Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 F from
F from  O
O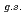 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:74.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 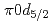 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O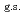 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Torigoe, Shuhei*; Hattori, Takayuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Abe, Hitoshi*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(13), p.134443_1 - 134443_7, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:52.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe and
Fe and  Co nuclear magnetic resonance studies
Co nuclear magnetic resonance studiesSakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Michioka, Chishiro*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; Takao, Kenta*; Shimoda, Aiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(6), p.064403_1 - 064403_10, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To specify preferential occupation sites of Co substituents and to clarify charge and spin states of Co ions in (La, Co)-cosubstituted hexagonal magnetoplumbite-type (M-type) Sr ferrite,  Fe and
Fe and  Co nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra are measured under zero and external magnetic fields using powdered and single crystalline specimens. To a considerable degree, the charge compensation between La
Co nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra are measured under zero and external magnetic fields using powdered and single crystalline specimens. To a considerable degree, the charge compensation between La and Co
and Co works in the equal (La, Co)-codoped case, where more than half of the Co ions are considered to be present in the minority spin
works in the equal (La, Co)-codoped case, where more than half of the Co ions are considered to be present in the minority spin 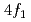 sites at the center of the oxygen tetrahedra, with the
sites at the center of the oxygen tetrahedra, with the  = 3/2 state carrying a small orbital moment owing to spin-orbit interaction. The remaining small number of high-spin Co
= 3/2 state carrying a small orbital moment owing to spin-orbit interaction. The remaining small number of high-spin Co (
( = 3/2,
= 3/2,  = 1) ions with unquenched orbital moments would be distributed to the other octahedral
= 1) ions with unquenched orbital moments would be distributed to the other octahedral 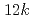 ,
, 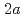 , and
, and 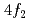 sites.
sites.
 imaging device of high spatial resolution ZnO scintillator
imaging device of high spatial resolution ZnO scintillatorNakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Takeda, Kohei*; Nishi, Ryosuke*; Minami, Yuki*; Cadatal-Raduban, M.*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(12), p.122202_1 - 122202_4, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:38.03(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate the potential of a hydrothermal method-grown ZnO as a high-spatial resolution imaging device for in-situ soft X-ray laser diagnostics by characterizing the exciton emission patterns. By plotting the emission pattern radii at each position, we estimated the evolution of the beam radius around the focal point. The beam profile of the Ni-like Ag ion plasma laser was estimated from the waist radii as 29 and 21 m, the divergence angle as 7.2 and 11 mrad and the M2 factor as 47 and 50 in the horizontal- and vertical-axis, respectively. Spatial resolution of the magnifier was estimated to be 6
m, the divergence angle as 7.2 and 11 mrad and the M2 factor as 47 and 50 in the horizontal- and vertical-axis, respectively. Spatial resolution of the magnifier was estimated to be 6 m and is expected to improve by optimizing the optics of the magnifier and using a telescope. Our results would enhance the use of ZnO as an imaging device that would play a crucial role in the development and application of soft X-ray light sources.
m and is expected to improve by optimizing the optics of the magnifier and using a telescope. Our results would enhance the use of ZnO as an imaging device that would play a crucial role in the development and application of soft X-ray light sources.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.

Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Sakai, Hironori; Aoki, Dai*; Ikeda, Shugo; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Settai, Rikio*; Harima, Hisatomo*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(2), p.024704_1 - 024704_6, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in growing a high-quality single crystal of LuCoGa with the HoCoGa
with the HoCoGa -type tetragonal crystal structure by the Ga self-flux method. The lattice parameters, fractional coordinates, and thermal parameters were determined from single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurements. We also measured the electrical resistivity, specific heat, and the de Haas-van Alphen (dHvA) effect. The Fermi surface mainly consists of two nearly cylindrical Fermi surfaces, which are well explained by the results of full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FLAPW) energy band calculations.
-type tetragonal crystal structure by the Ga self-flux method. The lattice parameters, fractional coordinates, and thermal parameters were determined from single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurements. We also measured the electrical resistivity, specific heat, and the de Haas-van Alphen (dHvA) effect. The Fermi surface mainly consists of two nearly cylindrical Fermi surfaces, which are well explained by the results of full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FLAPW) energy band calculations.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Takahashi, Kenji*; Sakai, Shingo*; Tezuka, Hiroaki*; Hiejima, Yusuke*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Watanabe, Masayoshi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 111(18), p.4807 - 4811, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:68.99(Chemistry, Physical) and Co mixture
and Co mixtureLavrentiev, V.*; Abe, Hiroaki*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Seiji; Narumi, Kazumasa
Chemical Physics Letters, 424(1-3), p.101 - 104, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.41(Chemistry, Physical)We present transmission electron beam identification of C -based polymeric chains in the mixture between Co and C
-based polymeric chains in the mixture between Co and C simultaneously deposited on (001) NaCl at room temperature. Estimation of intrachain distances taken from the direct image suggests bridging position of Co atoms between buckyballs. The chains tend to be coupled due to Coulomb interaction between the charged units of the polymers. We have confirmed the charge transfer between Co and C
simultaneously deposited on (001) NaCl at room temperature. Estimation of intrachain distances taken from the direct image suggests bridging position of Co atoms between buckyballs. The chains tend to be coupled due to Coulomb interaction between the charged units of the polymers. We have confirmed the charge transfer between Co and C detecting 0.6 eV upward shift of C
detecting 0.6 eV upward shift of C LUMO-derived peak in the electron-energy-loss spectrum of mixture. The systematic shifts of energy-loss
LUMO-derived peak in the electron-energy-loss spectrum of mixture. The systematic shifts of energy-loss 
 peaks imply distortion of C
peaks imply distortion of C cages belonging to the polymeric chains.
cages belonging to the polymeric chains.
Endo, Kiyoshi*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Yoshida, Fumiyo*; Nakai, Kei*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Akira*; Ishii, Keizo*; Sakai, Takuro; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th World Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ISNCT-11) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2004/10
Micro PIXE, which is installed in a single end accelerator in JAERI, was used for quantitative analysis of boron and gadolinium distribution in a cell level. The micro beam of 1  m diameter is possible to observe the distribution. In the adjustment procedure of the sample, first is a fix of mylar film by using a glass ring and a bite ring of 2cm diameter. Next the 9L cells were scattered on the washed film, and is cultivated on 37
m diameter is possible to observe the distribution. In the adjustment procedure of the sample, first is a fix of mylar film by using a glass ring and a bite ring of 2cm diameter. Next the 9L cells were scattered on the washed film, and is cultivated on 37 C in medium until they form the mono-layer. After the Gd-BOPTA was added, it incubates for the 24-72 hour on 37
C in medium until they form the mono-layer. After the Gd-BOPTA was added, it incubates for the 24-72 hour on 37 C. The film is washed in the THAM liquid, and is directly put on liquid nitrogen. A vacuum drying for 24 hours is conducted in order to fix a film on holder. It is important to uniformly fix the cell in distribution analysis in the cell using Micro PIXE. In recent result, it became possible that the distribution of P, S, Gd, etc. was analyzed. But we could not distinguish whether K and Gd exist in the cell or whether it exists around the cell. It was indicated that these elements was leaked by the reason of cell breaking or other on the cytoplasm.
C. The film is washed in the THAM liquid, and is directly put on liquid nitrogen. A vacuum drying for 24 hours is conducted in order to fix a film on holder. It is important to uniformly fix the cell in distribution analysis in the cell using Micro PIXE. In recent result, it became possible that the distribution of P, S, Gd, etc. was analyzed. But we could not distinguish whether K and Gd exist in the cell or whether it exists around the cell. It was indicated that these elements was leaked by the reason of cell breaking or other on the cytoplasm.
Lavrentiev, V.; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Abe, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji
Fullerenes, Nanotubes, and Carbon Nanostructures, 12(1-2), p.519 - 528, 2004/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.41(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Okumura, Masahiko; Onishi, Hiroaki; Yamada, Susumu; Sakai, Toru; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirade, Tetsuya; Minei, Shuntaro; Sakai, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
LSO scintillators have high density, short lifetime of light emission and high light strength, and that are applied for PET. The commonly used positron annihilation lifetime measurement system has BaF scintillators, because BaF
scintillators, because BaF scintillator has very fast light emission which is a great advantage for a good time resolution. On the other hand, LSO has a advantage on the high counting rate. We have tried to use LSO scintillators for the positron annihilation lifetime measurements. The system with LSO scintillators gave 5 times higher counting rate than with BaF
scintillator has very fast light emission which is a great advantage for a good time resolution. On the other hand, LSO has a advantage on the high counting rate. We have tried to use LSO scintillators for the positron annihilation lifetime measurements. The system with LSO scintillators gave 5 times higher counting rate than with BaF scintillators, and 315ps time resolution (FWHM) which is just 50 ps worth than BaF
scintillators, and 315ps time resolution (FWHM) which is just 50 ps worth than BaF . The irradiation effects on the sample for long measurement time is not negligible and then LSO scintillators provide a better system for these measurements.
. The irradiation effects on the sample for long measurement time is not negligible and then LSO scintillators provide a better system for these measurements.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Sakai, Hiroaki; Minei, Shuntaro
no journal, ,
After the TEPCO Fukushima Nuclear power plant accident, there are several radio isotopes released from the plant. To detect these radioisotopes, photo-peaks on the energy spectra obtained by HPGe semiconductor detectors or scintillation detectors are used. The detection efficiency is in invers proportion to square of the distance between the detector and the radioisotopes. Therefore the detector and the sample must be inside of the heavy and expensive shield box made of lead. Cs-134 is the only radioisotope emitting several  -rays in our environment, now. In the case of the simultaneous measurement of the
-rays in our environment, now. In the case of the simultaneous measurement of the  -rays from Cs-134, the detection efficiency can be in invers proportion to the fourth power of the distance, and hence the shield is not needed. Therefore, this method can be applied not just in laboratory.
-rays from Cs-134, the detection efficiency can be in invers proportion to the fourth power of the distance, and hence the shield is not needed. Therefore, this method can be applied not just in laboratory.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Minei, Shuntaro; Sakai, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
LSO(Lu SiO
SiO :Ce) scintillator is often used for PET (Positron Emission Tomography) because of the high efficiency of
:Ce) scintillator is often used for PET (Positron Emission Tomography) because of the high efficiency of  -ray detection. By use of this scintillator, we succeeded to obtain high efficiency on the measurements of positron annihilation methods, such as positron annihilation lifetime measurement and age-momentum correlation measurement (AMOC). It can supply the smaller change of the sample during measurements caused by the positron irradiation effect.
-ray detection. By use of this scintillator, we succeeded to obtain high efficiency on the measurements of positron annihilation methods, such as positron annihilation lifetime measurement and age-momentum correlation measurement (AMOC). It can supply the smaller change of the sample during measurements caused by the positron irradiation effect.
Sakai, Hiroaki; Minei, Shuntaro; Hirade, Tetsuya; Oshima, Nagayasu*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Kinomura, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*
no journal, ,
It was reported that positronium (Ps) formation probability was enhanced very much with very high electric fields. The spur reaction model can not explain this Ps formation. We tried to investigate this Ps formation with high electric fields in polyimide (kapton) that has no Ps formation with no electric field. Then we found out that Ps formation was not possible even at high electric fields. However, the annihilation lifetime of free positrons was elongated and it was probably caused by the positron drift movement.
Sakai, Hiroaki; Minei, Shuntaro; Hirade, Tetsuya; Oshima, Nagayasu*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Kinomura, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*
no journal, ,
It was reported that the positronium (Ps) formation in polymers was enhanced near breakdown voltage. It cannot be explained by the Spur Reaction Model. We investigated the electric field effect on positron annihilation lifetime for Kapton that has no Ps formation. We observed elongation of the free positron annihilation lifetime instead of the enhancement of Ps formation. It is possible to explain that drift of positrons causes smaller annihilation probability, i.e. longer lifetime. Now it is possible to explain the Ps formation enhancement reported previously could be caused by the elongation of the lifetime of the free positrons.
Sakai, Hiroaki; Minei, Shuntaro; Hirade, Tetsuya; Oshima, Nagayasu*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Kinomura, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*
no journal, ,
It was reported that psoitronium (Ps) formation probability in polymers under high electric fields were enhanced. The spur reaction model explaining Ps formation in insulating materials cannot be applied for the enhancement under high electric fields. Then we studied the Ps formation mechanism under high electric fields by observing positron annihilation lifetime in Kapton (polyimide) that does not have any Ps formation. Then Ps was not formed even under high electric fields and the elongation of the lifetime of the positrons free from Ps formation. The elongation of the lifetime of the positron and Ps formation enhancement could not be judged by the methods applied in the previously reports.
Minei, Shuntaro; Oshima, Nagayasu*; Sakai, Hiroaki; Okubo, Nariaki; Kondo, Keietsu; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
In nuclear reactor materials, subnanometer-size vacancy type defects are induced by neutron irradiation. Although positron annihilation methods are effective techniques for evaluation of the vacancy type defects, it may be difficult to apply the methods for neutron irradiated samples, because of  -rays from highly neutron irradiated, i.e. radioactivated, samples. Recently, positron micro beam has been developed at AIST. Therefore, we are suggesting that smaller radioactivated samples emit fewer
-rays from highly neutron irradiated, i.e. radioactivated, samples. Recently, positron micro beam has been developed at AIST. Therefore, we are suggesting that smaller radioactivated samples emit fewer  -rays. Focused Ion beam (FIB) is one of the tools to prepare micrometer scale samples by ion sputtering, for example, for the transmission electron microscope. There is some possibility to have vacancy type defects in the samples induced by the FIB processing and it can make estimation of the pre-existing defects in the samples difficult. The results investigated by positron annihilation lifetime measurements for SUS316L showed that FIB can be applied.
-rays. Focused Ion beam (FIB) is one of the tools to prepare micrometer scale samples by ion sputtering, for example, for the transmission electron microscope. There is some possibility to have vacancy type defects in the samples induced by the FIB processing and it can make estimation of the pre-existing defects in the samples difficult. The results investigated by positron annihilation lifetime measurements for SUS316L showed that FIB can be applied.
Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Sakai, Toshihiro; Murakami, Hiroaki; Ishibashi, Masayuki
no journal, ,
Existing data was analyzed in order to understand Hydrological and Geological Characterization of deep subsurface structures in and around the Main Shaft fault at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. As a result, in response to the low permeability structure of the Main Shaft Fault, fault gouges and alteration parts are found to be continuously distributed in the wall of the Main Shaft. One of the most high-permeable structure was estimated to be constituted by low-angle fractures with a sheet-like calcite. Shear of low angle fractures showed relatively low permeability. It may be possible to understand the permeability structure of these features in a drilling survey of granitic rocks.