Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Noriaki; Hoshi, Hiroyuki*; Haji, Toshiki*; Sato, Katsushi*; Niki, Sota*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi (Internet), 131(1), p.59 - 70, 2025/04
To constrain the upper limit of the depositional age of the Tanabe Group, Early-Middle Miocene forearc basin deposit, this study obtained the detrital zircon U-Pb ages separated from eight sedimentary rock samples. We obtained 221 concordant ages from 330 zircon grains. The youngest grain age was 19.4 Ma, suggesting the upper limit of the depositional age is younger than 19.4 Ma, and no grain showed the depositional age indicated by foraminifera (16.3-15.1 Ma). Large-scale volcanic activities occurred in the Middle Miocene around Kii Peninsula, mainly after 15 Ma. The lack of grain younger than 15 Ma suggests that the Tanabe Group was deposited before 15 Ma. Sluggish volcanic activities in the provenance areas before 15 Ma may have caused the lack of zircons having ages close to the depositional period inferred from foraminifera.
Inoue, Rintaro*; Nagata, Yuya*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Sato, Sota*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Yamawaki, Tomonori*; Morishima, Ken*; Suginome, Michinori*; Sugiyama, Masaaki*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 161(5), p.054905_1 - 054905_8, 2024/08
 -Mo
-Mo O
O revealed by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculation
revealed by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculationSumida, Kazuki; Higaki, Sota*; Sato, Hitoshi*; Tsuru, Daichi*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Okuda, Taichi*; Kuroiwa, Yoshihiro*; Moriyoshi, Chikako*; Takase, Koichi*; Oguchi, Tamio*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(8), p.084706_1 - 084706_6, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:95.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Terasawa, Yukana*; Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Sota*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Asahi, Toru*
Acta Crystallographica Section E; Crystallographic Communications (Internet), 78(3), p.306 - 312, 2022/03
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t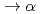 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Torii, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; Kanda, Sotaro*; Kawagoe, Kiyotomo*; Kawall, D.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kurosawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:82.41(Optics)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:167 Percentile:99.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
 edge
edgeIshii, Kenji*; Toyama, Takami*; Asano, Shun*; Sato, Kentaro*; Fujita, Masaki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Tsutsui, Kenji*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Miyawaki, Jun*; Niwa, Hideharu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 96(11), p.115148_1 - 115148_8, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:76.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Li
LiIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Jung, H. S.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 376, p.379 - 381, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:54.42(Instruments & Instrumentation) Li tracer
Li tracerIshiyama, Hironobu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oyaizu, Mitsuhiro*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Osa, Akihiko; Otokawa, Yoshinori; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 53(11), p.110303_1 - 110303_4, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:20.68(Physics, Applied)Ando, Masanori; Watanabe, Sota*; Kikuchi, Koichi*; Otani, Tomomi*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Asayama, Tai
Proceedings of the ASME 2013 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2013/07
New 2012 edition of JSME code for design and construction of fast reactors (FRs code) was published by Japan society of mechanical engineers (JSME). Main topic of the current JSME FRs code 2012 edition is registration of the two new materials, 316FR and Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. The design margins for the new materials to the rules for the components and piping serviced at elevated temperature described in the JSME FRs code were assessed. To confirm the design margins, a series of the assessment program for the new materials to the conventional design rules was performed using the evaluation of the experimental data and finite element analysis. Through these assessments, the enough design margins for new materials to the rules were confirmed.
Hosotani, Risa; Sato, Naomitsu*; Shimizu, Takehiko; KOBAYASHI, Hideo
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (25), p.25 - 32, 2004/00
To observe the airborne gamma radiation dose rate, monitoring posts are set up to a border of supervised area of JNC-OEC. Measurement values of some ionization chambers set at monitoring posts were increased by unknown origin signal at random times. To probe the cause, measurement of electric field intensity at the ionization chamber and immunity test at anechoic chamber are carry out. Result of examination made clear that measurement values are increased by specific frequency band electromagnetic wave. They were also clearly that ferrite cores and shield tube are effective as eliminate of an electromagnetic wave noise. When ferrite cores are attached to cables of ionization chambers, unknown increase of measurement value doesn't occur.
Ikemoto, Megumi*; Somekawa, Jun*; Neki, Arata*; Konishi, Ren*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To measure the kinetic energy of a recycling muon, we discussed how to reduce the background radiation and the trajectory of the transported recycling muons by simulation code.
Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To detect a recycling muon emitted after muon catalyzed fusion reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons from the target to a detector in a low background area. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using SIMONS and PHITS codes and designed an experimental system.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes, such as
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes, such as 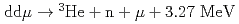 or
or 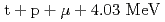 . In this work, we have investigated the shape and characteristic of solid hydrogen isotope target.
. In this work, we have investigated the shape and characteristic of solid hydrogen isotope target.
Konishi, Ren*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sasaki, Kyosuke*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
When muons are injected into a deuterium thin film target, muon molecules are formed. The muons released after intramolecular fusion (recycling muons) are important for the development of slow muon beams. In this study, corresponding to an experiment in which recycling muons are transported using a coaxial transport tube, the energy distribution of scattered muons, muons after deceleration, and background radiation due to bremsstrahlung by decay electrons and neutrons are analyzed by numerical simulations.
Sugiyama, Koichi*; Go, Shintaro*; Tomimatsu, Taro*; Kai, Tamito*; Nagae, Daisuke*; Ishibashi, Yuichi*; Matsunaga, Sotaro*; Nagata, Yuto*; Nishibata, Hiroki*; Washiyama, Kohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have successfully performed in-beam gamma-ray spectroscopy using the isomer-scope technique to study excited-state structure of neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei. The neutron-rich heavy-actinide nuclei were produced in the multinucleon-transfer reactions with a  Cm target and
Cm target and  O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E-
O projectiles accelerated with the JAEA tandem accelerator. Projectile-like scattered particles were detected with Si E- E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.
E telescopes placed at the backward angle, and target-like scattered particles of isomers were caught by an annular aluminum plate placed at about 60-mm downstream from the target. Four Ge detectors and 4 LaBr detectors were placed at the periphery of the aluminum plate, and detected gamma rays from the isomers. Gamma rays emitted from the actinide isomers were successfully observed with a good sensitivity owing to the tungsten shield placed between the target and the detectors.