Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Al
Al through directional Compton profile measurement
through directional Compton profile measurementKoizumi, Akihisa*; Kubo, Yasunori*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Sakurai, Yoshiharu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 88(3), p.034714_1 - 034714_6, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Baba, Hiromi*; Onizuka, Yoshihiko*; Nakao, Minoru*; Fukahori, Mai*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; Endo, Satoru*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.528 - 532, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.37(Environmental Sciences)The PHITS simulation were performed to reproduce the geometrical setup of an experiment that measured the microdosimetric energy distributions at the Kyoto University Reactor (KUR) where two types of tissue equivalent proportional counters (TEPC) were used, one with A-150 wall alone and another with a 50 ppm boron loaded A-150 wall. It was found that the PHITS code is a useful tool for the simulation of the energy deposited in tissue in BNCT based on the comparisons with experimental results.
Yanagie, Hironobu*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; Nakamura, Takemi; Higashi, Shushi*; Ikushima, Ichiro*; Morishita, Yasuyuki*; Shinohara, Atsuko*; Fujiwara, Mitsuteru*; Suzuki, Minoru*; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 14th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ICNCT-14) (CD-ROM), p.157 - 160, 2010/10
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
 X-ray diffraction measurement of the hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of aluminum and characterization of the recovered AlH
X-ray diffraction measurement of the hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of aluminum and characterization of the recovered AlH
Saito, Hiroyuki; Sakurai, Yoko; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 215, p.012127_1 - 012127_4, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:85.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Sakurai, Yoko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi
Proceedings of 18th International Symposium on Processing and Fabrication of Advanced Materials (PFAM-18), p.75 - 80, 2009/12
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:137 Percentile:97.72(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.892 - 899, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:86.6(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The concept for a compact DEMO reactor named "SlimCS" is presented. Distinctive features of the concept is low aspect ratio ( = 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low-
= 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low- , i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
, i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
Ishikawa, Masayori*; Ono, Koji*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Hiratsuka, Junichi*; Miyatake, Shinichi*; Kato, Itsuro*; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Kobayashi, Toru*; Kumada, Hiroaki; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ICNCT-12), p.397 - 400, 2006/10
An ultraminiature thermal neutron monitor which was named SOF detector (Scintillator with Optical Fiber detector) had been developed for BNCT treatment. We had been experienced 15 clinical trials using SOF detector until the end of 2005, some measurements got good results, and some got unacceptable results. One reason of the unacceptable results was due to dislocation of the detector during treatment. This is because it is difficult to fix the SOF detector on patient's skin without strong sticker. To overcome this problem, a loop-type SOF probe was developed. By using the loop-type SOF detector, fixing on the patient's skin was much easier.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Sato, Masayasu; Isono, Takaaki; Sakurai, Shinji; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; Suzuki, Satoshi; Ando, Masami; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1151 - 1158, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:123 Percentile:99.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Masayori*; Kumada, Hiroaki; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kaneko, Junichi*; Bengua, G.*; Unesaki, Hironobu*; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Kosako, Toshiso*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 551(2-3), p.448 - 457, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.7(Instruments & Instrumentation)A wide range thermal neutron detector was developed based on the Scintillator with Optical Fiber (SOF) detector which has been previously used for thermal neutron monitoring during boron neutron capture therapy irradiation. With this new detector system we intended to address the issues of real-time thermal neutron flux measurement and the simultaneous measurement of a wide range of thermal neutron flux in a BNCT irradiation field which were difficult to implement with the gold wire activation method. A good agreement between the thermal neutron flux measured by the gold wire activation method and the paired SOF detector system was observed. However, measurements which would normally take a few days to perform with the gold wire activation method were obtained in just about 15 min using the SOF detector system. We also confirmed the dynamic range of linearity for the SOF detector system to be in the order of magnitude of 1e-4.
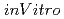 study
studyMatsumura, Akira*; Zhang, T.*; Nakai, Kei*; Endo, Kiyoshi*; Kumada, Hiroaki; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Fumiyo*; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Nose, Tadao*
Journal of Experimental and Clinical Cancer Research, 24(1), p.93 - 98, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kishi, Toshiaki; Torii, Yoshiya; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Kobayashi, Toru*
Proceedings of 11th World Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ISNCT-11) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2004/10
To carry out the boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) using the epithermal neutron, the epithermal neutron beam intensity was measured by using  Au reaction rate activated on the resonance absorption peak (4.9eV). Two scaling factors, which are the reactor power calibration factor and the calculation/experiment (C/E) scaling factor, are necessary in order to correct with the simulation and actual irradiation experiment. First, an optimum detector position was investigated using MCNP code. The result of MCNP calculation showed that the influence of subject placed at the collimator was below 1% when the detector was placed in the distance of over 20cm from the collimator. Therefore we installed the monitor holders near the bismuth block in order to set three gold wire monitors. The factors were determined in the calibration experiments that measure the thermal neutron flux in the phantom and reaction rate of the gold wire monitors. The monitoring technique to measure epithermal neutron beam intensity was applied to clinical irradiation with the epithermal neutron beam.
Au reaction rate activated on the resonance absorption peak (4.9eV). Two scaling factors, which are the reactor power calibration factor and the calculation/experiment (C/E) scaling factor, are necessary in order to correct with the simulation and actual irradiation experiment. First, an optimum detector position was investigated using MCNP code. The result of MCNP calculation showed that the influence of subject placed at the collimator was below 1% when the detector was placed in the distance of over 20cm from the collimator. Therefore we installed the monitor holders near the bismuth block in order to set three gold wire monitors. The factors were determined in the calibration experiments that measure the thermal neutron flux in the phantom and reaction rate of the gold wire monitors. The monitoring technique to measure epithermal neutron beam intensity was applied to clinical irradiation with the epithermal neutron beam.
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Kono, Nobuaki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Sakurai, Takeshi; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Mukaiyama, Takehiko; Raman, S.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 144(2), p.129 - 141, 2003/06
To evaluate neutron cross-section data of minor actinides, separated actinide samples and dosimetry samples were irradiated at the Dounreay Prototype Fast Reactor for 492 effective full power days. Based on the burnup calculations of major actinide and dosimetry samples, the neutron flux distribution and the flux level were adjusted at the locations where minor actinide samples were irradiated. The burnup calculations were carried out for minor actinides using the determined flux distribution and flux level. This paper discusses the burnup calculations and the validation of minor actinide cross-section data in evaluated nuclear data libraries. We find that we can obtain reliable FIMA (fission per initial metallic atom) values by using the 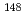 Nd method except that the uncertainties in the FIMA values are large for
Nd method except that the uncertainties in the FIMA values are large for  U,
U,  Pu, Am isotopes, and Cm isotopes because the
Pu, Am isotopes, and Cm isotopes because the  Nd yields are known poorly for these isotopes and are probably overestimated. For these isotopes, measurements to improve the fission-yield data are needed. We also find that, in general, the JENDL-3.2 nuclear data for the minor actinides are adequate for the conceptual design study of transmutation systems. But, there are some nuclides (especially
Nd yields are known poorly for these isotopes and are probably overestimated. For these isotopes, measurements to improve the fission-yield data are needed. We also find that, in general, the JENDL-3.2 nuclear data for the minor actinides are adequate for the conceptual design study of transmutation systems. But, there are some nuclides (especially  Pu and
Pu and  Pu) for which new measurements are needed particulary if the minor actinides constitute a major part of the nuclear fuel.
Pu) for which new measurements are needed particulary if the minor actinides constitute a major part of the nuclear fuel.
Shinohara, Nobuo; Kono, Nobuaki; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sakurai, Takeshi; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*; Raman, S.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 144(2), p.115 - 128, 2003/06
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Nobuo; Kono, Nobuaki; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sakurai, Takeshi; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*; Raman, S.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 144(2), p.115 - 128, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Kono, Nobuaki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Sakurai, Takeshi; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*; Raman, S.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 144(2), p.129 - 141, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sugie, Tatsuo; Hatae, Takaki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Fujita, Takaaki; Kusama, Yoshinori; Nishitani, Takeo; Isayama, Akihiko; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.482 - 511, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:3.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)The diagnostic system of JT-60U (JT-60upgrade) is composed of about 50 individual diagnostic devices. Recently, the detailed radial profile measurements of plasma parameters have been improved, so that the internal structure of plasmas has been explored. The understanding of plasma confinement has been enhanced by density and temperature fluctuation measurements using a mm-wave reflectometer and electron cyclotron emission measurements respectively. In addition, the real-time control experiments of electron density, neutron yield, radiated power and electron temperature gradient have been carried out successfully by corresponding diagnostic devices. These measurements and the real time control contribute to improving plasma performance. Diagnostic devices for next generation fusion devices such as a CO2 laser interferometer/polarimeter and a CO2 laser collective Thomson scattering system have been developed.
Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Ishida, Shinichi; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirai, Hiroshi; Koide, Yoshihiko; Fukuda, Takeshi; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.185 - 254, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:48.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)With the main aim of providing physics basis for ITER and the steady-state tokamak reactors, JT-60/JT-60U has been developing and optimizing the operational concepts, and extending the discharge regimes toward sustainment of high integrated performance in the reactor relevant parameter regime. In addition to achievement of the equivalent break-even condition (QDTeq up to 1.25) and a high fusion triple product = 1.5E21 m-3skeV, JT-60U has demonstrated the integrated performance of high confinement, high beta-N, full non-inductive current drive with a large fraction of bootstrap current in the reversed magnetic shear and in the high-beta-p ELMy H mode plasmas characterized by both internal and edge transport barriers. The key factors in optimizing these plasmas are profile and shape controls. As represented by discovery of various Internal Transport Barriers, JT-60/JT-60U has been emphasizing freedom and restriction of profiles in various confinement modes. JT-60U has demonstrated applicability of these high confinement modes to ITER and also clarified remaining issues.