Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sagisaka, Akito*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Kando, Masaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Optics Letters, 37(14), p.2868 - 2870, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:95.36(Optics)Using high contrast (10 :1) and high intensity (10
:1) and high intensity (10 W/cm
W/cm ) laser pulse with the duration of 40 fs from OPCPA/Ti:Sapphire laser, a 40 MeV proton bunch is obtained, which is a record for laser pulse with energy less than 10 J. The efficiency for generation of protons with kinetic energy above 15 MeV is 0.1%.
) laser pulse with the duration of 40 fs from OPCPA/Ti:Sapphire laser, a 40 MeV proton bunch is obtained, which is a record for laser pulse with energy less than 10 J. The efficiency for generation of protons with kinetic energy above 15 MeV is 0.1%.
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(4), p.048003_1 - 048003_2, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.46(Physics, Applied)A proton beam driven by a repetitive high-intensity-laser is utilized to induce a  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be nuclear reaction. The total activity of
Be nuclear reaction. The total activity of  Be are evaluated by two different methods. The activity obtained measuring the decay
Be are evaluated by two different methods. The activity obtained measuring the decay  -rays after 1912 shots at 1 Hz is 1.7
-rays after 1912 shots at 1 Hz is 1.7 0.2 Bq. This is in good agreement with 1.6
0.2 Bq. This is in good agreement with 1.6 0.3 Bq evaluated from the proton energy distribution measured using a time-of-flight detector and the nuclear reaction cross-sections. We conclude that the production of activity can be monitored in real time using the time-of-flight-detector placed inside a diverging proton beam coupled with a high-speed signal processing system.
0.3 Bq evaluated from the proton energy distribution measured using a time-of-flight detector and the nuclear reaction cross-sections. We conclude that the production of activity can be monitored in real time using the time-of-flight-detector placed inside a diverging proton beam coupled with a high-speed signal processing system.
Sugiyama, Akira; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Mori, Michiaki; Tanaka, Momoko; Sasao, Fumitaka; Kosuge, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.15 - 18, 2011/03
Main theme of our group in this middle term JAEA program is a development of high-averaged power short pulse laser system pumped by LDs (laser diodes). To realize this next term laser system, we have just started considering a Yb doped ceramics laser with a several members of KPSI. We have also developed a laser system named QUADRA (high-Quality Ultra ADvanced RAdiation Sources) in C-Phost program. In the first term up to FYH22, essential studies for QUADRA have been investigated. In the second term, QUADRA development will be merged with the next term laser system in JAEA to produce high powered THz radiation. In addition to these developments, we support to improve the performances of conventional high-power laser system, J-KAREN, for the requirement of advanced application studies in this middle term JAEA program.
Yogo, Akifumi; Maeda, Takuya; Hori, Toshihiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sagisaka, Akito; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 98(5), p.053701_1 - 053701_3, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:94.21(Physics, Applied)Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime*; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.669 - 675, 2010/09
This paper reviews the temporal contrast and spatial beam quality improvement techniques in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped-pulse amplification (CPA). We describe a low gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier that uses high energy, clean pulse seeding and is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 10 -10
-10 relative to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. We also report the use of a diffractive optical element for beam homogenization of a 100 J level Nd:glass green pump laser, achieving a flat-topped spatial profile with a filling factor near 80 %.
relative to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. We also report the use of a diffractive optical element for beam homogenization of a 100 J level Nd:glass green pump laser, achieving a flat-topped spatial profile with a filling factor near 80 %.
 ), high-intensity (500 TW) J-KAREN laser system
), high-intensity (500 TW) J-KAREN laser systemKiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2010-002, p.18 - 21, 2010/06
We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30 J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500 TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the final compressed pulse (without pumping the booster amplifier) we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescale, and is near 10
on the sub-nanosecond timescale, and is near 10 on the nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
on the nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanoue, Manabu*; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Wakai, Daisuke*; Sasao, Fumitaka*; Okada, Hajime; et al.
Optics Letters, 35(10), p.1497 - 1499, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:94.79(Optics)OPCPA (Optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification) operation with low gain by seeding with high energy, clean pulses is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 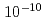 -
-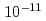 in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77%. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30-Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77%. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30-Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
Applied Optics, 49(11), p.2105 - 2115, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.71(Optics)We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30-J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500-TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the compressed pulse without pumping the final amplifier we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescales, and is near 10
on the sub-nanosecond timescales, and is near 10 on the nanosecond timescale prior to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with a near-perfect top-hat-like intensity distribution.
on the nanosecond timescale prior to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with a near-perfect top-hat-like intensity distribution.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Mori, Michiaki; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Orimo, Satoshi; Tampo, Motonobu; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Shimomura, Takuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sugiyama, Hironori*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ultrashort and high intensity laser can induce high energy protons. Proton beams have a wide range of applications such as in the production of radioisotopes and proton therapy. An energy of the proton beam has a wide distribution. The distribution of activity in depth is calculated while laser induced protons are injected into an iron plate.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30 J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500 TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the final compressed pulse we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
on the sub-nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nagashima, Keisuke; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Mori, Michiaki; Tanaka, Momoko; Sasao, Fumitaka; Kosuge, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Kiminori; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30 J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500 TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the final compressed pulse we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
on the sub-nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kando, Masaki; et al.
no journal, ,
We demonstrated the energetic proton generation using 40 fsec intense Ti:Sapphire laser pulses. By drastically increasing the interaction intensity approximately 1E21 W/cm with keeping a ultra high contrast of 1E10:1, even without using plasma mirror, over 40 MeV protons were detected with 800 nm thick Al foil.
with keeping a ultra high contrast of 1E10:1, even without using plasma mirror, over 40 MeV protons were detected with 800 nm thick Al foil.
Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Sagisaka, Akito; Kando, Masaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
no journal, ,
Without plasma mirror, the maximum proton energy of 40 MeV is obtained using a compact, high spatiotemporal-quality, high-intensity Ti:sapphire laser system with an intensity of 1E21 W/cm/cm for the first time to our knowledge.
Yogo, Akifumi; Sato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Maeda, Takuya; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Mori, Michiaki; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime*; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
no journal, ,
OPCPA (Optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification) operation with low gain by seeding with high energy, clean pulses is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 10 -10
-10 in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77 %. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30 Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77 %. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30 Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; et al.
no journal, ,
We present the results of the experiment of laser-driven proton acceleration by the interaction between laser and thin foil target. The maximum energy of the laser-driven protons increases as the intensity of the laser increases. In order to accelerate the proton beam toward higher energy with the limited energy of laser, we need to increase the intensity of the laser. For that purpose, we upgraded the laser mirrors in the beam line. As a result the intensity of the laser increases about one oreder of magnitude. With the tape target, we obtain proton beam whose maximum energy is 23 MeV. We also conducted the plasma mirror to increase the contrast of the laser. We show the detail of the proton acceleration results with the plasma mirror and nano-meter target.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime*; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Daito, Izuru; Sasao, Fumitaka; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30 J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500 TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the final compressed pulse we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
on the sub-nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
Ogura, Koichi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Kando, Masaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sagisaka, Akito; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Tampo, Motonobu; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; et al.
no journal, ,
High-intensity laser and mater interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. We have performed the experiment of proton generation from a thin-foil target for developing the laser-driven ion source. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror on the thin-foil target. The pulse duration of laser is  40 fs (FWHM). The estimated peak intensity is
40 fs (FWHM). The estimated peak intensity is  5
5 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . We observed the protons at the rear side of the target with a TOF(Time of Flight) proton spectrometer. The maximum energy of proton is
. We observed the protons at the rear side of the target with a TOF(Time of Flight) proton spectrometer. The maximum energy of proton is  7 MeV with a 2.5
7 MeV with a 2.5  m thick stainless-steel target.
m thick stainless-steel target.