Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 spectrometry of terrestrial gamma rays using portable germanium detectors in area of 80 km radius around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
spectrometry of terrestrial gamma rays using portable germanium detectors in area of 80 km radius around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power PlantMikami, Satoshi; Tanaka, Hiroyuki*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Ochi, Kotaro; Uno, Kiichiro*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Saito, Kimiaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(4), p.159 - 178, 2021/12
In order to know the background radiation level where the area affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in 2011, terrestrial gamma rays had been measured by using portable germanium detectors repeatedly from 2013 through 2019, at 370 locations within 80 km radius area centered on the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Radioactive concentrations of Uranium 238, Thorium 232, Potassium 40 and kerma rates in air due to terrestrial gamma rays were obtained at those locations based on the method of ICRU report 53. Averaged concentrations of  U,
U,  Th and
Th and  K were 18.8, 22.7, 428 Bq/kg, respectively, and kerma rate in air over the area was found to be 0.0402
K were 18.8, 22.7, 428 Bq/kg, respectively, and kerma rate in air over the area was found to be 0.0402  Gy/h. The obtained kerma rates in air were compared to those reported in literatures. It was confirmed that the data were correlated with each other, and were agreed within the range of their uncertainty. This is because the kerma rate in air due to terrestrial gamma rays is depend on geology. The similar trend to previous findings was observed that the kerma rate in air at locations geologically classified as Mesozoic era, Granite and Rhyolite were statistically significantly higher than the others.
Gy/h. The obtained kerma rates in air were compared to those reported in literatures. It was confirmed that the data were correlated with each other, and were agreed within the range of their uncertainty. This is because the kerma rate in air due to terrestrial gamma rays is depend on geology. The similar trend to previous findings was observed that the kerma rate in air at locations geologically classified as Mesozoic era, Granite and Rhyolite were statistically significantly higher than the others.
 gamma spectrometry intercomparison based on the information obtained through five intercomparisons during the Fukushima mapping project
gamma spectrometry intercomparison based on the information obtained through five intercomparisons during the Fukushima mapping projectMikami, Satoshi; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Matsuda, Hideo*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105938_1 - 105938_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.42(Environmental Sciences)Five intercomparisons of in situ  spectrometry by 6-7 participating teams have been conducted between December 2011 and August 2015 at sites in Fukushima prefecture which affected by the fallout of FDNPS accident occurred in March 2011. The evaluated deposition densities agreed within 5-6% in terms of coefficient of variation (CV) for radiocesium (
spectrometry by 6-7 participating teams have been conducted between December 2011 and August 2015 at sites in Fukushima prefecture which affected by the fallout of FDNPS accident occurred in March 2011. The evaluated deposition densities agreed within 5-6% in terms of coefficient of variation (CV) for radiocesium ( Cs and
Cs and  Cs), by our best achievement, and the ratio of
Cs), by our best achievement, and the ratio of  Cs/
Cs/ Cs in deposition density agreed within 1-2% in CV, through five intercomparisons. These results guarantee the accuracy of the measurements of the mapping project. Two different methods for intercomparison were conducted: (1) sequential measurements at an identical point; and (2) simultaneous measurements in a narrow area within 3 m radius. In a comparison between the two methods at a site, no significant difference was observed between the results. The standard protocols for the two different intercomparison methods were proposed based on our experience.
Cs in deposition density agreed within 1-2% in CV, through five intercomparisons. These results guarantee the accuracy of the measurements of the mapping project. Two different methods for intercomparison were conducted: (1) sequential measurements at an identical point; and (2) simultaneous measurements in a narrow area within 3 m radius. In a comparison between the two methods at a site, no significant difference was observed between the results. The standard protocols for the two different intercomparison methods were proposed based on our experience.
Mikami, Satoshi; Tanaka, Hiroyuki*; Matsuda, Hideo*; Sato, Shoji*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Suzuki, Takeo*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Ando, Masaki; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105941_1 - 105941_12, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:67.06(Environmental Sciences)The deposition densities of radiocesium and the air dose rates were repeatedly measured in a large number of undisturbed fields within the 80km zone that surrounds the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant site between 2011 and 2016, and features of their temporal changes were clarified. The average air dose rate excluding background radiation in this zone decreased to about 20% of the initial value during the period from June 2011 to August 2016, which was essentially a result of the radioactive decay of  Cs with a half-life of 2.06y. The air dose rate reduction was faster than that expected from the decay of radiocesium by a factor of about two, with most of this reduction being attributed to the penetration of radiocesium into the soil. The average deposition densities of
Cs with a half-life of 2.06y. The air dose rate reduction was faster than that expected from the decay of radiocesium by a factor of about two, with most of this reduction being attributed to the penetration of radiocesium into the soil. The average deposition densities of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs in fields that were not decontaminated were found to have decreased nearly according to their expected radioactive decay, which indicated that the movement of radiocesium in the horizontal direction was relatively small. The effect of decontamination was apparently observed in the measurements of air dose rates and deposition densities. Nominally, the average air dose rates in the measurement locations were reduced by about 20% by decontamination and other human activities, of which accurate quantitative analysis is and continue to be a challenge.
Cs in fields that were not decontaminated were found to have decreased nearly according to their expected radioactive decay, which indicated that the movement of radiocesium in the horizontal direction was relatively small. The effect of decontamination was apparently observed in the measurements of air dose rates and deposition densities. Nominally, the average air dose rates in the measurement locations were reduced by about 20% by decontamination and other human activities, of which accurate quantitative analysis is and continue to be a challenge.
Kinase, Sakae; Sato, Satoshi; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Yamamoto, Hideaki; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 167(1-3), p.340 - 343, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Environmental Sciences) spectrometry intercomparison in Fukushima, Japan
spectrometry intercomparison in Fukushima, JapanMikami, Satoshi; Sato, Shoji*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Saito, Kimiaki
Hoken Butsuri, 50(3), p.182 - 188, 2015/09
Intercomparison of in situ  spectrometry was organized at a site contaminated by the radioactive fallout that originated from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. This intercomparison was conducted by eight teams from four different institutions, which have contributed to the government-led project to construct distribution maps of radionuclides deposited on the ground soil. The resultant
spectrometry was organized at a site contaminated by the radioactive fallout that originated from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. This intercomparison was conducted by eight teams from four different institutions, which have contributed to the government-led project to construct distribution maps of radionuclides deposited on the ground soil. The resultant  Cs and
Cs and  Cs inventories evaluated by the participants agreed within 6% of the coefficient of variation, after correction for inhomogeneous distribution of the air dose rate. The evaluated
Cs inventories evaluated by the participants agreed within 6% of the coefficient of variation, after correction for inhomogeneous distribution of the air dose rate. The evaluated  K inventories agreed within 4% of the coefficient of variation. The authors estimated that these results were in good agreement for creating distribution maps of the radionuclide inventory in the ground soil.
K inventories agreed within 4% of the coefficient of variation. The authors estimated that these results were in good agreement for creating distribution maps of the radionuclide inventory in the ground soil.
Ichikawa, Shoichi; Kawanago, Sho; Nishio, Ryuichi; Wakimoto, Fumitsugu; Fujimura, Tomofumi; Kobayashi, Takanori; Sakamoto, Tsutomu
JAEA-Review 2015-009, 210 Pages, 2015/07
The loss of the retaining split pins (four pieces) for clevis pin were confirmed at the inspection of the pipe supports in the Monju prototype fast-breeder reactor in May, 2014. The split pins (two pieces) of ROD RESTRAINT and CONSTANT HANGER were fallen off. The split pins (two pieces) of MECHANICAL SNUBBER were broken at both ends of them. As a result of investigation, a dimple pattern was observed in a fracture surface of broken split pin. This observation result showed that fracture morphology is ductile fracture. A reproduction test, whether split pin was broken by loading the external force to the clevis pin, also gave the same fracture morphology. As the result of all cause investigation, the reason of the broken split pins is that the split pins were loaded shearing stress by the external force loaded to the clevis pin axial direction. The result of the cause investigation and a recurrence prevention measure of this trouble was be reported by this report.
Mikami, Satoshi; Maeyama, Takeshi*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Sato, Shoji*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Sato, Tetsuro*; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.250 - 259, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:80.13(Environmental Sciences)Mikami, Satoshi; Maeyama, Takeshi*; Hoshide, Yoshifumi*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Sato, Shoji*; Okuda, Naotoshi*; Demongeot, S.*; Gurriaran, R.*; Uwamino, Yoshitomo*; Kato, Hiroaki*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.320 - 343, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:92.94(Environmental Sciences)Kinase, Sakae; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*; Sato, Satoshi; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 160(4), p.318 - 321, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:92.29(Environmental Sciences)Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(1), p.015005_1 - 015005_7, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:45.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Transport analysis during the transient phase of heating (a dynamic transport study) applied to the plasma with internal transport barriers (ITBs) in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and the JT-60U tokamak is described. In the dynamic transport study the time of transition from the L-mode plasma to the ITB plasma is clearly determined by the onset of flattening of the temperature profile in the core region and a spontaneous phase transition from a zero curvature ITB (hyperbolic tangent shaped ITB) or a positive curvature ITB (concaved shaped ITB) to a negative curvature ITB (convex shaped ITB) and its back-transition are observed. The flattening of the core region of the ITB transition and the back-transition between a zero curvature ITB and a convex ITB suggest the strong interaction of turbulent transport in space.
 C tracer and coupling between source and sink organs
C tracer and coupling between source and sink organsSuwa, Ryuichi*; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Ishii, Satomi; Sakamoto, Koichi*; Nguyen, N. T.*; Saneoka, Hirofumi*; Mohapatra, P. K.*; Moghaieb, R. E.*; et al.
Plant Science, 175(3), p.210 - 216, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:45.41(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Sugimoto, Jun; Sakamoto, Ryuichi; Kushita, Kohei; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Hattori, Takamitsu; Matsuda, Kenji; Ikuta, Yuko; Sato, Koichi
Transactions of NESTet 2008 (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/05
Nuclear human resources development (HRD) in Japan has been identified as one of the most important issues these years in nuclear society, mostly due to the decrease of nuclear engineers in industries and students in universities, and to the difficulties of technical transfers. Nuclear Technology and Education Center (NuTEC) at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) aims at comprehensive nuclear education and training activities, which cover (1) education and training for domestic nuclear engineers, (2) cooperation with universities and (3) international cooperation. The main feature of NuTEC's training programs is that the curricula places emphasis on the laboratory exercise with well-equipped training facilities and expertise of lecturers mostly from JAEA. The wide spectrum of cooperative activities have been pursued with universities, which includes newly developed remote-education system, and also with international organizations, such as with FNCA countries and IAEA.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kubo, Hirotaka; Sueoka, Michiharu; Kawamata, Yoichi; Yoshida, Maiko; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Iio, Shunji*; Shimomura, Koji*; Ichige, Hisashi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(3), p.035011_1 - 035011_6, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.2(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A burning plasma simulation scheme has been developed with consideration for temperature dependence of the DT fusion reaction rate in JT-60U. The heating power for the simulation of alpha particle heating was calculated using real-time measurements of density and ion temperature. Response of a simulated fusion gain to the density was investigated in this scheme with constant heating power for the simulation of external heating, in order to understand burn controllability by the fuel density in a fusion reactor. When temperature dependence of the fusion reaction rate was assumed as square of ion temperature, density dependence of the simulated fusion gain stronger than square of density was observed. Transport analysis using a 1.5 dimension transport code indicated that the strong density dependence is induced due to both change in a confinement improvement factor and change in a pressure profile.
Yamada, Hiroshi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kamada, Yutaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1418 - 1424, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High densities exceeding the Greenwald limit by a factor of 1.7 have been obtained in discharges with high internal inductances of 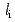 as high as 2.8 in JT-60U L-mode plasmas. The internal inductance, which is an index of the edge magnetic shear, is controlled by ramping down the plasma current. In addition to the extension of the operational regime, confinement performance remains as good as an H89PL factor of 1.5 even above the Greenwald limit. While the earlier work of a high
as high as 2.8 in JT-60U L-mode plasmas. The internal inductance, which is an index of the edge magnetic shear, is controlled by ramping down the plasma current. In addition to the extension of the operational regime, confinement performance remains as good as an H89PL factor of 1.5 even above the Greenwald limit. While the earlier work of a high 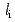 study has indicated that core confinement improvement, the additional improvement of the tolerance against the high density is turned out to be correlated with high edge temperature. The normalized density when the detachment characterized by the decrease in a D
study has indicated that core confinement improvement, the additional improvement of the tolerance against the high density is turned out to be correlated with high edge temperature. The normalized density when the detachment characterized by the decrease in a D signal at the divertor occurs is even higher in the case with no disruption than the case with a disruption. These comparisons have indicated that the improvement in thermal and particle transport does exist in the periphery and the edge in the high
signal at the divertor occurs is even higher in the case with no disruption than the case with a disruption. These comparisons have indicated that the improvement in thermal and particle transport does exist in the periphery and the edge in the high 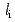 plasmas, and mitigation of the density limit is observed coincidently. Although the high
plasmas, and mitigation of the density limit is observed coincidently. Although the high 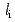 discharge studied here lies outside of the usual parameter space for a steady-state operation of tokamak, demonstration of a stable discharge with good confinement beyond the Greenwald limit suggest the magnetic shear at the edge is one key parameter to uncover physical element of the operational density limit.
discharge studied here lies outside of the usual parameter space for a steady-state operation of tokamak, demonstration of a stable discharge with good confinement beyond the Greenwald limit suggest the magnetic shear at the edge is one key parameter to uncover physical element of the operational density limit.
Shimomura, Koji*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Mimata, Hideyuki*; Iio, Shunji*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Tani, Keiji; Kubo, Hirotaka; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Hiratsuka, Hajime; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.953 - 960, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kubo, Hirotaka; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Ichige, Hisashi; Yonekawa, Izuru*; Kawamata, Yoichi; Iio, Shunji*; Sakamoto, Ryuichi*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 50(1), p.76 - 83, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.76(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.