Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsuoka, Seikichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Satake, Shinsuke*
Physics of Plasmas, 25(2), p.022510_1 - 022510_10, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:71.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Global full-f gyrokinetic simulations, in which the gyrokinetic equation is solved based on the first principle without the scale separation with respect to the plasma distribution function, is attracting much attention in the plasma transport simulation studies. In this work, in order to apply a global full-f gyrokinetic simulation code GT5D to stellarator plasmas with complicated three-dimensional magnetic field configurations, we extend finite difference scheme of GT5D and develop a new interface code which incorporates the three-dimensional magnetic equilibria provided by a standard equilibrium code, VMEC. A series of benchmark calculations are carried out for the numerical verification of GT5D. It is successfully demonstrated that GT5D well reproduces results of a theoretical analysis and another global neoclassical transport code.
Kanno, Ryutaro*; Nunami, Masanori*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Matsuoka, Seikichi; Takamaru, Hisanori*
Nuclear Fusion, 58(1), p.016033_1 - 016033_7, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The electron heat transport in a torus plasma which involves a radially-bounded ergodic region, where flux surfaces are partially destroyed by perturbative magnetic fields, is studied. In this paper, we have demonstrated that the radial heat conduction by the particles' parallel motion is reduced by trapped particles.
Matsuoka, Seikichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Satake, Shinsuke*
Physics of Plasmas, 24(10), p.102522_1 - 102522_9, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.84(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In axisymmetric tokamak plasmas, effects of three-dimensional non-axisymmetric magnetic field perturbations caused by error fields etc. have attracted much attention from the view point of the control of the plasma performance and instabilities. Recent studies pointed out that there exists qualitative discrepancy in predicting the collisional viscosity driven by the perturbation between a theoretical bounce-averaged model and a global kinetic simulation. Clarifying the cause of the discrepancy by understanding the underlying mechanism is a key issue to establish a reliable basis for the NTV predictions. In this work, we perform two different kinds of global kinetic simulations for the NTV. As a result, it is first demonstrated that the discrepancy arises owing to the following two mechanisms related to the global particle orbit; (1) the effective magnitude of the perturbation becomes weak due to the loss of the resonant orbit, and (2) the phase mixing along the orbit arises and generates fine scale structures, resulting the damping of the NTV.
Huang, B.*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Sugama, Hideo*; Matsuoka, Seikichi
Physics of Plasmas, 24(2), p.022503_1 - 022503_19, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:48.09(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The drift kinetic equation describes the collisional (neoclassical) transport in plasmas. Recently, a novel radially-local approximation of the drift kinetic equation, which is called the zero orbit width (ZOW) model, is proposed. In this work, as a numerical verification of the neoclassical transport based on the ZOW model, we perform a series of benchmarks of the neoclassical transport and the parallel flow in three helical magnetic configurations using various types of radially-local approximation models including the ZOW model. We found that the neoclassical transport of the ZOW model can reproduce that based on the other models when the radial electric field and thus the 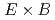 drift is large. Also, it is demonstrated that an unphysical large radial transport, which arises in the neoclassical transport of the other models when the
drift is large. Also, it is demonstrated that an unphysical large radial transport, which arises in the neoclassical transport of the other models when the 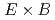 drift is small and compared to the magnetic drift, can be mitigated in the ZOW model.
drift is small and compared to the magnetic drift, can be mitigated in the ZOW model.
Kanno, Ryutaro*; Nunami, Masanori*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Matsuoka, Seikichi; Takamaru, Hisanori*
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 56(6-8), p.592 - 597, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A drift-kinetic 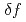 simulation code is developed for estimating collisional transport in quasi-steady state of toroidal plasma affected by resonant magnetic perturbations and radial electric field. In this paper, validity of the code is confirmed through several test calculations. It is found that radial electron flux is reduced by positive radial-electric field, although radial diffusion of electron is strongly affected by chaotic field-lines under an assumption of zero electric field.
simulation code is developed for estimating collisional transport in quasi-steady state of toroidal plasma affected by resonant magnetic perturbations and radial electric field. In this paper, validity of the code is confirmed through several test calculations. It is found that radial electron flux is reduced by positive radial-electric field, although radial diffusion of electron is strongly affected by chaotic field-lines under an assumption of zero electric field.
Sugama, Hideo*; Matsuoka, Seikichi; Satake, Shinsuke*; Kanno, Ryutaro*
Physics of Plasmas, 23(4), p.042502_1 - 042502_11, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:33.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A novel radially local approximation of the drift kinetic equation is presented. The new drift kinetic equation that includes both 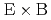 and tangential magnetic drift terms is written in the conservative form and it has favorable properties for numerical simulation that any additional terms for particle and energy sources are unnecessary for obtaining stationary solutions under the radially local approximation. These solutions satisfy the intrinsic ambipolarity condition for neoclassical particle fluxes in the presence of quasisymmetry of the magnetic field strength. Also, another radially local drift kinetic equation is presented, from which the positive definiteness of entropy production due to neoclassical transport and Onsager symmetry of neoclassical transport coefficients are derived while it sacrifices the ambipolarity condition for neoclassical particle fluxes in axisymmetric and quasi-symmetric systems.
and tangential magnetic drift terms is written in the conservative form and it has favorable properties for numerical simulation that any additional terms for particle and energy sources are unnecessary for obtaining stationary solutions under the radially local approximation. These solutions satisfy the intrinsic ambipolarity condition for neoclassical particle fluxes in the presence of quasisymmetry of the magnetic field strength. Also, another radially local drift kinetic equation is presented, from which the positive definiteness of entropy production due to neoclassical transport and Onsager symmetry of neoclassical transport coefficients are derived while it sacrifices the ambipolarity condition for neoclassical particle fluxes in axisymmetric and quasi-symmetric systems.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(7), p.073033_1 - 073033_11, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Matsuoka, Seikichi*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and the Monte Carlo Method (M&C + SNA + MC 2015) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2015/04
The quality and performance of a parallel pseudo-random number generator (PRNG), KMATH_RANDOM, are investigated using a Monte Carlo particle simulation code for the plasma transport. The library is based on Mersenne Twister with jump routines and provides a numerical tool which is suitable and easy-to-use on massively parallel supercomputers such as K-computer. The library enables the particle code to increase the parallelization up to several thousand processes without loosing the quality and performance of the PRNG. As a result, the particle code can use large amounts of random numbers, which results in removing unphysical phenomena caused by a numerical noise.
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Matsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Nuclear Fusion, 54(11), p.114005_1 - 114005_14, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:58.21(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Matsunaga, Go; Ide, Shunsuke; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 37D, p.P1.182_1 - P1.182_4, 2013/07


 flows in helical plasmas
flows in helical plasmasWatanabe, Tomohiko*; Nunami, Masanori*; Sugama, Hideo*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Matsuoka, Seikichi*; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Maeyama, Shinya; Tanaka, Kenji*
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/10
Satake, Shinsuke*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sugama, Hideo*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
Computer Physics Communications, 181(6), p.1069 - 1076, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:82.90(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Two simulation codes that solve the drift-kinetic or gyrokinetic equation in toroidal plasmas are benchmarked by comparing the simulation results of neoclassical transport. In a tokamak configuration, neoclassical radial heat flux and the force balance relation, which relates the parallel mean flow with radial electric field and temperature gradient, are compared between these two codes, and their results are also compared with the local neoclassical transport theory. It is found that the simulation results of the two codes coincide very well in a wide rage of plasma collisionality parameter 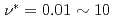 and also agree with the theoretical estimations. The time evolution of radial electric field and particle flux, and the radial profile of the geodesic acoustic mode frequency also coincide very well.
and also agree with the theoretical estimations. The time evolution of radial electric field and particle flux, and the radial profile of the geodesic acoustic mode frequency also coincide very well.
Isayama, Akihiko; Iwama, Naofumi*; Hosoda, Yosuke*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Isei, Nobuaki; Ishida, Shinichi; Sato, Masayasu
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2, 42(3), p.L329 - L331, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.50(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
no journal, ,
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Matsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
no journal, ,
Matsuoka, Seikichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Satake, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
Effects of non-axisymmetric magnetic field perturbations have attracted much attention from the view point of the control of the plasma performance and instabilities. The perturbations cause the neoclassical toroidal viscosity (NTV) due to the non-ambipolar particle transport. Recent studies pointed out that the qualitative discrepancy of the NTV prediction exist between a theoretical bounce-averaged model and a global kinetic simulation. It is crucial to clarify the cause of the discrepancy to establish a reliable basis for the NTV predictions. In this work, we perform two types of global kinetic simulations for the NTV to investigate the discrepancy from the theoretical model. As a result, it is first demonstrated that the discrepancy arises due to the following two mechanisms; the absence of the magnetic field shear effect in the bounce-averaged model and the so-called transient particle orbit caused by the non-axisymmetric perturbations.
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Matsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Urano, Hajime; Ide, Shunsuke; Hayashi, Nobuhiko
no journal, ,
Matsuoka, Seikichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Satake, Shinsuke*
no journal, ,
When non-axisymmetric magnetic perturbations are imposed in axisymmetric tokamaks, broken axisymmetry induces the neoclassical viscosity, and affects momentum transport and resulting plasma rotation profiles. In this work, we estimate the neoclassical toroidal viscosity using full-f gyrokinetic simulations, and verify calculation methods and obtained results. We discuss the parameter dependency of the neoclassical toroidal viscosity in the presence of small resonant magnetic perturbations, based on comparisons against analytic theories and neoclassical transport codes.