiodiglycolamic acid framework was determined to be 3.71
of the thiodiglycolamic acid framework was determined to be 3.71  0.06 in water (0.1 M LiCl, 25
0.06 in water (0.1 M LiCl, 25 C ) by potentiometric titration, indicating that T-DODGAA is a slightly weaker acid than DODGAA (p
C ) by potentiometric titration, indicating that T-DODGAA is a slightly weaker acid than DODGAA (p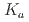 = 3.54
= 3.54  0.03). T-DODGAA can quantitatively extract various metal ions from the 56 metal ions through a proton-exchange reaction. T-DODGAA provided higher extraction performance than DODGAA for Hf(IV), Cr(III), Fe(III), Ni(II), Cu(II), Pd(II), Ag(I), Au(III), Hg(II), Al(III), and Ga(III), especially for soft metal ions. Furthermore, to demonstrate the practical feasibility of T-DODGAA for hydrometallurgy and metal recycling, we performed selective separation tests of rare metal ions such as Sc(III), Ni(II), Co(II), Pd(II), Au(III), In(III), and Ga(II) in metal-mixed extraction systems.
0.03). T-DODGAA can quantitatively extract various metal ions from the 56 metal ions through a proton-exchange reaction. T-DODGAA provided higher extraction performance than DODGAA for Hf(IV), Cr(III), Fe(III), Ni(II), Cu(II), Pd(II), Ag(I), Au(III), Hg(II), Al(III), and Ga(III), especially for soft metal ions. Furthermore, to demonstrate the practical feasibility of T-DODGAA for hydrometallurgy and metal recycling, we performed selective separation tests of rare metal ions such as Sc(III), Ni(II), Co(II), Pd(II), Au(III), In(III), and Ga(II) in metal-mixed extraction systems.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okumura, Masahiko; Ueda, Yuki; Saito, Takumi*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yomogida, Takumi; Sazaki, Gen*; Ikeda, Atsushi
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 7, p.128_1 - 128_13, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Miyazaki, Kanako*; Takehara, Masato*; Minomo, Kenta*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Saito, Takumi*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Takano, Masahide; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 470(15), p.134104_1 - 134104_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Engineering, Environmental)Mei, H.; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Sugiura, Yuki; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 162, p.105926_1 - 105926_8, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Saito, Takumi*; Nishi, Shusaku*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 3(12), p.4103 - 4112, 2023/12
Saito, Takumi*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okubo, Takahiro*; Miura, Daisuke*; Kumada, Takayuki
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(26), p.9802 - 9810, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.13(Engineering, Environmental)Murota, Kento*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Saito, Takumi*
Applied Geochemistry, 152, p.105620_1 - 105620_11, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:63.49(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Hirata, Sakiko*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Meiji, Shogo*; Tamekuni, Seita*; Okudera, Kosuke*; Hamada, Shoken*; Sakamoto, Chihiro*; Honda, Takumi*; Matsushita, Kosuke*; Muramatsu, Satoru*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(1), p.474 - 486, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.08(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Tachi, Yukio; Saito, Takumi*; Kirishima, Akira*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 64(5), p.290 - 295, 2022/05
, 64(5), p.290 - 295, 2022/05
no abstracts in English
 C control rods in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors during meltdown; B-Li isotopic signatures in cesium-rich microparticles
C control rods in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors during meltdown; B-Li isotopic signatures in cesium-rich microparticlesFueda, Kazuki*; Takami, Ryu*; Minomo, Kenta*; Morooka, Kazuya*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Saito, Takumi*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Onuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, p.128214_1 - 128214_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.41(Engineering, Environmental) ion complex; Presence of a Rh
ion complex; Presence of a Rh Intermediate in Direct Photoreduction
Intermediate in Direct PhotoreductionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(12), p.5607 - 5616, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.33(Chemistry, Physical)The reaction mechanism of the direct photoreduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh
species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh
species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh . Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh
. Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh
species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh species. The Rh
species. The Rh species were assigned to Rh
species were assigned to Rh , Rh
, Rh , and Rh
, and Rh species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
 Rh
Rh
 Rh
Rh . A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh
. A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh
, photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , and photooxidation of Rh
, and photooxidation of Rh , well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh
, well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh species.
species.
Mei, H.; Aoyagi, Noboru; Saito, Takumi*; Kozai, Naofumi; Sugiura, Yuki; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 136, p.105178_1 - 105178_8, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:89.42(Geochemistry & Geophysics) and Tb
and Tb measured by gel electrophoresis techniques
measured by gel electrophoresis techniquesNakano, Sumika*; Marumo, Kazuki*; Kazami, Rintaro*; Saito, Takumi*; Haraga, Tomoko; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Saito, Shingo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 55(22), p.15172 - 15180, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.63(Engineering, Environmental)Humic acid (HA) can strongly complex with metal ions to form a supramolecular assembly via coordination binding. However, determining the supramolecular size distribution and stoichiometry between small HA unit molecules constituting HA supramolecule and metal ions has proven to be challenging. Here, we investigated the changes in the size distributions of HAs induced by Cu and Tb
and Tb ions using a unique polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the separation and quantification of HA complexes and metal ions bound, followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and EEM-PARAFAC. It was found that the supramolecular behaviors of Cu
ions using a unique polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the separation and quantification of HA complexes and metal ions bound, followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and EEM-PARAFAC. It was found that the supramolecular behaviors of Cu and Tb
and Tb complexes with HA collected from peat and deep groundwater (HHA) differed. Our results suggest that this supramolecular stoichiometry is related to the abundance of sulfur atoms in the elemental composition of HHA. Our results provide new insights into HA supramolecules formed via metal complexation.
complexes with HA collected from peat and deep groundwater (HHA) differed. Our results suggest that this supramolecular stoichiometry is related to the abundance of sulfur atoms in the elemental composition of HHA. Our results provide new insights into HA supramolecules formed via metal complexation.
Zhou, Q.*; Saito, Takumi*; Suzuki, Seiya; Yano, Kimihiko; Suzuki, Shunichi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.461 - 472, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:70.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)Saeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Tsuji, Takuya; Oba, Hironori*
Analytical Sciences, 36(11), p.1371 - 1378, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.69(Chemistry, Analytical)We measured X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and Raman spectra of isopolymolybdates(VI) in HNO solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo
solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo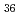 O
O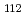 (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [Mo
[Mo O
O (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [HMoO
[HMoO (H
(H O)
O) ]
] in the highly concentrated HNO
in the highly concentrated HNO solution.
solution.