Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Hiroki; Sawabe, Yuki; Ishiyama, Tatsuya*; Sakaki, Hironao*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011014_1 - 011014_6, 2021/03
In J-PARC Linac and RCS, beam operation that does not exceed the allowable (limit) amount of integrated particles per hour must be performed. Then, to measure and monitor the integrated particles for each beam destination, the monitoring system of number of particles was developed. In this system, in order to monitor the number of particles correctly and reliably, it is indispensable to eliminate the mistake (error) of beam current measurement. Therefore, we have developed a particle counter that measures the number of particles correctly and reliably at a 25 Hz period by supervising the timing signals for beam measurement. In this paper, the functions of the monitoring system of number of particles will be described focusing on the timing signal supervising function of the particle counter.
Kon, Akira; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Ogura, Koichi; Mori, Michiaki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kando, Masaki; Kondo, Kiminori
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 717, p.012103_1 - 012103_4, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:66.84(Physics, Applied)Nishiuchi, Mamiko*; Sakaki, Hironao*; Esirkepov, T. Zh.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Pirozhkov, A. S.*; Sagisaka, Akito*; et al.
Plasma Physics Reports, 42(4), p.327 - 337, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:59.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A combination of a petawatt laser and nuclear physics techniques can crucially facilitate the measurement of exotic nuclei properties. With numerical simulations and laser-driven experiments we show prospects for the Laser-driven Exotic Nuclei extraction-acceleration method proposed in [M. Nishiuchi et al., Phys. Plasmas 22, 033107 (2015)]: a femtosecond petawatt laser, irradiating a target bombarded by an external ion beam, extracts from the target and accelerates to few GeV highly charged short-lived heavy exotic nuclei created in the target via nuclear reactions.
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Fukuda, Yuji
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 58(3), p.034013_1 - 034013_6, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:77.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to understand the synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas dynamics, we have conducted ion acceleration experiments using CO clusters (250 nm in dia.) embedded in background H
clusters (250 nm in dia.) embedded in background H gas with the J-KAREN laser (1 J, 40 fs, 10
gas with the J-KAREN laser (1 J, 40 fs, 10 contrast) at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of etch pit positions on CR-39 and their structures including the etch pit growth behavior analysis with the multi-step etching technique, energy spectra for protons from the background gas and carbon/oxygen ions from the clusters are obtained separately. The maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are determined as 1.6 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles.
contrast) at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of etch pit positions on CR-39 and their structures including the etch pit growth behavior analysis with the multi-step etching technique, energy spectra for protons from the background gas and carbon/oxygen ions from the clusters are obtained separately. The maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are determined as 1.6 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles.
Yogo, Akifumi*; Bulanov, S. V.; Mori, Michiaki; Ogura, Koichi; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kanasaki, Masato*; Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Bolton, P.; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 58(2), p.025003_1 - 025003_7, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.03(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Oks, E.*; Dalimier, E.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Andreev, A.*; Koga, J. K.; Sakaki, Hironao; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 23(25), p.31991 - 32005, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.91(Optics)We present experiments dealing with a femtosecond laser-driven cluster-based plasma, where by analyzing the nonlinear phenomenon of satellites of spectral lines of Ar XVII, we revealed the nonlinear phenomenon of the generation of the second harmonic of the laser frequency. For performing this analysis we developed new results in the theory of satellites of spectral lines. From such lineshape analysis we found, in particular, that the efficiency of converting the short (40 fs) intense (3 10
10 W/cm
W/cm ) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
) incident laser light into the second harmonic was 2%. This result is in the excellent agreement with the 2-Dimensional Particle-In-Cell (2D PIC) simulation that we also performed. There is also an order of magnitude agreement between the thresholds for the SHG found from the line shape analysis and from the 2D PIC simulations.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao
Isotope News, (739), p.15 - 20, 2015/11
We introduce the multi-charged heavy-ion acceleration mechanisms and the recent results obtained at the KPSI JAEA. We also propose the novel application of the laser-driven multi-charged heavy ion beam.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(10), p.677 - 681, 2015/10
, 57(10), p.677 - 681, 2015/10
Light, such as, High intensity short pulse laser interacting with the thin-foil target, accelerates the almost fully stripped Iron ions towards the energy of 0.9 GeV. It is quite difficult for the conventional ion sources to make the highly charged heavy ions within few tens of femtoseconds and at the same time accelerates them towards higher energies. The achievement explained here is one new step towards the novel type compact ion sources.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Narita, Takahiro; Usami, Hiroki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kojima, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.756 - 759, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Kanasaki, Masato; et al.
Research Using Extreme Light; Entering New Frontiers with Petawatt-Class Lasers II (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9515), p.95151D_1 - 95151D_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Experimental demonstration of multi-charged heavy ion acceleration from the interaction between the ultra-intense short pulse laser system and the metal target is presented. The laser pulse of  10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of
10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of  10
10 from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of
from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of  10
10 Wcm
Wcm interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T.*; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 22(3), p.033107_1 - 033107_8, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:96.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic low-emittance high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a compact radio isotope source in combination with conventional technology.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Kon, Akira; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kanasaki, Masato*; et al.
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 21(1), p.1601118_1 - 1601118_18, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:95.3(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)This paper reviews the development of a high-contrast high-intensity petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser for research on high field science. We discuss in detail the design, performance and characterization of the laser. We also describe the on-going upgrade of the laser system and some applications for the laser in relativistic dominated laser-matter interactions.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Y.; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science XI; Springer Series in Chemical Physics, Vol.109, p.215 - 233, 2015/00
Clusters formed in supersonic gas expansion through a three-staged conical nozzle have been verified by measuring the angular distribution of the light scattered from cluster target. The size distirbutions of the clusters are calculated based on the Mie theory. The reliability of the size measurement is verified to be an experimental error of 10% using standard particles. The mean sizes of CO clusters for the cases of CO
clusters for the cases of CO /H
/H and CO
and CO /He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26
/He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26  m and 0.22
m and 0.22  m, respectively. For the CO
m, respectively. For the CO /H
/H , the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5
, the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5 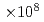 clusters/cm
clusters/cm by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Maebara, Sunao; Kojima, Toshiyuki; Narita, Takahiro; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi; Sakaki, Hironao; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2066 - 2070, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takahashi, Hiroki; Narita, Takahiro; Nishiyama, Koichi; Usami, Hiroki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kasugai, Atsushi; Kojima, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.799 - 802, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Hiroki; Kojima, Toshiyuki; Narita, Takahiro; Maebara, Sunao; Sakaki, Hironao; Suzuki, Hiromitsu
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.724 - 727, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Hiroki; Maebara, Sunao; Sakaki, Hironao; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.261 - 263, 2014/04
An development of accelerator-based neutron irradiation facility is planning to develop materials for a demonstration fusion reactor. To obtain a 14 MeV neutron energy using the neutron-generating D-Li stripping reaction, an injection into liquid lithium flow by a 40 MeV deuteron beam is employed in IFMIF design concept. In the acceleration of deuteron beam, the activation due to the beam loss is critical issue. The activation analyses for the air in an accelerator vault are carried out by PHITS code and DCHAIN code using the experimental data for deuteron induced thick target neutron yield at 5 MeV and 9 MeV for source term.
Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Jinno, Satoshi; Kanasaki, Masato; Yogo, Akifumi; Kondo, Kiminori; Saito, Fumihiro; Fukami, Tomoyo; Ueno, Masayuki; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.182 - 185, 2014/04
The concept of a compact ion particle accelerator has become attractive in view of recent progress in laser-driven ions acceleration. In the development of many applications of laser-accelerated ions, it is necessary for securing the radiation safety to calculate the dose evaluation. The dose was measured with the radio-photoluminescent (RPL) glass dosimeter on the test beamline of at laser-driven accelerator. The Monte Carlo code, PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code system) simulation is shown to be reasonably predictive at the test beamline for measured with the RPL glass dosimeter. We compare of the measured dose level on the laser-driven accelerator with the result of PHITS code in this report.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Okada, Hajime; Shimomura, Takuya; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Tanoue, Manabu; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Yogo, Akifumi; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 1, p.015095_1 - 015095_5, 2014/03
We present the design and characterization of a high-contrast, petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser system. Two saturable absorbers and low-gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier in the double CPA laser chain have improved the temporal contrast to 1.4 10
10 on the subnanosecond time scale at 70 terawatt level. Final uncompressed broadband pulse energy is 28 J, indicating the potential for reaching peak power near 600 terawatt. We also discuss our upgrade to over petawatt level at a 0.1 Hz repetition rate briefly.
on the subnanosecond time scale at 70 terawatt level. Final uncompressed broadband pulse energy is 28 J, indicating the potential for reaching peak power near 600 terawatt. We also discuss our upgrade to over petawatt level at a 0.1 Hz repetition rate briefly.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Maeda, Shota; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukami, Tomoyo; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A705_1 - 02A705_4, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)High intensity laser-plasma interaction has attracted considerable interest for a number of years. The laser-plasma interaction is accompanied by generation of various charged particle beams. Results of simultaneous novel measurements of electron-induced photonuclear neutrons (photoneutron), which are a diagnostic of the laser-plasma interaction, are proposed to use for optimization of the laser-plasma ion generation. The proposed method is demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity os 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.