Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sueyoshi, Tetsuro*; Kotaki, Tetsuya*; Furuki, Yuichi*; Fujiyoshi, Takanori*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Ozaki, Toshinori*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Kudo, Masaki*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Ishikawa, Norito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(2), p.023001_1 - 023001_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.47(Physics, Applied)We show that Xe ion irradiation with 80 MeV to GdBa Cu
Cu Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at
Oy-coated conductors creates different morphologies of columnar defects (CDs) depending on the irradiation angles relative to the c-axis: continuous CDs with a larger diameter are formed for oblique irradiation at 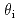 = 45
= 45 , whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (
, whereas the same ion beam at a different angle (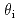 = 0
= 0 ) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density
) induces the formation of discontinuous CDs. The direction-dependent morphologies of CDs significantly affect the angular behavior of the critical current density  .
.
Furuta, Etsuko*; Nakahara, Hiromichi*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Matsue, Hideaki; Sakane, Hitoshi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 278(3), p.553 - 557, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.28(Chemistry, Analytical)In Japan, cosmetics which declared hormesis effect are available through Internet. The existence of a daughter nuclides of Th and U series, however, were observed by measurements of the  rays with a high purity Ge detector. In this study, in order to clarify the contents of trace elements, the hormesis cosmetics including radiation sources were analyzed using instrumental neutron activation analysis method (INAA), prompt
rays with a high purity Ge detector. In this study, in order to clarify the contents of trace elements, the hormesis cosmetics including radiation sources were analyzed using instrumental neutron activation analysis method (INAA), prompt  activation analysis (PGAA) and neutron activation analysis with multiple
activation analysis (PGAA) and neutron activation analysis with multiple  ray detection (NAAMG). In the conference, we will report the results of analysis data which including heavy metallic and actinide elements. Furthermore, we will evaluate a possibility of uptake of heavy metal elements and radiation sources, and will discuss the influence of them to human body.
ray detection (NAAMG). In the conference, we will report the results of analysis data which including heavy metallic and actinide elements. Furthermore, we will evaluate a possibility of uptake of heavy metal elements and radiation sources, and will discuss the influence of them to human body.
 N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction as a
N reaction as a  -ray intensity standard up to 11 MeV
-ray intensity standard up to 11 MeVMiyazaki, Itaru*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Takayama, Hirokazu*; Kasaishi, Masafumi*; Tojo, Akinori*; Furuta, Masataka*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Suematsu, Osamu*; Narasaki, Hiromichi*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(6), p.481 - 486, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)The intensities of the prompt  rays from the
rays from the  N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C
N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C D
D N
N ) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of
) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of  -ray energy.
-ray energy.
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisMatsue, Hideaki; Sakane, Hitoshi*
Konkurito Tekuno, 27(2), p.9 - 12, 2008/02
no abstracts in English
 Ge spectrometer
Ge spectrometerKoizumi, Mitsuo; Osa, Akihiko; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Mizumoto, Motoharu; Oshima, Masumi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*; Harada, Hideo*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 562(2), p.767 - 770, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to measure the neutron capture cross section of minor actinides, we have proposed the use of a 4 Ge spectrometer. A Time-of-Flight neutron beam line for the experiment has been constructed at the KURRI electron LINAC. The assembling of the 4
Ge spectrometer. A Time-of-Flight neutron beam line for the experiment has been constructed at the KURRI electron LINAC. The assembling of the 4 Ge spectrometer is in progress. We are also developing a new data acquisition system based on a digital processing technique.
Ge spectrometer is in progress. We are also developing a new data acquisition system based on a digital processing technique.
Harada, Hideo; Sakane, Hitoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hori, Junichi*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*
Nuclear Data Needs for Generation IV Nuclear Energy Systems, p.216 - 221, 2006/05
Recent activities on the measurement of neutron capture cross sections by a Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Kyoto university group is reviewed focusing on  Np and
Np and  Np. Firstly, an experimental issue on the measurement of thermal-neutron capture cross section and resonance integral of
Np. Firstly, an experimental issue on the measurement of thermal-neutron capture cross section and resonance integral of  Np is discussed. In second, the effectiveness of utilizing a double-neutron capture reaction for the measurement of the neutron capture cross section for short-lived nuclei
Np is discussed. In second, the effectiveness of utilizing a double-neutron capture reaction for the measurement of the neutron capture cross section for short-lived nuclei  Np is discussed. In third, the measurements of the energy dependence of the neutron capture cross section of
Np is discussed. In third, the measurements of the energy dependence of the neutron capture cross section of  Np are reviewed focusing on the experimental progress, including a total-energy detector and a flash-ADC based data-taking system. The experimental results were compared each other and also with some nuclear data libraries to make the problems clear.
Np are reviewed focusing on the experimental progress, including a total-energy detector and a flash-ADC based data-taking system. The experimental results were compared each other and also with some nuclear data libraries to make the problems clear.
 -ray spectroscopic studies
-ray spectroscopic studiesFurutaka, Kazuyoshi; Harada, Hideo; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Yamana, Hajimu*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamamoto, Shuji*; Hori, Junichi*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Osaki, Toshiro*; et al.
KURRI Progress Report 2004, P. 16, 2005/09
This report describes the studies done through spectroscopic method of high-energy  ray to determine neutron capture cross sections of radioactive nuclides, in FY2004 at the Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto University. The following three items are described. (1) Development of a method to determine thermal neutron capture cross sections by prompt
ray to determine neutron capture cross sections of radioactive nuclides, in FY2004 at the Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto University. The following three items are described. (1) Development of a method to determine thermal neutron capture cross sections by prompt  -ray measurements, (2) Evaluation of a large BGO detector system as a total-energy detector, and (3) neutron capture cross-section measurements by TOF method.
-ray measurements, (2) Evaluation of a large BGO detector system as a total-energy detector, and (3) neutron capture cross-section measurements by TOF method.
Miyazaki, Itaru*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Kawade, Kiyoshi*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Harada, Hideo
JNC TY8400 2005-002, 40 Pages, 2005/06
Accurate cross section data for the neutron capture of long-lived fission products (LLFP) are needed for developing a nuclear transmutation technology which reduces radioactive wastes by transmuting nuclides that have half-lives of as long as a few million years to other nuclides that have much shorter half-lives. There are some nuclides, whose cross sections cannot be measured in activation method. Utilization of prompt gamma-rays is expected to solve this problem. The aim of present study was twofold: (i) to measure emission probabilities of the high energy gamma-ray, up to 10MeV, emitted from  N(
N( )
) N reaction, which are usually used as standards, in order to improve their accuracies and (ii) to develop a measurement method for neutron capture cross sections by using prompt gamma-rays. Emission probabilities of principal prompt gamma-rays from
N reaction, which are usually used as standards, in order to improve their accuracies and (ii) to develop a measurement method for neutron capture cross sections by using prompt gamma-rays. Emission probabilities of principal prompt gamma-rays from  N(
N( )
) N reaction were determined with 0.2-0.9% errors. For ten nuclides,
N reaction were determined with 0.2-0.9% errors. For ten nuclides,  Na,
Na,  Al,
Al, 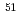 V,
V,  Mn,
Mn,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Cu,
Cu, 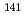 Pr,
Pr,  W, and
W, and  Au capture cross sections were measured by using prompt gamma-rays and gamma-rays following b-decay. By comparing both cross section values, it was found that emission probabilities of prompt gamma-rays reported in the literatures were systematically larger than those inferred from the cross sections that were determined in activation methods. The cross section of a
Au capture cross sections were measured by using prompt gamma-rays and gamma-rays following b-decay. By comparing both cross section values, it was found that emission probabilities of prompt gamma-rays reported in the literatures were systematically larger than those inferred from the cross sections that were determined in activation methods. The cross section of a 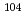 Pd(
Pd( )
)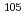 Pd reaction at thermal energy was measured. Considering transmutation of the nuclide, the cross section of
Pd reaction at thermal energy was measured. Considering transmutation of the nuclide, the cross section of 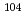 Pd(
Pd( ), which is an isotope of palladium, is also necessary. A lower limit of the cross section was determined with 6% accuracy. Additionally, a method of estimating an upper limit was examined by noting similarity of nuclear structures to the neighboring nuclides. It was estimated that the observed lower limit of emission probabilities correspond to 79% of the cross section.
), which is an isotope of palladium, is also necessary. A lower limit of the cross section was determined with 6% accuracy. Additionally, a method of estimating an upper limit was examined by noting similarity of nuclear structures to the neighboring nuclides. It was estimated that the observed lower limit of emission probabilities correspond to 79% of the cross section.
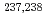 Np
NpHarada, Hideo; Sakane, Hitoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hori, Junichi*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*
JAERI-Conf 2005-003, p.121 - 125, 2005/00
Recent progress on the measurement of neutron capture cross sections is reviewed forcusing on Np-237 and Np-238.
 Np from 0.02 to 100 eV
Np from 0.02 to 100 eVShcherbakov, O.; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Kobayashi, Katsuhei*; Yamamoto, Shuji*; Harada, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(2), p.135 - 144, 2005/00
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:83.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)The neutron capture cross section of Np-237 has been measured in the energy range of 0.02 eV - 100 eV. For the first time, the capture cross section of Np-237 was measured using the total energy  -ray detector. The results have been compared with evaluated nuclear data libraries.
-ray detector. The results have been compared with evaluated nuclear data libraries.
 -ray spectra
-ray spectraSakane, Hitoshi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Shcherbakov, O.; Harada, Hideo; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*
AIP Conference Proceedings 769, p.1000 - 1002, 2004/09
Thermal neutron capture cross sections of N-14 and Al-27 were measured by unfolding prompt  -ray spectra in order to confirm the effectiveness of these methods. By comparing the present results with other results, the effectiveness of the present methods was confirmed.
-ray spectra in order to confirm the effectiveness of these methods. By comparing the present results with other results, the effectiveness of the present methods was confirmed.
Harada, Hideo; Nakamura, Shoji; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Shcherbakov, O.; Sakane, Hitoshi; Kobayashi, Katsuhei*; Yamamoto, Shuji*
KURRI Progress Report 2003, P. 171, 2004/09
Researches and developments done at Research Reactor Institute of Kyoto University in FY2003 are summarized. Researches on measurement of neutron capture cross sections by activation method, development of a method to determine thermal neutron capture cross section by prompt  -ray measurements, and neutron capture cross section measurements by Time-of-Flight method are briefly mentioned.
-ray measurements, and neutron capture cross section measurements by Time-of-Flight method are briefly mentioned.
Shcherbakov, O.; Harada, Hideo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Kobayashi, Katsuhei*; Yamamoto, Shuji*
ND2004 Abstracts, LA-UR-04-5900, p.133, 133 Pages, 2004/09
The neutron capture cross section of Np-237 has been measured for the energy range between thermal to 100 eV using a TOF method. The developed system composed of JNC-BGO detector and FADC data taking is presented together with the obtained result.
Sakane, Hitoshi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Shcherbakov, O.; Harada, Hideo; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*
JAERI-Conf 2004-005, p.202 - 206, 2004/04
A Ge crystal dimension of a pair-spectrometer system was optimized to improve its performance for the prompt  -ray spectroscopy. To study the performance of the pair-spectrometer system, the prototype system was developed and applied to the measurement of prompt
-ray spectroscopy. To study the performance of the pair-spectrometer system, the prototype system was developed and applied to the measurement of prompt  -rays which are emitted from 15N produced in thermal neutron capture reaction, in the energy range up to 10.8 MeV.
-rays which are emitted from 15N produced in thermal neutron capture reaction, in the energy range up to 10.8 MeV.
Shcherbakov, O.; Harada, Hideo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Kobayashi, Katsuhei*; Yamamoto, Shuji*
AIP Conference Proceedings 769, p.1007 - 1010, 2004/00
The neutron capture cross section of Np-237 has been measured relative to the B-10(n,alpha)Li-7 cross section in the energy range from 0.02 to 100 eV. The measurements were carried out by the time-of-flight method using the 8.54 liters BGO scintillator as a 4-pi capture  ray detector and the 46 MeV Linac as a pulsed neutron source. The results of present measurements have been compared with experimental data of other authors and evaluated data.
ray detector and the 46 MeV Linac as a pulsed neutron source. The results of present measurements have been compared with experimental data of other authors and evaluated data.
 ray spectra
ray spectraSakane, Hitoshi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Shcherbakov, O.; Harada, Hideo; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*
Absracts [246] P.131, 131 Pages, 2004/00
A Method of thermal neutron capture cross section measurement by unfolding prompt  ray spectra were developed. Response function for unfolding spectra was constructed by using EGS-4 code. To check the reliability of the response function, prompt
ray spectra were developed. Response function for unfolding spectra was constructed by using EGS-4 code. To check the reliability of the response function, prompt  rays emitted from
rays emitted from  N produced in thermal neutron capture reaction were reproduced.
N produced in thermal neutron capture reaction were reproduced.
 O(n,p)
O(n,p) N reaction by 14MeV neutrons
N reaction by 14MeV neutronsKasugai, Yoshimi; Ikeda, Yujiro; Sakane, Hitoshi*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 136(2), p.258 - 264, 2000/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Furuta, Etsuko*; Nakahara, Hiromichi*; Oura, Yasuji*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Matsue, Hideaki; Sakane, Hitoshi*
no journal, ,
Cosmetics which declared hormesis effects are available through Internet. The existence of a daughter nuclides of Th and U series were observed by measuring the  rays with a high purity Ge detector. In this study, in order to clarify the contents of trace elements, the hormesis cosmetics were analyzed using prompt
rays with a high purity Ge detector. In this study, in order to clarify the contents of trace elements, the hormesis cosmetics were analyzed using prompt  activation analysis and observed by SEM-EDX. Main elements of the hormesis cosmetics are some rare earth elements such as La, Ce, Sm and Gd. The ratio of Gd/Sm included in all the hormesis cosmetics is 0.70, and the ratio is different from general cosmetics. Furthermore, we evaluated a possibility of radiation exposure. The influence of
activation analysis and observed by SEM-EDX. Main elements of the hormesis cosmetics are some rare earth elements such as La, Ce, Sm and Gd. The ratio of Gd/Sm included in all the hormesis cosmetics is 0.70, and the ratio is different from general cosmetics. Furthermore, we evaluated a possibility of radiation exposure. The influence of  rays to skin surface from some hormesis cosmetics was, for example, over 50 mSv per year. The addition of the radioisotope to cosmetics is prohibited in some countries by the laws. The examination of the object that should prohibit the addition of the radioisotope is necessary.
rays to skin surface from some hormesis cosmetics was, for example, over 50 mSv per year. The addition of the radioisotope to cosmetics is prohibited in some countries by the laws. The examination of the object that should prohibit the addition of the radioisotope is necessary.