Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu; Jin, Q.*; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 207, p.111180_1 - 111180_8, 2024/05
The impacts of mathematical models and associated parameters on radon ( Rn) and thoron (
Rn) and thoron (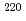 Rn) exhalation rates based on in-situ testing at building interior solid walls were demonstrated to improve data analysis techniques.The results showed that the heterogeneity of their activity concentrations within the measurement system was more significant for thoron than radon. The diurnal variation in indoor radon should be considered for better data quality. In conclusion, a model should be appropriately made and selected under the purposes and accuracy requirements of the exhalation test.
Rn) exhalation rates based on in-situ testing at building interior solid walls were demonstrated to improve data analysis techniques.The results showed that the heterogeneity of their activity concentrations within the measurement system was more significant for thoron than radon. The diurnal variation in indoor radon should be considered for better data quality. In conclusion, a model should be appropriately made and selected under the purposes and accuracy requirements of the exhalation test.
Nakajima, Junya; Hirota, Seiko*; Tsuji, Tomoya; Watanabe, Yuki; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kobayashi, Noriko*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(1), p.13 - 20, 2023/04
no abstracts in English
Di Palma, A.; Adamo, P.*; Dohi, Terumi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Sakoda, Akihiro; Sato, Kazuhiko; Iijima, Kazuki
Chemosphere, 308, Part 1, p.136179_1 - 136179_13, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.8(Environmental Sciences)The present study shows the use of mosses transplanted in bags, called as moss bags, as biosensors of airborne radioactive dusts in the environment of the evacuated zone of Fukushima. A standardized protocol was applied and three moss species were used. Background sites of Okayama Prefecture were used for comparison. In the Fukushima area, the moss bags were able to accumulate radiocaesium in all exposure sites and periods, with Sphagnum palustre moss acting as the most performant moss. The radiocaesium activity concentrations dectected in mosses were in strong agreement with the Cs deposition levels and decontamination status of each exposure site. The accumulation of soil-derived radiocaesium by moss bags was supported by autoradiography and electron microscopy analyses. The linear dependency of Cs accumulation with the exposure time allowed a radiocaesium quantitative assessment.
Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sun, L.*; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Otsu, Iwao*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), p.10750_1 - 10750_14, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)Reactive sulfur species (RSS) involve oxidative stress deeply and contribute anti-inflammatory effect, but no studied have focused on RSS changes after irradiation. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed the metabolites, focusing on RSS in mouse brain following radon inhalation. The ratio of oxidized glutathione to reduced glutathione and proportion of RSS in GSH or cysteine increased by radon inhalation. The sulfur ion might bind to GSH or cysteine chemically under conditions of oxidative stress, even at very low-dose exposure. We performed the overall assessment of high-dimensional data by applying machine learning and showed the specific characteristics of the effects by the exposure conditions. Our results suggested that RSS could produce a biological defense against oxidative stress following radon inhalation.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*; Naoe, Shota*; Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 63(5), p.719 - 729, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.19(Biology)Andresz, S.*; Papp, C.*; Clarijs, T.*; Sakoda, Akihiro; S ez-Mu
ez-Mu oz, M.*; Qiu, R.*
oz, M.*; Qiu, R.*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(3), p.031516_1 - 031516_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)While online working seems to become more common since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, social media has the potential to offer greater interactivity and networking capacities. It seems therefore relevant for the IRPA Young Generation Network to investigate the usage of social media by the young generation in radiation protection trough a survey disseminated online. It was also the opportunity to investigate the early feedbacks about on-line learning. The survey collected 89 answers from 15 countries. The most commonly used social media platforms are first Facebook, then LinkedIn and Twitter, but other social media where reported too. The respondents have a multi-objectives approach on social media, using it for different purposes (chiefly for sharing of news and RP related information/education material) and different audiences (ex. public, professional audience), and are not frenetic users based on the frequencies of publication and consultation and the challenges they see within social media. The survey collected the view of the young generation about their practical experience about learning in virtual setting and its advantages and disadvantages vs. in-person. Most participants expressed mixed-feeling about on-line learning. These results show that the young generation can play a role in supporting the extra and intra-communication of the RP community.
 Be activity concentrations in the atmosphere
Be activity concentrations in the atmosphereNarazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), p.10128_1 - 10128_9, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:27.46(Environmental Sciences)In March 2013, increased  Be activity concentrations in the atmosphere were observed for successive days in Dazaifu, western Japan. The daily
Be activity concentrations in the atmosphere were observed for successive days in Dazaifu, western Japan. The daily  Be activity concentration averages ranged from 0.93 to 14 mBq/m
Be activity concentration averages ranged from 0.93 to 14 mBq/m , with a monthly average of 8.3 mBq/m
, with a monthly average of 8.3 mBq/m . This average was the highest among the monthly averages observed between 1999 and 2015 and higher than the monthly average over this period (4.7 mBq/m
. This average was the highest among the monthly averages observed between 1999 and 2015 and higher than the monthly average over this period (4.7 mBq/m ) plus twice the standard deviation (1.7
) plus twice the standard deviation (1.7  2 mBq/m
2 mBq/m = 8.1 mBq/m
= 8.1 mBq/m ). Also, this exceeded the monthly average (6.0 mBq/m
). Also, this exceeded the monthly average (6.0 mBq/m ) only for March 1999-2015, excluding 2013, where the cosmic-ray intensity, a component producing
) only for March 1999-2015, excluding 2013, where the cosmic-ray intensity, a component producing  Be, decreased. Based on the backward trajectory analysis results, the inflow of air from the stratosphere and upper troposphere at high latitudes that frequently occurred in March 2013 was considered the reason for the
Be, decreased. Based on the backward trajectory analysis results, the inflow of air from the stratosphere and upper troposphere at high latitudes that frequently occurred in March 2013 was considered the reason for the  Be activity concentration increase.
Be activity concentration increase.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*; Kanzaki, Norie; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13), p.7761_1 - 7761_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)In specific situations such as bathing in a radon spa, where the radon activity concentration in thermal water is far higher than that in air, it has been revealed that radon uptake via skin can occur and should be considered for more precise dose evaluation. The primary aim of the present study was to numerically demonstrate the distribution as well as the degree of diffusion of radon in the skin, with a focus on its surface layers (i.e., stratum corneum). We made a biokinetic model that included diffusion theory at the stratum corneum, and measured radon solubility in the stratum corneum to get a crucial parameter. The implementation of the model suggested that the diffusion coefficient in the stratum corneum was as low as general radon-proof sheets. The depth profile of radon in the skin was found to be that after a 20-minute immersion in water, the radon activity concentration at the top surface skin layer was approximately 1000 times higher than that at the viable skin layer. The information on the position of radon as a radiation source would contribute to special dose evaluation where specific target cell layers are assumed for the skin.
Horai, Sawako*; Murakami, Shoichi*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Nakashita, Rumiko*; Kunisue, Tatsuya*; Ishimori, Yuu
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(6), p.415_1 - 415_25, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.07(Environmental Sciences)This study conducted an investigation of trace element behavior at a former uranium (U) mining site and evaluated environmental impacts to biota. Concentrations of trace elements were determined in sediments, water, and three organism types (insects, frogs, and newts) from three zones in the former U mining site. Concentrations of As and U in the sediments and water samples were the highest at the mill tailings pond site, where post-U extraction remnants have been accumulated. Additionally, among the organisms analyzed the highest levels of these elements/isotopes were found in newts from MP. Considering data analyses of the whole-body element concentrations, bioaccumulation factors, and 
 N values for the organisms, it was concluded that newts might be the most vulnerable species in this location. Further monitoring and more accurate evaluation of the ecological impacts are preferred for this former U mining site.
N values for the organisms, it was concluded that newts might be the most vulnerable species in this location. Further monitoring and more accurate evaluation of the ecological impacts are preferred for this former U mining site.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Tsuji, Tomoya; Hirota, Seiko*; Watanabe, Yuki
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 57(2), p.108 - 114, 2022/06
no abstracts in English
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Naoe, Shota*; Murakami, Kaito*; Yukimine, Ryohei*; Fujimoto, Yuki*; Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 70(2), p.154 - 159, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.52(Nutrition & Dietetics)Hasan, Md. M.*; Janik, M.*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(12), p.770_1 - 770_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.39(Environmental Sciences)Potentially higher cancer risk due to exposure from natural background radiation was indicated for Bangladeshi population by estimations based on the countrywide study. Several regions with elevated natural background exhibited higher soil radium and thorium contents than the world average. Being the decay products of these radioactive elements, natural radon isotopes could constitute environmental risk factors for internal radiation exposure to the lungs of people living in these areas. Although lung cancer is one of most prevalent types of cancer in Bangladesh, its status and features are still unclear. To clarify the present status of one of the potential risk factors for lung cancer in the country, this review intends to ascertain the countrywide radon exposure, and its pathways by types of local dwelling and by regions; which would provide an indication of the internal exposures in areas of elevated natural background radiation and radionuclides of soil as well as an understanding of the preliminary contribution of environmental radon on the country's lung cancer prevalence. In this review, countrywide air radon exposures for Bangladeshi dwellings and workplaces are organized from peer-reviewed published papers. Radon has been identified as one of influential sources of radiation dose in Bangladesh with its higher radon exhalation and emanation rate from soil. A novel nationwide depiction of the overall indoor and soil radon levels for Bangladesh has been made through radiation maps. This would be helpful for designing future systematic radon/radiological surveys and research on the country's lung cancer prevalence.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Nomura, Naoki*; Kuroda, Yujiro*; Kono, Takahiko; Naito, Wataru*; Yoshida, Hiroko*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 41(4), p.1258 - 1287, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.18(Environmental Sciences)Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, many radiation experts directly experienced a vast gap between ideal and real public understanding (PU) of radiation in risk communication. Therefore, this study collated and reviewed information about PU activities for radiation and its risk that six Japanese academic societies - which seemed to be socially neutral expert communities - related to radiation and radiation risk conducted before and after the accident. Activities these radiation-related societies provided to general public were discussed from the following perspectives: (1) difficulties in two-way communication due to resources, motivation, public interest and concerns; (2) balance between academic research and PU activities; (3) academic societies' building trust with the public whilst ensuring member experts' neutrality and independence; (4) discussions among academic societies to prepare for public engagement. We hope that this paper encourages experts and academic societies in radiation protection to hold more national and international discussions about their roles in public communication and outreach.
 Be; Particle size distribution and chemical composition of
Be; Particle size distribution and chemical composition of  Be-carrying aerosols in the atmosphere in Japan
Be-carrying aerosols in the atmosphere in JapanNarazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Takahashi, Shunta*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 237, p.106690_1 - 106690_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:20.86(Environmental Sciences)The particle size distributions of airborne aerosols with  Be were measured using cascade impactors at Dazaifu, a city in western Japan, in 2018 to observe their seasonal variation.
Be were measured using cascade impactors at Dazaifu, a city in western Japan, in 2018 to observe their seasonal variation.  Be was found to be attached to aerosols with a particle size of less than 2.1
Be was found to be attached to aerosols with a particle size of less than 2.1  m; in general, particles sized 0.43-0.65
m; in general, particles sized 0.43-0.65  m had the highest
m had the highest  Be activity concentrations. The activity median aerodynamic diameter (AMAD) of
Be activity concentrations. The activity median aerodynamic diameter (AMAD) of  Be was in the range of 0.39-0.52
Be was in the range of 0.39-0.52  m, which is the size range of particles that can reach human alveoli, and had an annual mean of 0.43
m, which is the size range of particles that can reach human alveoli, and had an annual mean of 0.43 0.035
0.035  m. The activity concentrations of
m. The activity concentrations of  Be were significantly lower in summer, which affected its activity concentrations in the particle size distributions of
Be were significantly lower in summer, which affected its activity concentrations in the particle size distributions of  Be. The particle size distribution of
Be. The particle size distribution of  Be-carrying aerosols was also affected by that of the aerosol particles in the atmosphere. Finally, findings suggest that
Be-carrying aerosols was also affected by that of the aerosol particles in the atmosphere. Finally, findings suggest that  Be was mainly attached to sulfate aerosols (particularly ammonium sulfate aerosols).
Be was mainly attached to sulfate aerosols (particularly ammonium sulfate aerosols).
Yoshida, Hiroko*; Kuroda, Yujiro*; Kono, Takahiko; Naito, Wataru*; Sakoda, Akihiro
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 46(3), p.134 - 142, 2021/09
The Japan Health Physics Society established a task group on "Public Understanding after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident" in the 2018-2019 fiscal year. This task group collected and analyzed various activities that had been made for promotion of public understanding since the Fukushima accident, and then discussed some issues such as expert's roles. This paper outlines a panel session for this task group held at the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Health Physics Society (Online). This session consisted of (1) reporting what the task group achieved, (2) having comments by two designated experts in the fields of sociology and ethics, (3) making a panel discussion with three representatives from the task group and the two designated speakers, and (4) summarizing this session by a rapporteur.
Andresz, S.*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Ha, W.-H.*; Kabrt, F.*; Kono, Takahiko; S ez Mu
ez Mu oz, M.*; Nusrat, O.*; Papp, C.*; Qiu, R.*; Bryant, P.*
oz, M.*; Nusrat, O.*; Papp, C.*; Qiu, R.*; Bryant, P.*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 46(3), p.143 - 150, 2021/09
The Young Generation Network (YGN) was officially established as part of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA) in the spring of 2018. Since then, it has been dedicated to a variety of activities to promote communication, collaboration and professional development of students and young professionals in the area of radiation protection and its allied fields. This article reports our recent activities from the middle of 2018 to the beginning of 2021, with highlights on some important events: (1) Joint JHPS-SRP-KARP Workshop of Young Generation Network (December 2019 in Japan); (2) Contribution to Nuclear Energy Agency Workshop on Optimization - Rethinking the Art of Reasonable (January 2020 in Portugal); (3) Survey on the impact of COVID-19 on radiation protection among IRPA YGN members (March 2020); (4) Contribution to IRPA15 (January-February 2021; online). The discussion and insight obtained from each activity are also summarized. The IRPA YGN will aim to achieve its on-going activities and continue to follow the ways paved in the Strategic Agenda and despite the challenges raised by the COVID-19 pandemic. Namely, running an international survey (for example, on the usage of social media in radiation protection, and on the long-term consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic), engaging national YGNs, extending the network, finding new relationships with networks with an interest in the young generation and participation in (remote) events will be aspired for.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Shuto, Hina*; Naoe, Shota*; Yano, Junki*; Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Hanamoto, Katsumi*; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Terato, Hiroaki*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(5), p.861 - 867, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:55.27(Biology)Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu; Kanzaki, Norie; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(4), p.634 - 644, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.06(Biology)It is held that the skin dose from radon progeny is not negligibly small and that introducing cancer is a possible consequence under normal circumstances, while there are a number of uncertainties in terms of related parameters such as activity concentrations in air, target cells in skin, skin covering materials, and deposition velocities. Meanwhile, an interesting proposal emerged in that skin exposure to natural radon-rich thermal water as part of balneotherapy can produce an immune response to induce beneficial health effects. The goal of the present study was to obtain generic dose coefficients with a focus on the radon progeny deposited on the skin in air or water in relation to risk or therapeutic assessments. We thus first estimated the skin deposition velocities of radon progeny in the two media based on data from the latest human studies. Using the optimized velocities, skin dosimetry was then performed under different assumptions regarding alpha-emitting source position and target cell (i.e., basal cells or Langerhans cells). Furthermore, the impact of the radon progeny deposition on effective doses from all exposure pathways relating to "radon exposure" was assessed using various possible scenarios. It was found that in both exposure media, effective doses from radon progeny inhalation are one to four orders of magnitude higher than those from the other pathways. In addition, absorbed doses on the skin can be the highest among all pathways when the radon activity concentrations in water are two or more orders of magnitude higher than those in air.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Shuto, Hina*; Yano, Junki*; Naoe, Shota*; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Hanamoto, Katsumi*; Terato, Hiroaki*; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(2), p.206 - 216, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.83(Biology)Radon inhalation activates antioxidative functions in mouse organs, thereby contributing to inhibition of oxidative stress-induced damage. Therefore, in this study, we evaluated the redox state of various organs in mice following radon inhalation. Mice inhaled radon at concentrations of 2 or 20 kBq/m for 1, 3, or 10 days. The relationship between antioxidative function and oxidative stress was evaluated by principal component analysis (PCA) and correlation coefficient compared with control mice subjected to sham inhalation. These findings suggested that radon inhalation altered the redox state in organs, but that the characteristics varied depending on the redox state in organs.
for 1, 3, or 10 days. The relationship between antioxidative function and oxidative stress was evaluated by principal component analysis (PCA) and correlation coefficient compared with control mice subjected to sham inhalation. These findings suggested that radon inhalation altered the redox state in organs, but that the characteristics varied depending on the redox state in organs.
Yoshida, Hiroko*; Kuroda, Yujiro*; Kono, Takahiko; Naito, Wataru*; Sakoda, Akihiro
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 55(4), p.257 - 263, 2020/12
no abstracts in English