Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Yasushi*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012028_1 - 012028_6, 2023/10
To observe flow velocity distributions by Neutron Imaging, suitable tracer is necessary. The requirements are its density, its visibility, and its wettability (if applied to liquid metal). Gold cadmium tracers have been developed for the Pb-Bi two-phase flow, however, the visibility have not been verified depending on the particle size and the measurement system. As the candidates of tracer particles, Ag, Cd, Au-Cd, and Ag-Cd have been tested by varying its compositions and its diameters. Results show enough visibility if the particles size is larger than 1mm. In addition, Cd tracer particles were applied to the fluidized bed, where the bed materials are metallic particle made of stainless steel, with 1mm diameter. The diameter of Cd trace is about 1.5 mm. From the neutron imaging, the visibility of the tracers is enough to measure the velocity distributions in the fluidized bed.
Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012024_1 - 012024_6, 2023/10
Gas-liquid two-phase flow appears in many heat-exchanging devices. To understand the phenomena in such devices, the two-phase flow dynamics should be clarified. In this study, high-speed neutron imaging is applied to the measurements of two-phase flow dynamics, and the accuracy of the void fraction measurement is investigated.
Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012005_1 - 012005_6, 2023/10
The Japan Research Ractor-3 (JRR-3) is operation resumed on February 26, 2021, and the shared use was also restarted in July, 2021. With the resumption of JRR-3 operation, two imaging facilities called TNRF and CNRF have also resumed their utilization. In this presentation, we report the details of these two neutron facilities.
Song, K.*; Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Gas entrainment (GE) phenomena caused by a free surface vortex may cause the disturbance in core power of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). For this reason, the entrained gas flow rate by the GE should be evaluated accurately for the practical safety design of SFRs. In this study, for the purpose of examining the applicability of CFD for the accurate evaluation of GE phenomena, a CFD is applied to the simulation of the free surface vortex and accompanied GE phenomena in a cylindrical vessel with a suction pipe, and the CFD results and the experimental data of the GE are compared. As a result, the CFD and experiments show similar two-phase flow pattern inside the suction pipe, and the shape of the gas core at the free surface is also very similar. Therefore, it is confirmed that the CFD can predict the GE phenomena triggered by a free surface vortex properly and accurately within the acceptable error range.
Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi
Konsoryu, 37(1), p.73 - 78, 2023/03
Gas-liquid two-phase flow is a very complicated flow phenomenon that involves the interaction between gas and liquid phases. Recently, an accurate simulation technique of two-phase flow has been developed. However, the validation of the simulated results is insufficient due to less experimental data. It is especially difficult to measure interfacial behavior with significant spatiotemporal fluctuation. To understand such phenomena, measurement methods with high spatial and temporal resolutions are required. Neutron imaging is a powerful tool for two-phase flow visualization. In this study, two-phase flow in the narrow rectangular channel was visualized by high-speed neutron imaging.
Yamamoto, Seishiro*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Konsoryu, 37(1), p.79 - 85, 2023/03
Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 569, p.153921_1 - 153921_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Seishiro*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Torikawa, Tomoaki*; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Konsoryu, 36(1), p.63 - 69, 2022/03
On free surface of a sodium cooled fast reactor, gas entrainment can be caused by free surface vortices, which may result in disturbance in core power. It is important to develop an evaluation model to predict accurately entrained gas flow rate. In this study, entrained gas flow rate a simple gas entrainment experiment is conducted with focusing on effect of pressure difference between upper and lower tanks. Pressure difference between upper and lower tanks are controlled by changing gas pressure in lower tank. As a result, it is confirmed that the entrained gas flow rate increases with increasing pressure difference between upper and lower tanks. By visualization of swirling annular flow in suction pipe, it is also observed that pressure drop in suction pipe increases with increase in entrained gas flow rate, which implies that entrained gas flow rate can be predicted by evaluation model based on pressure drop in swirling annular flow region.
Ariyoshi, Gen; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011044_1 - 011044_6, 2021/03
 He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Oba, Yojiro; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Onodera, Yohei*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.160 - 164, 2020/02
Lead Bismuth eutectic (LBE) is a promising candidate of the coolant for accelerator driven system (ADS) and fast breeder reactor. Neutron transmission imaging is a powerful technique to investigate the LBE in flow channel. However, previous studies have focused on the analysis of the neutron transmission spectra due to Bragg diffraction (Bragg edge transmission) from the solid phase of the LBE. If the neutron transmission spectra due to the diffraction from a liquid phase can be observed, it is useful to study the behavior of the molten LBE in the flow channel. Therefore, the energy-resolved neutron transmission imaging measurements of the molten LBE was carried out. The observed neutron transmission spectra can be explained by those calculated from the scattering profiles of the molten LBE. This indicates that the structure of the molten LBE can be characterized and mapped using the neutron transmission imaging.
Ito, Daisuke*; Kurisaki, Tatsuya*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.6430 - 6439, 2019/08
In core disruptive accident of sodium-cooled fast reactor, cooling of residual fuel debris formed in the reactor core is one of important factors to achieve in-vessel retention of the fuel. To clarify the feasibility of the cooling which is called "in-place cooling", characteristics of gas-liquid two-phase flow in the debris bed must be well understood. Since the debris bed can be formed in a confined flow channel in the core, effect of the channel wall cannot be neglected. Thus, this study aims to clarify the effect of the wall on two-phase flow characteristics in the debris bed, which was simulated as a particle bed packed in a pipe. The pressure drop was measured and compared with results by previous models, and porosity and void fraction distributions were measured by X-ray radiography. Then, the pressure drop evaluation model was modified considering the wall effect, and the applicability of the models was discussed.
Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Ezure, Toshiki; Matsushita, Kentaro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Imai, Yasutomo*
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.6632 - 6642, 2019/08
In this paper, a mechanistic model is proposed to calculate the entrained gas flow rate by a free surface vortex. The model contains the theoretical equation of transient gas core elongation and the empirical equation of critical gas core length for gas bubble detachment. Based on those two equations, the entrained gas flow rate is calculated as the portion of the gas core elongated beyond the critical gas core length per unit time. Then, the mechanistic model was applied to the calculation of the entrained gas flow rate in a simple water experiment. As a result, it is confirmed that the entrained gas flow rate grows rapidly when the liquid (water) flow rate, which determine the strength of a free surface vortex, exceeds a certain threshold value.
 He
He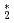 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.89(Physics, Applied)Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya
Journal of Visualization, 22(5), p.889 - 895, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.33(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Kurisaki, Tatsuya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Imaizumi, Yuya; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Proceedings of 11th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-11) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2018/11
In the evaluation of the in-place cooling which is for the residual core materials in the severe accident of sodium-cooled fast reactors, pressure loss of two-phase flow in debris bed is one of the important factors. Although Lipinski model is already proposed for the pressure loss evaluation, the accuracy would decrease when the porosity is not homogeneous. Thus, experiment to measure the pressure loss in a packed bed of non-homogeneous porosity distribution was conducted, and the Lipinski model was modified dividing the cross section to evaluate the pressure loss in it. As a result, it was confirmed that agreement of the experimental values with the values by modified Lipinski model was better than that with the original Lipinski model.
Ito, Daisuke*; Ito, Kei*; Saito, Yasushi*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Matsuba, Kenichi; Kamiyama, Kenji
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 334, p.90 - 95, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.60(Nuclear Science & Technology)Two-phase flow through porous media must be well understood to develop a severe accident analysis code not only for light water reactor but also sodium-cooled fast reactor. When a core disruptive accident occurs in sodium-cooled fast reactor, the fuel inside the core become melted and interacts with the coolant. As a result, gas-liquid two-phase flow will be formed in the debris bed, which may have porous nature depending on the cooling process. In such condition, the local porosity and its distribution are very important to characterize two-phase flow field in the porous media. In this study, X-ray radiography was applied to measure the local porosity in the packed bed of spheres. The radial profiles were estimated from the chordal profiles measured by the X-ray method and compared with the previous porosity model. In addition, the void fraction radial profiles were also obtained in air-water two-phase flow.
Ito, Daisuke*; Rivera, M. N.*; Saito, Yasushi*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Kamiyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Toru*
Proceedings of 17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/09