Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakashita, Tetsuya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 14(8), p.e0221579_1 - e0221579_20, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Cataracts have long been known, but a biologically based mathematical model is still unavailable for cataratogenesis. We here report for the first time an in silico model for cataractogenesis. First, a simplified cell proliferation model was developed for human lens growth based on stem and progenitor cell proliferation as well as epithelial-fiber cell differentiation. Then, a model for spontaneous cataractogenesis was developed to reproduce the human data on a relationship between age and cataract incidence. Finally, a model for radiation cataractogenesis was developed that can reproduce the human data on a relationship between dose and cataract onset at various ages, which was further applied to estimate cataract incidence following chronic lifetime exposure.
Shinohara, Ayaka*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yamaguchi, Aiko*; Ishioka, Noriko*; Tsushima, Yoshito*
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 32(2), p.114 - 122, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:38.49(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Radionuclide therapy with low-energy auger electron emitters could potentially provide high anti-tumor efficacy while keeping normal organs toxicity low. In this study, we evaluated the usefulness of auger electron emitter  I and compared it with beta-emitter
I and compared it with beta-emitter  I for tumor treatment in 2D and 3D cell culture models. The computer simulation model for 2D and 3D cell culture were constructed, and the absorbed radiation dose of
I for tumor treatment in 2D and 3D cell culture models. The computer simulation model for 2D and 3D cell culture were constructed, and the absorbed radiation dose of  I or
I or  I in each model were calculated by using a Monte Carlo simulation code (PHITS). The therapeutic effect of
I in each model were calculated by using a Monte Carlo simulation code (PHITS). The therapeutic effect of  I was comparable to that of
I was comparable to that of  I in 2D model, but the efficacy was inferior to that of
I in 2D model, but the efficacy was inferior to that of  I-MIBG in 3D model, since crossfire effect is negligible and the homogeneous distribution of radionuclide was insufficient.
I-MIBG in 3D model, since crossfire effect is negligible and the homogeneous distribution of radionuclide was insufficient.
Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Ikeda, Hiroko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 67, 2016/02
The role of nitric oxide (NO) in bystander effect was investigated. Human fibroblasts were irradiated with  -rays (LET: 0.2 keV/
-rays (LET: 0.2 keV/ m) or carbon-ion beam (108 keV/
m) or carbon-ion beam (108 keV/ m), and then, co-cultured with the non-irradiated cells. After 24 h culture, the survival rates of non-irradiated cells and the concentrations of nitrate, an oxide of NO, in the medium were measured. The survival rates of non-irradiated cells decreased in dose-dependent and radiation quality-independent manners. Negative relationships between survival rates and nitrite concentrations existed, indicating the amounts of produced NO are an important determinant of bystander effects. Next, a reagent producing two molecules of NO in a half-life of 100 min was added in the culture medium. After incubation of 24 h the survival rates of treated cells did not decrease, suggesting NO produced intracellularly has an important role to lead the bystander effect but is not the signal molecule for intercellular communication.
m), and then, co-cultured with the non-irradiated cells. After 24 h culture, the survival rates of non-irradiated cells and the concentrations of nitrate, an oxide of NO, in the medium were measured. The survival rates of non-irradiated cells decreased in dose-dependent and radiation quality-independent manners. Negative relationships between survival rates and nitrite concentrations existed, indicating the amounts of produced NO are an important determinant of bystander effects. Next, a reagent producing two molecules of NO in a half-life of 100 min was added in the culture medium. After incubation of 24 h the survival rates of treated cells did not decrease, suggesting NO produced intracellularly has an important role to lead the bystander effect but is not the signal molecule for intercellular communication.
Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Ikeda, Hiroko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 75, 2015/03
We investigated the bystander effect induced by  -rays or carbon ions and analyzed the role of nitric oxide (NO) in the effect. Normal human fibroblasts were used. Cells inoculated on a porous membrane were irradiated with varying doses of
-rays or carbon ions and analyzed the role of nitric oxide (NO) in the effect. Normal human fibroblasts were used. Cells inoculated on a porous membrane were irradiated with varying doses of  -rays or carbon ions. Irradiated cells were then non-contact co-cultured with non-irradiated cells for 24 h. After co-culture, the survival rates of non-irradiated bystander cells co-cultured with irradiated cells decreased with increasing dose and bottomed out at 0.5 Gy or higher doses. This indicates that the bystander effect is dependent on irradiation dose but independent of radiation quality. Next, a specific NO scavenger c-PTIO was added to the culture medium during irradiation and co-culture. This treatment prevented the reduction in survival rates of bystander cells, clearly indicating that NO has an important role in the bystander effect.
-rays or carbon ions. Irradiated cells were then non-contact co-cultured with non-irradiated cells for 24 h. After co-culture, the survival rates of non-irradiated bystander cells co-cultured with irradiated cells decreased with increasing dose and bottomed out at 0.5 Gy or higher doses. This indicates that the bystander effect is dependent on irradiation dose but independent of radiation quality. Next, a specific NO scavenger c-PTIO was added to the culture medium during irradiation and co-culture. This treatment prevented the reduction in survival rates of bystander cells, clearly indicating that NO has an important role in the bystander effect.
Wada, Seiichi*; Ando, Tatsuhiko*; Watanabe, Aya*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 79, 2015/03
So far, we clarified that X-ray irradiation induced cell killing by bystander effect mediated-secreted factor. This phenomenon was related with sphingomyelinase (SMase). In this study we analyzed mechanism of secreted SMase from irradiated cells after irradiation. SMase was detected in the culture medium after irradiation by SDS-PAGE. Then, SMase was detected in the exosome of culture medium, but not out of exosome after irradiation. This result indicates that SMase was secreted as exosome from the irradiated cells.
Watanabe, Kazuyo*; Akitsuki, Takashi*; Shimura, Sachiko*; Gusev, O.*; Cornette, R.*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Okuda, Takashi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 87, 2015/03
The Sleeping Chironomid, 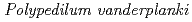 can stand complete desiccation (anhydrobiosis) and also shows radio-resistance. Recently, we have generated cultured cell (Pv11) originated from
can stand complete desiccation (anhydrobiosis) and also shows radio-resistance. Recently, we have generated cultured cell (Pv11) originated from 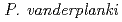 embryo which can also stand complete dehydration. In this study, we examine the tolerance of cultured cell Pv11 against ionbeam irradiation.
embryo which can also stand complete dehydration. In this study, we examine the tolerance of cultured cell Pv11 against ionbeam irradiation.
Ueda, Daisuke*; Shirai, Koji*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 84, 2015/03
In this study, we investigated the effects of irradiation to the silkworm eggs at various developmental stages. First, we tried the irradiation to the unfertilized eggs (at 1.5 hour after oviposition). At this stage, the female pronucleus and the sperm nucleus are observed in the eggs, but not fertilized. After irradiation, the irradiated eggs stopped the development after fertilization. About 2 hours after, the egg restarted the nuclear cleavage. This result indicates the DNA damage on pronuleus cannot prevent the fertilization. We also investigated the effects of irradiation to the egg at the nuclear cleavage stage (at 6 hour after oviposition). The egg also stopped the development after irradiation, but the duration time of the developmental arrest was almost two times longer (about 4 hours) than that of the egg irradiated at fertilization.
Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 73, 2015/03
Using a collimating heavy-ion microbeam system, we have explored various effects of heavy-ion hit on biological materials. However, there are limitations of the collimating system in the size of the microbeam spot and in the irradiation speed that cannot be overcome in principle. Thus, we started the development of a focusing microbeam system for target-irradiating individual cells more precisely. In this year, we established the protocol for irradiating "actual" cell sample with scanned beam. In the experiment, the HeLa cells were inoculated on a CR-39 film, then place on the sample stage. The microscopic image of cells was analyzed, and the cells were irradiated with scanned neon microbeam. After irradiation, we found the correspondence of the distribution pattern of the ion hit positions and the  -H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
-H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
Suzuki, Michiyo; Hattori, Yuya; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 88, 2015/03
Tomita, Masanori*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 77, 2015/03
Radiation-induced bystander responses are defined as responses in cells that have not been directly targeted by radiation but are in the neighborhood of cells that have been directly exposed. In this study, we aim to clarify a role of bystander response to sustain the homeostasis of damaged tissue using heavy-ion microbeams. We established the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation method to a 3D cultured human epidermis. Using this method, a viable cell rate of the 3D cultured human epidermis irradiated with 260 MeV  Ne-ion microbeams or broadbeams was analyzed by the MTT method.
Ne-ion microbeams or broadbeams was analyzed by the MTT method.
 mutants to microbeam irradiation
mutants to microbeam irradiationSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hattori, Yuya; Ikeda, Hiroko; Muto, Yasuko*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shirai, Kana*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 74, 2015/03
An increasing body of data indicates that ionizing radiation affects the nervous system and alters its function. Recently, we reported that chemotaxis of  during the salt chemotaxis learning (SCL), that is conditioned taste aversion to NaCl, was modulated by carbon ion irradiation, i.e. accelerated decrease in chemotaxis to NaCl during the SCL. However, we had no direct evidence for the interaction of ionizing radiation with the central neuronal tissue (nerve ring) in
during the salt chemotaxis learning (SCL), that is conditioned taste aversion to NaCl, was modulated by carbon ion irradiation, i.e. accelerated decrease in chemotaxis to NaCl during the SCL. However, we had no direct evidence for the interaction of ionizing radiation with the central neuronal tissue (nerve ring) in  . Microbeam irradiation is useful to analyze direct radiation effects at a cellular or tissue level. Thus, we applied the microbeam irradiation of the
. Microbeam irradiation is useful to analyze direct radiation effects at a cellular or tissue level. Thus, we applied the microbeam irradiation of the  nerve ring and examined the effect on the SCL.
nerve ring and examined the effect on the SCL.
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Tomita, Masanori*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Maeda, Munetoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Hiroko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 76, 2015/03
The objective of this project is to elucidate molecular mechanisms for the induction of radioadaptive response through radiation-induced bystander responses induced by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams in JAEA. We found that the adaptive response was induced by Ar (520 MeV  Ar
Ar ) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that
) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that 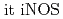 expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
Yokota, Wataru; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Okumura, Susumu; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Yoshida, Kenichi; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-018, 103 Pages, 2014/09
The world's first microbeam focusing technology for heavy ions of hundreds MeV accelerated by a cyclotron has been developed at the TIARA facility in the Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The technology enables us to form a microbeam of less than 1  m in diameter and to shoot a specified point on a target by one ion (single-ion hit) with spatial accuracy of microbeam size. In the course of the development, a cyclotron technology to accelerate a small energy-spread beam of hundres MeV, which is necessary for focusing to 1
m in diameter and to shoot a specified point on a target by one ion (single-ion hit) with spatial accuracy of microbeam size. In the course of the development, a cyclotron technology to accelerate a small energy-spread beam of hundres MeV, which is necessary for focusing to 1  m, has been developed as well as a beam focusing apparatus, beam size measurement and so forth based on the several-MeV microbeam/single-ion hit system of the TIARA electrostatic accelerators. Applicability of the technologies was examined by actual use in irradiation experiment and the result were fed back to them. This paper reports the process and the results of the development over ten years.
m, has been developed as well as a beam focusing apparatus, beam size measurement and so forth based on the several-MeV microbeam/single-ion hit system of the TIARA electrostatic accelerators. Applicability of the technologies was examined by actual use in irradiation experiment and the result were fed back to them. This paper reports the process and the results of the development over ten years.
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hara, Takamitsu*; Fujimichi, Yuki*
Hoshasen Seibutsu Kenkyu, 49(3), p.318 - 331, 2014/09
Over the past half century, a colony formation assay has been most commonly used to evaluate cellular radiosensitivity. Our colony formation assay of primary normal human diploid fibroblasts and the analysis of the size and cell numbers in abortive colonies comprising  50 cells and clonogenic colonies comprising
50 cells and clonogenic colonies comprising  50 cells led to observations that can potentially answer a fundamental question of what is actually being evaluated in the colony formation assay, and a new phenomenon was also unveiled with the colony formation assay whereby the higher the dose the larger the size of colonies arising from irradiated primary normal human diploid ocular lens epithelial cells. This paper shall review these findings.
50 cells led to observations that can potentially answer a fundamental question of what is actually being evaluated in the colony formation assay, and a new phenomenon was also unveiled with the colony formation assay whereby the higher the dose the larger the size of colonies arising from irradiated primary normal human diploid ocular lens epithelial cells. This paper shall review these findings.
Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kawaguchi, Isao*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(3), p.423 - 431, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.46(Biology)Our previous analysis with a branching process model showed that the relative cell death (RCD) in human fibroblasts can persist over 16 generations following irradiation with low linear energy transfer (LET)  -rays. Here we further set out to evaluate the RCD persistency in abortive colonies arising from normal human fibroblasts exposed to high-LET carbon ions (18.3 MeV/u, 108 keV/
-rays. Here we further set out to evaluate the RCD persistency in abortive colonies arising from normal human fibroblasts exposed to high-LET carbon ions (18.3 MeV/u, 108 keV/ m). We found that the abortive colony size distribution determined by biological experiments follows the linear relationship on the log-log plot, and that the Monte Carlo simulation using the RCD probability estimated from such linear relationship well simulates the experimentally determined surviving fraction and the relative biological effectiveness (RBE). We identified the short-term phase and long-term phase for the persistent RCD, as was the case for
m). We found that the abortive colony size distribution determined by biological experiments follows the linear relationship on the log-log plot, and that the Monte Carlo simulation using the RCD probability estimated from such linear relationship well simulates the experimentally determined surviving fraction and the relative biological effectiveness (RBE). We identified the short-term phase and long-term phase for the persistent RCD, as was the case for  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kawaguchi, Isao*; Ouchi, Noriyuki; Hara, Takamitsu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Saito, Kimiaki
PLOS ONE (Internet), 8(7), p.e70291_1 - e70291_10, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.01(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Clonogenicity gives important information about the cellular reproductive potential following ionizing irradiation. We firstly plotted the experimentally determined colony size distribution of abortive colonies in irradiated normal human fibroblasts, and found the linear relationship on the log-log plot. By applying the simple model of branching processes to the linear relationship, we found the persistent reproductive cell death (RCD) over several generations following irradiation. To verify the estimated probability of RCD, abortive colony size distribution ( 15 cells/colony) and the surviving fraction were simulated by the Monte Carlo computational approach. Radiation-induced RCD (i.e. excess probability) lasted over 16 generations and mainly consisted of two components in the early and late phases. We found that short-term RCD is critical to the abortive colony size distribution, and long-lasting RDC is important for the dose response of the surviving fraction.
15 cells/colony) and the surviving fraction were simulated by the Monte Carlo computational approach. Radiation-induced RCD (i.e. excess probability) lasted over 16 generations and mainly consisted of two components in the early and late phases. We found that short-term RCD is critical to the abortive colony size distribution, and long-lasting RDC is important for the dose response of the surviving fraction.

Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.21 - 25, 2012/10
High linear energy transfer (LET) radiation is important cosmic rays that has neurobiological effects: it is known to induce conditioned taste aversion, and suppress neurogenesis that may underlie cognitive impairment. However, the impact of high-LET radiation on other learning effects remains largely unknown. Here, we focus on kinetics of the radiation response for the salt chemotaxis learning (SCL) behavior in the nameatode,  , because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET
, because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET  -irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation (
-irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of
m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of 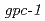 mutant showed that the G-protein
mutant showed that the G-protein  subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C.
subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C. 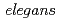 .
.
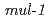 , induced by ionizing radiation in
, induced by ionizing radiation in 
Kimura, Takafumi*; Takanami, Takako*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Higashitani, Atsushi*
Radiation Research, 178(4), p.313 - 320, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.17(Biology)Here, we found that exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) induce certain innate immune response gene of 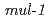 in the intestine. Pre-treatment with IR before seeding on
in the intestine. Pre-treatment with IR before seeding on 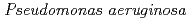 lawn plate, significantly increased survival rate in the nematode. IR induction of
lawn plate, significantly increased survival rate in the nematode. IR induction of 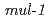 gene was highly dependent on the ELT-2 transcription factor and p38 MAPK. Moreover, the insulin/IGF-1 signal pathway works as an enhancer of induction of this gene. Silencing of the
gene was highly dependent on the ELT-2 transcription factor and p38 MAPK. Moreover, the insulin/IGF-1 signal pathway works as an enhancer of induction of this gene. Silencing of the 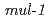 gene led to growth retardation after IR irradiation. Finally, we describe the cross-tolerance between the responses to radiation exposure and innate immune system.
gene led to growth retardation after IR irradiation. Finally, we describe the cross-tolerance between the responses to radiation exposure and innate immune system.
 against high-LET radiation exposure
against high-LET radiation exposureSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.7 - 11, 2012/07
Here, we investigated the resistance to high-LET radiation exposure for two behaviors of the nematode,  , which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation (
, which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of
m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of  is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
 to extreme environments
to extreme environmentsHorikawa, Daiki*; Yamaguchi, Ayami*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Tanaka, Daisuke*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yukuhiro, Fumiko*; Kuwahara, Hirokazu*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; et al.
Astrobiology, 12(4), p.283 - 289, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:68.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We examined the hatchability of hydrated and anhydrobiotic eggs of the tardigrade  to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.