Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMRMatsumura, Hiroki*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 13 of others*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)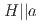 in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 11 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Vali ka, M.*; Haidamak, T.*; Cabala, A.*; Posp
ka, M.*; Haidamak, T.*; Cabala, A.*; Posp
 il, J.*; Bastien, G.*; Sechovsk
il, J.*; Bastien, G.*; Sechovsk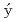 , V.*; Prokle
, V.*; Prokle ka, J.*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; et al.
ka, J.*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(9), p.094415_1 - 094415_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(14), p.L140502_1 - L140502_6, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:86.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The normal-conducting state of the superconductor UTe is studied by entropy analysis for magnetic fields along the
is studied by entropy analysis for magnetic fields along the  -axis, obtained from magnetization using the relation
-axis, obtained from magnetization using the relation 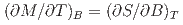 . We observe a strong increase in entropy with magnetic field due to metamagnetic fluctuations (spatially uniform,
. We observe a strong increase in entropy with magnetic field due to metamagnetic fluctuations (spatially uniform, 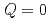 ). The field dependence is well described by the Hertz-Millis-Moriya theory for quantum criticality of itinerant metamagnetism. Notably, the lower bound of the quantum-critical region coincides well with the position of the minimum in the superconducting transition temperature
). The field dependence is well described by the Hertz-Millis-Moriya theory for quantum criticality of itinerant metamagnetism. Notably, the lower bound of the quantum-critical region coincides well with the position of the minimum in the superconducting transition temperature 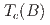 . Hence, our results suggest that
. Hence, our results suggest that 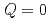 fluctuations reinforce the superconductivity.
fluctuations reinforce the superconductivity.

Suetsugu, Shota*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; 12 of others*
Science Advances (Internet), 10(6), p.eadk3772_1 - eadk3772_6, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:95.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)
Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Aoki, Dai*; Knebel, G.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(22), p.226503_1 - 226503_7, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:85.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary) ; Improvement of
; Improvement of  and multiple superconducting phase diagram
and multiple superconducting phase diagramSakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori
Kotai Butsuri, 58(10), p.529 - 536, 2023/10
We have succeeded to grow high-quality UTe single crystals with excess uranium through molten salt flux method. We have also studied the superconducting phase diagram using the high-quality crystal applying the fields up to 25 T along the magnetic hard
single crystals with excess uranium through molten salt flux method. We have also studied the superconducting phase diagram using the high-quality crystal applying the fields up to 25 T along the magnetic hard  axis.
axis.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Yanase, Yoichi*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(14), p.144502_1 - 144502_5, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:64.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The vortex dynamics in the spin-triplet superconductor, UTe , are studied by measuring the DC electrical resistivity with currents along the
, are studied by measuring the DC electrical resistivity with currents along the  -axis under magnetic fields along the
-axis under magnetic fields along the  -axis. Surprisingly, we have discovered an island region of low critical current deep inside the superconducting (SC) state, well below the SC upper critical field, attributed to a weakening of vortex pinning. Notably, this region coincides with the recently proposed intermediate-field SC state. We discuss the possibility of nonsingular vortices in the intermediate state, where SC order parameter does not vanish entirely in the vortex cores due to the mixing of multiple SC components.
-axis. Surprisingly, we have discovered an island region of low critical current deep inside the superconducting (SC) state, well below the SC upper critical field, attributed to a weakening of vortex pinning. Notably, this region coincides with the recently proposed intermediate-field SC state. We discuss the possibility of nonsingular vortices in the intermediate state, where SC order parameter does not vanish entirely in the vortex cores due to the mixing of multiple SC components.

Kinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Matsumura, Hiroki*; Hori, Fumiya*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 9(30), p.2736_1 - 2736_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:88.25(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -axis knight shift on UTe
-axis knight shift on UTe with
with  = 2.1 K
= 2.1 KMatsumura, Hiroki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(6), p.063701_1 - 063701_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:98.12(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Nakamine, Genki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(5), p.053702_1 - 053702_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:77.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary) probed by anisotropic low-energy excitations
probed by anisotropic low-energy excitationsIshihara, Kota*; Roppongi, Masaki*; Kobayashi, Masayuki*; Imamura, Kumpei*; Mizukami, Yuta*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Hashimoto, Kenichiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.2966_1 - 2966_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:97.70(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The superconducting symmetry of the heavy fermion uranium-based superconductor UTe is investigated using low temperature penetration depth measurements. The anisotropic low-energy quasiparticle excitations indicates multiple superconducting components in a chiral complex form. The most consistent is a chiral non-unitary state.
is investigated using low temperature penetration depth measurements. The anisotropic low-energy quasiparticle excitations indicates multiple superconducting components in a chiral complex form. The most consistent is a chiral non-unitary state.
 along hard magnetic axis
along hard magnetic axisSakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review Letters, 130(19), p.196002_1 - 196002_6, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:96.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The superconducting (SC) phase diagram in uranium ditelluride is explored under magnetic fields ( ) along the hard magnetic
) along the hard magnetic  -axis using a high-quality single crystal with
-axis using a high-quality single crystal with  = 2.1 K. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the
= 2.1 K. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the 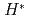 of
of 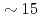 T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near
T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near 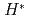 , indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
, indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 78(5), p.267 - 272, 2023/04
no abstracts in English

Ishihara, Kota*; Kobayashi, Masayuki*; Imamura, Kumpei*; Konczykowski, M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Hashimoto, Kenichiro*; Shibauchi, Takasada*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 5(2), p.L022002_1 - L022002_6, 2023/04
Lower superconducting critical fields 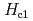 of UTe
of UTe have been determined. Orthorhombic UTe
have been determined. Orthorhombic UTe has magnetic easy axis along the
has magnetic easy axis along the  -axis. We found
-axis. We found 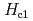 perpendicular to
perpendicular to  showed anomalous enhancement. By comparing with anisotropy of upper critical fields, effect of magnetic fluctuations on superconductivity is suggested.
showed anomalous enhancement. By comparing with anisotropy of upper critical fields, effect of magnetic fluctuations on superconductivity is suggested.
 Te
Te
Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(3), p.034704_1 - 034704_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the physical properties of a single crystal of uranium telluride U Te
Te . We have confirmed that U
. We have confirmed that U Te
Te crystallizes in the hexagonal structure with three nonequivalent crystallographic uranium sites. The paramagnetic moments are estimated to be approximately 1
crystallizes in the hexagonal structure with three nonequivalent crystallographic uranium sites. The paramagnetic moments are estimated to be approximately 1 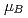 per the uranium site, assuming a uniform moment on all the sites. A ferromagnetic phase transition occurs at
per the uranium site, assuming a uniform moment on all the sites. A ferromagnetic phase transition occurs at  = 48 K, where the in-plane magnetization increases sharply, whereas the out of-plane component does not increase significantly. With decreasing temperature further below
= 48 K, where the in-plane magnetization increases sharply, whereas the out of-plane component does not increase significantly. With decreasing temperature further below  under field-cooling conditions, the out-of-plane component increases rapidly around T
under field-cooling conditions, the out-of-plane component increases rapidly around T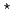 = 26 K. In contrast, the in-plane component hardly changes at T
= 26 K. In contrast, the in-plane component hardly changes at T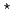 . Specific heat measurement indicates no
. Specific heat measurement indicates no  -type anomaly around T
-type anomaly around T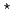 , so this is a cross-over suggesting a reorientation of the ordering moments or successive magnetic ordering on the part of the multiple uranium sites.
, so this is a cross-over suggesting a reorientation of the ordering moments or successive magnetic ordering on the part of the multiple uranium sites.
 induced by magnetic field
induced by magnetic fieldKinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(6), p.L060502_1 - L060502_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:92.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 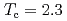 K for
K for 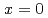 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 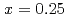 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 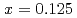 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 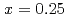 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 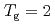 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 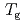 with a
with a 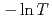 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
 Rh
Rh Ga explored by
Ga explored by 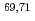 Ga nuclear quadrupole resonance
Ga nuclear quadrupole resonanceYamamoto, Shingo*; Fujii, Takuto*; Luther, S.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Hironori; B rtl, F.*; Ranjith, K. M.*; Rosner, H.*; Wosnitza, J.*; Strydom, A. M.*; et al.
rtl, F.*; Ranjith, K. M.*; Rosner, H.*; Wosnitza, J.*; Strydom, A. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(11), p.115125_1 - 115125_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the microscopic magnetic properties, the nature of the 130 K phase transition, and the ground state in the recently synthesized compound Ce Rh
Rh Ga by use of
Ga by use of 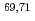 Ga nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR). The NQR spectra clearly show an unusual phase transition at
Ga nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR). The NQR spectra clearly show an unusual phase transition at 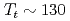 K, yielding a splitting of the high-temperature single NQR line into two well-resolved NQR lines, providing evidence for two crystallographically inequivalent Ga sites. The NQR frequencies are in good agreement with fully relativistic calculations of the band structure. Our NQR results indicate the absence of magnetic or charge order down to 0.3 K. The temperature dependence of the spin-lattice relaxation rate
K, yielding a splitting of the high-temperature single NQR line into two well-resolved NQR lines, providing evidence for two crystallographically inequivalent Ga sites. The NQR frequencies are in good agreement with fully relativistic calculations of the band structure. Our NQR results indicate the absence of magnetic or charge order down to 0.3 K. The temperature dependence of the spin-lattice relaxation rate  shows three distinct regimes, with onset temperatures at
shows three distinct regimes, with onset temperatures at 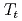 and 2 K. The temperature-independent
and 2 K. The temperature-independent  , observed between
, observed between 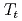 and 2 K, crosses over to a Korringa process,
and 2 K, crosses over to a Korringa process, 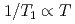 , below
, below  2 K, which evidences a rare two-ion Kondo scenario: The system evolves into a dense Kondo coherent state below 2.0 and 0.8 K probed by the two different Ga sites.
2 K, which evidences a rare two-ion Kondo scenario: The system evolves into a dense Kondo coherent state below 2.0 and 0.8 K probed by the two different Ga sites.

Aoki, Dai*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Ishizuka, Jun*; Yanase, Yoichi*; Harima, Hisatomo*; Nakamura, Ai*; Li, D.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(8), p.083704_1 - 083704_5, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:98.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)