Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Tsuchiya, Yuji*; Mohan, S.*; Taniguchi, Tomotaka*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*; Kitamura, Hisashi*; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 25(8), p.084008_1 - 084008_14, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:85 Percentile:93.2(Physics, Applied)Various kinds of energetic particles are irradiated into iron-based superconductors, and their effects on the critical current density 
 and vortex dynamics have been systematically studied. It is found that
and vortex dynamics have been systematically studied. It is found that 
 is enhanced and vortex dynamics is strongly suppressed by energetic particles having a sufficient energy deposition rate, similar to the case of high temperature cuprate superconductors. The enhancement of
is enhanced and vortex dynamics is strongly suppressed by energetic particles having a sufficient energy deposition rate, similar to the case of high temperature cuprate superconductors. The enhancement of 
 , in general, persists up to much higher irradiation doses than in cuprates. However, details of the effect of irradiation depend on the kind of ion species and their energies. Even with the same ions and energies, the effect is not universal for different kinds of iron-based superconductors. The correlated nature of defects created by heavy-ion irradiation is confirmed by the angular dependence of irreversible magnetization.
, in general, persists up to much higher irradiation doses than in cuprates. However, details of the effect of irradiation depend on the kind of ion species and their energies. Even with the same ions and energies, the effect is not universal for different kinds of iron-based superconductors. The correlated nature of defects created by heavy-ion irradiation is confirmed by the angular dependence of irreversible magnetization.
 /Si by ion implantation
/Si by ion implantationTakahiro, Katsumi*; Ninakuchi, Yuki*; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Isshiki, Toshiyuki*; Nishio, Koji*; Sasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nishiyama, Fumitaka*
Applied Surface Science, 258(19), p.7322 - 7326, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.02(Chemistry, Physical)A nanometer-sized metallic particle embedded in a transparent dielectric exhibits a nonlinear susceptibility, and going to be applied to nonlinear optical devices. In the present study, well-ordered arrangements of Ag nanoparticles have been found for Ag-implanted SiO . Thermally grown SiO
. Thermally grown SiO on Si were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to fluences of 0.37-1.2
on Si were implanted with 350 keV-Ag ions to fluences of 0.37-1.2  10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveal the presence of a two-dimensional array of Ag nanoparticles of 25-40 nm in diameter located at a depth of
. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveal the presence of a two-dimensional array of Ag nanoparticles of 25-40 nm in diameter located at a depth of  130 nm, together with the self-organization of tiny Ag nanoparticles aligned along the SiO
130 nm, together with the self-organization of tiny Ag nanoparticles aligned along the SiO /Si interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirm the stability of these Ag nanoparticles embedded in the SiO
/Si interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction confirm the stability of these Ag nanoparticles embedded in the SiO /Si is found to be stable against oxidation and sulfidation when stored in ambient conditions for more than one and a half year.
/Si is found to be stable against oxidation and sulfidation when stored in ambient conditions for more than one and a half year.
Yamaguchi, Kenji; Esaka, Fumitaka; Sasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Hojo, Kiichi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 37(2), p.245 - 250, 2012/06
"Semiconducting silicides", such as  -FeSi
-FeSi , BaSi
, BaSi , Mg
, Mg Si, etc. are composed of elements which are non or less toxic and are naturally abundant, so that they are considered to be ecologically friendly. These materials are being investigated for applications in optoelectronics, photovoltaics, photonics, thermoelectrics, and so on. In order to fabricate silicide films on crystalline Si substrate, sputter-etching (SE) of the substrate with low energy ion beams has been successfully applied. When the conditions are met, a highly-oriented
Si, etc. are composed of elements which are non or less toxic and are naturally abundant, so that they are considered to be ecologically friendly. These materials are being investigated for applications in optoelectronics, photovoltaics, photonics, thermoelectrics, and so on. In order to fabricate silicide films on crystalline Si substrate, sputter-etching (SE) of the substrate with low energy ion beams has been successfully applied. When the conditions are met, a highly-oriented  -FeSi
-FeSi (100) film can be grown on Si (100) substrate by means of ion beam sputter deposition method. According to cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation, the interface of the SE-treated substrate and the film deposited at 973 K is smooth, although some defects are produced as a result of this treatment. On the other hand, a combination of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) revealed that relatively homogeneous
(100) film can be grown on Si (100) substrate by means of ion beam sputter deposition method. According to cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation, the interface of the SE-treated substrate and the film deposited at 973 K is smooth, although some defects are produced as a result of this treatment. On the other hand, a combination of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) revealed that relatively homogeneous  -FeSi
-FeSi surface is formed at this temperature. In order to further improve the film properties with smaller amount of defects, SE-treatment is performed with the ions whose incident energy is below 1 keV. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed that highly-oriented
surface is formed at this temperature. In order to further improve the film properties with smaller amount of defects, SE-treatment is performed with the ions whose incident energy is below 1 keV. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed that highly-oriented  -FeSi
-FeSi (100) film can be also obtained with SE-treatment by 0.8 keV Ne
(100) film can be also obtained with SE-treatment by 0.8 keV Ne ions, as in the case of 3.0 keV Ne
ions, as in the case of 3.0 keV Ne .
.
Sasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Okayasu, Satoru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 272, p.318 - 321, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Radiation effects for film formation and nanostructural changes of iron disilicide thin film have been discussed.
 -FeSi
-FeSi /Si(100) interface using ion irradiated substrate
/Si(100) interface using ion irradiated substrateSasase, Masato*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Hiroki*
Thin Solid Films, 520(9), p.3490 - 3492, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Thin uniform  -FeSi
-FeSi films were fabricated on ion irradiated Si(100) substrates to achieve an atomically flat interface. Ion irradiation produces a surface with more defects than chemical etching, however, it is expected that the presence of defects can promote the formation of compound films such as
films were fabricated on ion irradiated Si(100) substrates to achieve an atomically flat interface. Ion irradiation produces a surface with more defects than chemical etching, however, it is expected that the presence of defects can promote the formation of compound films such as  -FeSi
-FeSi that require interdiffusion and reaction processes. However, excess defects can also result in random nucleation, poor crystallinity and a rough interface. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy was used to determine the optimum conditions for ion irradiation of the substrate to obtain a clear
that require interdiffusion and reaction processes. However, excess defects can also result in random nucleation, poor crystallinity and a rough interface. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy was used to determine the optimum conditions for ion irradiation of the substrate to obtain a clear  -FeSi
-FeSi /Si interface.
/Si interface.
Shigeta, Tatsuo*; Sasase, Masato*; Endo, Nobuyuki*; Nagatomo, Jinro*
Heisei-22-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Nempo, 13, P. 73, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*; Kitamura, Hisashi*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Kambara, Tadashi*; Kanai, Yasuyuki*
Physica C, 471, p.777 - 780, 2011/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.25(Physics, Applied)Magnetic relaxations in Ba(Fe Co
Co )
) As
As before and after swift particle irradiations are measured. The normalized relaxation rate S shows a clear suppression in a pristine sample at low fields below the self-field. Heavy-ion irradiations suppress these anomalies considerably, although there still remain weak features depending on ion species and/or energies. In a proton irradiated sample, the low-field anomaly of S survives although it is smeared compared with that in a pristine sample. All these results indicate that the low-field anomaly of S is suppressed by defects, and correlated defects have stronger effects.
before and after swift particle irradiations are measured. The normalized relaxation rate S shows a clear suppression in a pristine sample at low fields below the self-field. Heavy-ion irradiations suppress these anomalies considerably, although there still remain weak features depending on ion species and/or energies. In a proton irradiated sample, the low-field anomaly of S survives although it is smeared compared with that in a pristine sample. All these results indicate that the low-field anomaly of S is suppressed by defects, and correlated defects have stronger effects.
 Co
Co )
) As
As
Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Tsuchiya, Yuji*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*
Physica C, 470(Suppl.1), p.S360 - S362, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.48(Physics, Applied)We report effects of heavy-ion irradiation in Ba(Fe Co
Co )
) As
As single crystals. The columnar defects with about 40% of the irradiation dose are confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. Magneto-optical imaging and bulk magnetization measurements reveal strong enhancement of the critical current density in the irradiated region. The vortex creep rate is also strongly suppressed by the columnar defects. Effects of heavy-ion irradiation into Ba(Fe
single crystals. The columnar defects with about 40% of the irradiation dose are confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. Magneto-optical imaging and bulk magnetization measurements reveal strong enhancement of the critical current density in the irradiated region. The vortex creep rate is also strongly suppressed by the columnar defects. Effects of heavy-ion irradiation into Ba(Fe Co
Co )
) As
As and cuprate superconductors are compared.
and cuprate superconductors are compared.
 As
As with columnar defects introduced by heavy-Ion irradiation
with columnar defects introduced by heavy-Ion irradiationNakajima, Yasuyuki*; Tsuchiya, Yuji*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*; Kitamura, Hisashi*; Murakami, Takeshi*
Physica C, 470(20), p.1103 - 1105, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Applied)We report the formation of columnar defects in Co-doped BaFe As
As single crystals with different heavy ion irradiations. The formation of columnar defects by 200 MeV Au ion irradiation is confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and their density is about 40% of the irradiation dose. Magneto-optical imaging and bulk magnetization measurements reveal that the critical current density
single crystals with different heavy ion irradiations. The formation of columnar defects by 200 MeV Au ion irradiation is confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and their density is about 40% of the irradiation dose. Magneto-optical imaging and bulk magnetization measurements reveal that the critical current density 
 is enhanced in the 200 MeV Au and 800 MeV Xe ion irradiated samples while
is enhanced in the 200 MeV Au and 800 MeV Xe ion irradiated samples while 
 is unchanged in the 200 MeV Ni ion irradiated sample. We also find that vortex creep rates are strongly suppressed by the columnar defects. We compare the effect of heavy-ion irradiation into Co-doped BaFe
is unchanged in the 200 MeV Ni ion irradiated sample. We also find that vortex creep rates are strongly suppressed by the columnar defects. We compare the effect of heavy-ion irradiation into Co-doped BaFe As
As and cuprate superconductors.
and cuprate superconductors.
Sasase, Masato*
Heisei-21-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Nempo, 12, P. 52, 2010/10
no abstracts in English
Shigeta, Tatsuo*; Amada, Kenichi*; Sasase, Masato*; Endo, Nobuyuki*; Nagatomo, Jinro*
Heisei-21-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Nempo, 12, P. 78, 2010/10
no abstracts in English
 Co
Co )
) As
As single crystals
single crystalsTamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Tsuchiya, Yuji*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 23(5), p.605 - 608, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Superconducting properties are evaluated for high-quality single crystals of Ba(Fe Co
Co )
) As
As in a wide range of doping levels. The critical current density,
in a wide range of doping levels. The critical current density, 
 , in an optimally-doped crystal (Tc
, in an optimally-doped crystal (Tc  24 K) shows a fishtail effect with its value over 10
24 K) shows a fishtail effect with its value over 10 A/cm
A/cm even at 5 T below 10 K. Magneto-optical imaging has clarified rather homogeneous supercurrent flow in the crystal, in spite of a large amount of impurities. In the heavy-ion irradiated sample, the presence of columnar defects are confirmed and
even at 5 T below 10 K. Magneto-optical imaging has clarified rather homogeneous supercurrent flow in the crystal, in spite of a large amount of impurities. In the heavy-ion irradiated sample, the presence of columnar defects are confirmed and 
 has been enhanced by a factor of five at low temperatures, reaching 6
has been enhanced by a factor of five at low temperatures, reaching 6  10
10 A/cm
A/cm at 2 K under zero field. Flux creep rate in the heavy-ion irradiated sample has been reduced in accordance with the enhancement of
at 2 K under zero field. Flux creep rate in the heavy-ion irradiated sample has been reduced in accordance with the enhancement of 
 .
.
 -FeSi
-FeSi thin films fabricated by ion beam sputter deposition
thin films fabricated by ion beam sputter depositionEsaka, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Yamada, Yoichi*; Sasase, Masato*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Shamoto, Shinichi; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi
Applied Surface Science, 256(10), p.3155 - 3159, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:56.9(Chemistry, Physical)A combination of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) using synchrotron radiation is applied to clarify surface chemical states of  -FeSi
-FeSi films fabricated by an ion-beam sputtering deposition method. The differences in the chemical states of the films fabricated at substrate temperatures of 873, 973 and 1173 K are investigated.
films fabricated by an ion-beam sputtering deposition method. The differences in the chemical states of the films fabricated at substrate temperatures of 873, 973 and 1173 K are investigated.
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Esaka, Fumitaka; Matsue, Hideaki; Sasase, Masato*
Bunseki, 2009(11), p.612 - 618, 2009/11
Present status and future prospects are discssed on the analysis of profiling by quantum beams.
Sasase, Masato*
Heisei-20-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Kenkyu Seika Hokokushu, 11, p.75 - 77, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Shigeta, Tatsuo*; Amada, Kenichi*; Sasase, Masato*; Endo, Nobuyuki*; Nagatomo, Jinro*
Heisei-20-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Kenkyu Seika Hokokushu, 11, P. 87, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Suzuki, Hiroshi*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamada, Yoichi; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Sasase, Masato*; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(6), p.292 - 295, 2009/07
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Esaka, Fumitaka; Sasase, Masato*
Proceedings of Asia Steel International Conference 2009 (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2009/05
Initial surface oxidation of stainless steels was investigated by energy-tunable synchrotron radiation excited X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS). Depth profiling with a few nm range using excitation energies between 1800 and 3700 eV was performed for the steels before and after oxidation at 373, 473, 673, 873 and 1073 K. The result for the steel oxidized at 473 K indicated that the formation of Fe oxides on the surface is dominant in the initial stage of oxidation. By further oxidation above 873 K, significant increases in the ratios of Cr oxides to Fe oxides were observed, suggesting the formation of Cr oxide layers more than a few nm on the steels. These results imply that SR-XPS is a powerful tool for non-destructive depth profiling with nm depth.
Nagata, Shinji*; Sasase, Masato*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; Inoue, Aichi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Shikama, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 267(8-9), p.1514 - 1517, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)In this study, effects of the ion implantation on the phase transformation and nano-crystalline formation were examined in Zr-based metallic glasses. Samples were 2 mm thick plates and thin films of Zr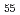 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu prepared by casting in a copper mold and by using RF magnetron sputtering, respectively. Ions of Mg, P, Au and Bi with 100-500 keV were implanted in the samples up to 2
prepared by casting in a copper mold and by using RF magnetron sputtering, respectively. Ions of Mg, P, Au and Bi with 100-500 keV were implanted in the samples up to 2  10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm at room temperature. Nano-crystalline structure was found in implanted samples by TEM observation, while the long-range order in the structure was not found for the X-ray diffraction patterns. The electron diffraction patterns indicated the formation of fcc-Zr
at room temperature. Nano-crystalline structure was found in implanted samples by TEM observation, while the long-range order in the structure was not found for the X-ray diffraction patterns. The electron diffraction patterns indicated the formation of fcc-Zr Cu in the P, Au, and Bi implanted region. Changes of the binding energy of the core level electron and valence band structure suggested the formation of Au-Zr or Au-Cu alloys in the Au ion implanted region.
Cu in the P, Au, and Bi implanted region. Changes of the binding energy of the core level electron and valence band structure suggested the formation of Au-Zr or Au-Cu alloys in the Au ion implanted region.
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Yamada, Yoichi; Sasase, Masato*; Esaka, Fumitaka
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 100, p.012044_1 - 012044_4, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:88.21(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Non-destructive depth profile analysis with better depth resolution is required for the characterization of nano-materials. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is the typically non-destructive analysis, however, XPS with fixed excitation energy source cannot provide depth profile without additional technique. On the other hand, analyzing depth of XPS can be varied with the energy tunable excitation source, such as the synchrotron-radiation (SR), since the escape depth of the photoelectrons depends on their kinetic energy. In the present study, Ge thin films (2,4 nm) on two different Si substrates (hydrogen terminated, native oxide) has been analyzed to obtain depth profile of the thin film and buried interface of Ge/Si under the film with two different Si substrates. The XPS spectra clearly show the difference obtained from the varied analyzing depth. These results suggest that the SR-XPS can be applicable for non-destructive depth profile analysis of surface and buried interface.