Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:48.53(Chemistry, Physical) Ga K-edge XANES study of Ga-exchanged zeolites at high temperatures under different atmospheres including vacuum, CO, and pressurized H
Ga K-edge XANES study of Ga-exchanged zeolites at high temperatures under different atmospheres including vacuum, CO, and pressurized H
Huang, M.*; Kinjo, Tetsuya*; Yasumura, Shunsaku*; Toyao, Takashi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Shimizu, Kenichi*; Namiki, Norikazu*; Maeno, Zen*
Catalysis Science & Technology, 13(23), p.6832 - 6838, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012005_1 - 012005_6, 2023/10
The Japan Research Ractor-3 (JRR-3) is operation resumed on February 26, 2021, and the shared use was also restarted in July, 2021. With the resumption of JRR-3 operation, two imaging facilities called TNRF and CNRF have also resumed their utilization. In this presentation, we report the details of these two neutron facilities.
 symmetry for anisotropic
symmetry for anisotropic 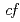 hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi
hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Higashiya, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165121_1 - 165121_10, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:94.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:69.46(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Saito, Kei*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Takai, Kenichi*
Key Engineering Materials, 967, p.11 - 16, 2023/07
Hydrogen-enhanced strain-induced vacancy, one of the defects associated with promising hydrogen embrittlement mechanisms, was validated for tempered martensitic steel showing quasi-cleavage fracture with a tensile strength of 1500 MPa level by slow strain rate tensile test in-situ electrochemical hydrogen charging. The effect of newly formed vacancy-type defects on mechanical properties of tempered martensitic steel was also studied. Combined use of low-temperature thermal desorption spectroscopy (L-TDS) and the tensile test revealed the following three things: (i) hydrogen enhanced the accumulation of vacancy-type defects with plastic straining, (ii) accumulated vacancy-type defects deteriorated the ductility of the tempered martensitic steel after hydrogen release, and (iii) aging in the range from 50 C to 150
C to 150 C after applying given plastic strain with hydrogen charging decreased the amount of newly formed vacancy-type defects, and then resulted in the recovery of the ductility.
C after applying given plastic strain with hydrogen charging decreased the amount of newly formed vacancy-type defects, and then resulted in the recovery of the ductility.
Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 569, p.153921_1 - 153921_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:42.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O
Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Okane, Tetsuo; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Harii, Kazuya; Ieda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011192_1 - 011192_6, 2020/03
High energy X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements were carried out for the Spin Seebeck system Pt/Y Fe
Fe O
O (YIG). This system was found to show anomalous Hall effect, possible due to the formation of intermetallic compounds between Fe
(YIG). This system was found to show anomalous Hall effect, possible due to the formation of intermetallic compounds between Fe and Pt. To reveal this possibility, we have measured the Fe 1s photoelectron peaks by using HAXPES. It was found that the Fe ions consist of Fe
and Pt. To reveal this possibility, we have measured the Fe 1s photoelectron peaks by using HAXPES. It was found that the Fe ions consist of Fe in YIG and metallic Fe. The formation of the metallic state is consistent with the proposed origin of the anomalous Hall effect. Other spectra such as Pt 4f will be presented at the conference.
in YIG and metallic Fe. The formation of the metallic state is consistent with the proposed origin of the anomalous Hall effect. Other spectra such as Pt 4f will be presented at the conference.
 He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Saito, Kimiaki; Mikami, Satoshi; Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinase, Sakae; Tsuda, Shuichi; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Sato, Tetsuro*; Seki, Akiyuki; Yamamoto, Hideaki*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105878_1 - 105878_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:80.38(Environmental Sciences)Sato, Tetsuro*; Ando, Masaki; Sato, Masako*; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105973_1 - 105973_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38.64(Environmental Sciences)A method was devised for estimation of external doses of Fukushima residents expected to return to their homes after evacuation orders are lifted. 211 residents expected to return to six towns and villages were surveyed in FY 2014, FY 2015, and FY2016. Interviewing returning residents about their expected life patterns after returning, air dose rate were measured along the reported personal trails representing their patterns of movement in daily life. Excluding 15 residents from whose homes we were unable to take air dose rate measurements, the maximum external effective dose and the average external effective dose were estimated respectively as 4.9 mSv/y and 0.86 mSv/y. Although the mean values and dispersion of external effective doses differ depending on the evacuation level, for 93.3% of all residents, the estimated external effective doses were less than 2 mSv/y. The average exposure dose at home accounts for 66.8% of the annual exposure dose.
Saito, Kimiaki; Mikami, Satoshi; Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinase, Sakae; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tetsuro*; Seki, Akiyuki; Sanada, Yukihisa; Wainwright-Murakami, Haruko*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 44(4), p.128 - 148, 2019/12
Saito, Kei*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Takai, Kenichi*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 50(11), p.5091 - 5102, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:84.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An attempt was made to separate and identify hydrogen peaks desorbed from lattice defects formed by plastic-strain in the presence of hydrogen in tempered martensitic steel showing quasi-cleavage fracture using thermal desorption spectroscopy from a low temperature (L-TDS) and positron annihilation spectroscopy (PAS). The L-TDS results made it possible to separate two peaks, namely, that of the original desorption and also that of new desorption. The PAS results revealed that the new desorption obtained by L-TDS corresponded to vacancy-type defects. Hydrogen enhanced vacancy-type defect concentration, approximately 10 order in terms of atomic ratio, formed within 1.5 mm from the fracture surface, These results indicate that the accumulation of excess vacancy-type defects enhanced by hydrogen in the local region can lead to nanovoid nucleation and coalescence in plastic deformation, resulting in quasi-cleavage fracture of tempered martensitic steel.
order in terms of atomic ratio, formed within 1.5 mm from the fracture surface, These results indicate that the accumulation of excess vacancy-type defects enhanced by hydrogen in the local region can lead to nanovoid nucleation and coalescence in plastic deformation, resulting in quasi-cleavage fracture of tempered martensitic steel.
 He
He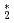 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.92(Physics, Applied)Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya
Journal of Visualization, 22(5), p.889 - 895, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.47(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
 states of uranium compounds revealed by 4
states of uranium compounds revealed by 4 -5
-5 resonant photoelectron spectroscopy
resonant photoelectron spectroscopyFujimori, Shinichi; Kobata, Masaaki; Takeda, Yukiharu; Okane, Tetsuo; Saito, Yuji; Fujimori, Atsushi; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035109_1 - 035109_5, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sakamoto, Tetsuo*; Morita, Masato*; Kanenari, Keita*; Tomita, Hideki*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Saito, Kosuke*; Ohashi, Masaya*; Kato, Kotaro*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Kawai, Toshihide*; et al.
Analytical Sciences, 34(11), p.1265 - 1270, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:34.22(Chemistry, Analytical) Si
Si studied by photoelectron spectroscopy (INVITED)
studied by photoelectron spectroscopy (INVITED)Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; Okane, Tetsuo; Saito, Yuji; Fujimori, Atsushi; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.82 - 85, 2018/11