Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sanada, Yukihisa; Munakata, Masahiro; Mori, Airi; Ishizaki, Azusa; Shimada, Kazumasa; Hirouchi, Jun; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu; Urabe, Yoshimi; Nakanishi, Chika*; Yamada, Tsutomu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-016, 131 Pages, 2016/10
By the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), caused by the East Japan earthquake and the following tsunami occurred on March 11, 2011, a large amount of radioactive materials was released from the NPS. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring using manned helicopter was conducted around FDNPS. In addition, background dose rate monitoring was conducted around Sendai Nuclear Power Station. These results of the aerial radiation monitoring using the manned helicopter in the fiscal 2015 were summarized in the report.
Isozaki, Misaki; Sasaki, Shinji; Maeda, Koji; Katsuyama, Kozo
JAEA-Technology 2015-058, 28 Pages, 2016/03
During irradiation in the fast reactor "JOYO", the changes of fuel structures with the formation of central void occur in the uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuels (MOX fuels) because of radial temperature gradient. The changes of element (U, Pu, and so on) distributions along radial direction proceed from these changes. Therefore, it is important to study the changes of fuel structures of the minute area in fuel pellet and the changes of element distribution behavior for development of fast reactor fuels. In order to make detailed observations of microstructure and elemental analyses of fuel samples, a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) equipped with a wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (WDS) and an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) were installed in Fuel Monitoring Facility (FMF). The samples of this FE-SEM are very high radioactivity because the samples contain the nuclear fuel elements (U, Pu, etc.), the fission products (Cs, Rh, etc.) and activation product (Co, Mn etc.). Owing to this, it is necessary to prevent leakage of radioactive materials (particularly, U, Pu is need tight accountancy in law) and to protect operators from radiation. In this installation of FE-SEM, it is selected JSM-7001F (made by JEOL) for base model. The notable modified points were as follows. (1) To protect operators from radiation, lead shields was installed around FE-SEM. (2) To prevent leakage of radioactive materials, the instrument was attached to a remote control air-tight sample transfer unit between a shielded hot cell and the FE-SEM and the instrument was fixing rigid structure without vibration damper. (3) The design and manufacture the lead shields with consideration of instrument maintainability. This paper was described the summary of FE-SEM, the notable modified points, the ways of FE-SEM installation, the result of performance test.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Koyama, Shinichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 113(1), p.619 - 621, 2015/10
In order to evaluate the microstructural change behavior of Am-MOX fuels at the initial stage of irradiation, detailed investigations using image analysis were performed on X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) images and on ceramographs from fuels irradiated in both B11 and B14.
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Kinoshita, Takeshi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Asano, Takahiro*; Sasaki, Yoshito; et al.
FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 86(3), p.532 - 543, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:36.87(Microbiology)Anaerobic microbial activity has a major influence on the subsurface environment, and should be considered in subsurface activities including the construction of radioactive waste repositories. We investigated denitrification and methanogenesis in anoxic groundwater from 140 m depth in two boreholes, where the redox potential fluctuated. The average maximum potential denitrification rates, measured under anaerobic conditions in the two boreholes using an  N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
N tracer. Methanogenesis candidates were detected by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Although the stable isotope signatures suggested that some of the dissolved methane was of biogenic origin, no potential for methane production was evident during the incubations. The groundwater at 140 m depth did not contain oxygen, had an Eh ranging from -144 to 6.8 mV, and was found to be a potential field for denitrification.
Shinohara, Masanori; Motegi, Toshihiro; Saito, Kenji; Haga, Hiroyuki; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Takada, Kiyoshi*; Higashimura, Keisuke*; Fujii, Junichi*; Ukai, Takayuki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-032, 29 Pages, 2012/11
An event, in which one of WRMs were disabled to detect the neutron flux in the reactor core, occurred during the period of reactor shut down of HTTR in March, 2010. The actual life time of WRM was unexpectedly shorter than the past developed life time. Investigation of the cause of the outage of WRM toward the recovery of the life time up to the past developed life is one of the issues to develop the technology basis of HTGR. Then, two experimental investigations were carried out to reveal the cause of the malfunction by specifying the damaged part causing the event in the WRM. One is an experiment using a mock-up sample test which strength degradation on assembly accuracy and heat cycle to specify the damaged part in the WRM. The other is a destructive test in FMF to specify the damaged part in the WRM. This report summarized the results of the destructive test and the experimental investigation using the mock-up to reveal the cause of malfunction of WRM.
Hanada, Masaya; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Inoue, Takashi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Komata, Masao; Kojima, Atsushi; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.208 - 213, 2010/08
A large negative ion source with an ion extraction area of 110 cm  45 cm has been developed to produce 500 keV, 22 A D
45 cm has been developed to produce 500 keV, 22 A D ion beams required for JT-60 Super Advanced. To realize the JT-60SA negative ion source, the JT-60 negative ion source has been modified and tested on the negative-ion-based neutral beam injector on JT-60U. A 500 keV H
ion beams required for JT-60 Super Advanced. To realize the JT-60SA negative ion source, the JT-60 negative ion source has been modified and tested on the negative-ion-based neutral beam injector on JT-60U. A 500 keV H ion beam has been produced at 3 A without a significant degradation of beam optics. This is the first demonstration of a high energy negative ion acceleration of more than one-ampere to 500 keV in the world. The beam current density of 90 A/m
ion beam has been produced at 3 A without a significant degradation of beam optics. This is the first demonstration of a high energy negative ion acceleration of more than one-ampere to 500 keV in the world. The beam current density of 90 A/m is being increased to meet 130 A/m
is being increased to meet 130 A/m of the design value for JT-60SA by tuning the operation parameters. A long pulse injection of 30 s has been achieved at a injection D
of the design value for JT-60SA by tuning the operation parameters. A long pulse injection of 30 s has been achieved at a injection D power of 3 MW. The injection energy, defined as the product of the injection time and power, reaches 80 MJ by neutralizing a 340 keV, 27 A D
power of 3 MW. The injection energy, defined as the product of the injection time and power, reaches 80 MJ by neutralizing a 340 keV, 27 A D ion beam produced with two negative ion sources.
ion beam produced with two negative ion sources.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Hanada, Masaya; Kamada, Masaki; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1519 - 1529, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:45.09(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The JT-60SA N-NBI system is required to inject 10 MW for 100 s at 500 keV. Three key issues should be solved for the JT-60SA N-NBI ion source. One is to improve the voltage holding capability. Recent R&D tests suggested that the accelerator with a large area of grids may need a high margin in the design of electric field and a long time for conditioning. The second issue is to reduce the grid power loading. It was found that some beamlets were strongly deflected due to beamlet-beamlet interaction and strike on the grounded grid. The grids are to be designed by taking account of beamlet-beamlet interaction in three-dimensional simulation. Third is to maintain the D- production for 100 s. A simple cooling structure is proposed for the active cooled plasma grid, where a key is the temperature gradient on the plasma grid for uniform D- production. The modified N-NBI ion source will start on JT-60SA in 2015.
 (
(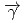 ,
,
 )
) and
and  (
(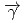 ,
,
 )
)
 reactions for
reactions for 
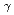 =1.5-2.4 GeV
=1.5-2.4 GeVZegers, R. G. T.*; Sumihama, Mizuki*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Dat , S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(9), p.092001_1 - 092001_4, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 = +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutron
= +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutronNakano, Takashi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Date, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(1), p.012002_1 - 012002_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:1023 Percentile:99.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Abe, Kazuyuki; Sasaki, Shinji; Kikuchi, Shin; Katsuyama, Kozo; Nagamine, Tsuyoshi; Matsumoto, Shinichiro
JNC TN9430 2002-003, 52 Pages, 2002/05
Irradiation tests of Absorber Material Irradiation Rig (AMIR) have been continuously conducted, using the experimental fast reactor Joyo. AMIR-6, which was submitted for post-irradiation-examinations (PIE) this time, was irradiated in order to evaluate the limit of failure in control rods and confirm the effect of method for suppression of relocation caused by cracking of boron carbide (B C) pellets. According to this purpose, gap size between B
C) pellets. According to this purpose, gap size between B C pellet and cladding tube (inner capsule tube), enrichment of
C pellet and cladding tube (inner capsule tube), enrichment of  B, thickness of cladding tube and its material were changed in this test. In addition, thin shroud tube wrapping B
B, thickness of cladding tube and its material were changed in this test. In addition, thin shroud tube wrapping B C pellets was used as the method for suppression of relocation. Capsules were loaded in compartments, which had the upper and lower stairs, and irradiation rig AMIR-6 was constructed of seven compartments in total. The irradiation capsule had double tubes, namely inner capsule tube and outer capsule tube. Between these tubes, sodium was filled. AMIR-6 was irradiated at the 6 raw in Joyo Mark-II core up to 106
C pellets was used as the method for suppression of relocation. Capsules were loaded in compartments, which had the upper and lower stairs, and irradiation rig AMIR-6 was constructed of seven compartments in total. The irradiation capsule had double tubes, namely inner capsule tube and outer capsule tube. Between these tubes, sodium was filled. AMIR-6 was irradiated at the 6 raw in Joyo Mark-II core up to 106 10
10 cap/m
cap/m (max. burn-up) and 3.82
(max. burn-up) and 3.82 10
10 n/m
n/m (max, fluence). Irradiation temperatures were evaluated from 530 to 890
(max, fluence). Irradiation temperatures were evaluated from 530 to 890  C in design. Extraordinary results were observed for lower capsules by weight measurement performed. So, detailed visual inspection was carried out for these capsules. Consequently, sodium entered from the crack of screwhead attached to the outer tube in three irradiation capsules, whose weight increased. It was recognized that the sodium level between cladding tube and outer tube was lower in six capsules of lower stairs. Cladding crack was found out in three cladding tubes of lower irradiation capsule. It was suggested that the crack become for decrease of strength of cladding tube because those temperature increased at the position where sodium was not filled. The irradiation capsule using a shroud tube showed no diameter increase and ovality in the cladding.
C in design. Extraordinary results were observed for lower capsules by weight measurement performed. So, detailed visual inspection was carried out for these capsules. Consequently, sodium entered from the crack of screwhead attached to the outer tube in three irradiation capsules, whose weight increased. It was recognized that the sodium level between cladding tube and outer tube was lower in six capsules of lower stairs. Cladding crack was found out in three cladding tubes of lower irradiation capsule. It was suggested that the crack become for decrease of strength of cladding tube because those temperature increased at the position where sodium was not filled. The irradiation capsule using a shroud tube showed no diameter increase and ovality in the cladding.
Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Katsuyama, Chie*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Kato, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Kato, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Donomae, Takako; Osato, Yukihiro*; Onuma, Yasuhiro*; Nukaga, Sadayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Chie*; Nashimoto, Hiroaki*; Ishibashi, Tomotaka*; Furuta, Kazuki*; Nagaosa, Kazuyo*; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Asano, Takahiro; Sasaki, Yoshito; Aoki, Kazuhiro; Suwa, Yuichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Higashiuchi, Atsushi; Maeda, Koji; Otani, Akira; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Chigira, Takayuki*; Murata, Hirotoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Higashiuchi, Atsushi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Otani, Akira; Chigira, Takayuki*; Murata, Hirotoshi*
no journal, ,
In the development of remote decontamination technology of the reactor building, we were carried out a detailed analysis of concrete samples (hereinafter referred to as "core sample") taken from TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereinafter referred to as "1F") Unit 1 reactor building first floor south side floor, etc..
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Harada, Miyu*; Murano, Yuka*; Tomita, Kaori*; Hayashi, Nobuhiro*; Tabata, Makoto*; Kawai, Hideyuki*; Okudaira, Kyoko*; Imai, Eiichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsai, T.-H.; Sasaki, Shinji; Katsuyama, Kozo; Maeda, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Tsuyoshi; Sasaki, Hikaru; Hoshi, Katsuya; Fujita, Hiroki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aratani, Kenta; Matsushima, Akira; Takiya, Hiroaki; Awatani, Yuto; Sasaki, Katsuya*; Maehata, Hidehiko*; Maruyama, Akira*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English