Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2024-014, 54 Pages, 2025/02
XAFS measurements in the soft X-ray region are suitable for evaluating the chemical state of the surface layer of a measurement sample because the X-ray transmittance is low. In this study, the purpose of the study was to confirm the difference between the coagulated surface layer and the inside of the simulated waste glasses by measuring the K-edge of the glass constituent elements boron, oxygen, sodium, and silicon, and the L edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp
edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp structures (BO
structures (BO ) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L
) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L -edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
-edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
Takayama, Yusuke; Sato, Daisuke*; Sugita, Yutaka
Kansai Geo-Symposium 2024; Chikasui Jiban Kankyo, Bosai, Keisoku Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shinpojiumu Rombunshu, p.115 - 119, 2024/11
During the initial phases after closure of a high-level radioactive waste repository, the temperature of the buffer material will increase. Therefore, fundamental properties regarding the temperature dependence of bentonite, which is the main material of the buffer material, have been tested. The number of tests for the temperature dependence of displacement behavior is less than the number of tests for the temperature dependence of swelling pressure and permeability. In this paper, two tests were conducted using a consolidation test device that can control temperature conditions. One is a cyclic loading and unloading test under temperature conditions from room temperature to 80  C. The second is a temperature rise and fall test from room temperature to 80
C. The second is a temperature rise and fall test from room temperature to 80  C under stable loading condition. It was clarified that large deformations occur in the specimen under high temperature conditions, that the deformation associated with temperature changes is affected by the past stress path, and that irreversible deformation occurs under normal consolidation conditions.
C under stable loading condition. It was clarified that large deformations occur in the specimen under high temperature conditions, that the deformation associated with temperature changes is affected by the past stress path, and that irreversible deformation occurs under normal consolidation conditions.
Katsuoka, Nanako; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Sato, Nobuaki*
2023-Nendo "Busshitsu, Debaisu Ryoiki Kyodo Kenkyu Kyoten" Kenkyu Seika, Katsudo Hokokusho (Internet), 1 Pages, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Mikami, Satoshi; Tokiyoshi, Masanori*; Sato, Rina*; Tanaka, Daisuke*; Yoshimura, Kazuya
Nihon Hoshasen Anzen Kanri Gakkai-Shi, 23(1), p.10 - 17, 2024/06
Taisei Corporation and Infocube LAFLA Co., Ltd. have developed the smartphone-wirelessly-connected dosemeters, aiming to apply it to real-time exposure management of multiple decontamination workers. In order to grasp the basic characteristics of the developed dosemeters, they were calibrated and tested their characteristics such as energy dependency, angle of incidence dependency, etc. at photon calibration fields in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The results showed generally good characteristics in each test. We evaluated that the dosemeters can be effectively used for decontamination work.
 F
FKatsumata, Tetsuhiro*; Suzuki, Ryo*; Sato, Naoto*; Oda, Ryoya*; Motoyama, Shingo*; Suzuki, Shumpei*; Nakashima, Mamoru*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*; Mori, Daisuke*; Aimi, Akihisa*; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 36(8), p.3697 - 3704, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)A perovskite-type oxynitride BaFeO F was prepared by high-pressure synthesis. Since the SHG signal was observed in the obtained material, suggesting the existence of spontaneous polarization, the mechanism of polarization was investigated by synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction. The obtained pair distribution functions were fitted, and a local polarization mechanism with different orientations was found. Since BaFeO
F was prepared by high-pressure synthesis. Since the SHG signal was observed in the obtained material, suggesting the existence of spontaneous polarization, the mechanism of polarization was investigated by synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction. The obtained pair distribution functions were fitted, and a local polarization mechanism with different orientations was found. Since BaFeO F is also a magnetic material, a magnetic domain and a ferroelectric domain are considered to coexist.
F is also a magnetic material, a magnetic domain and a ferroelectric domain are considered to coexist.
Tonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 589, p.154862_1 - 154862_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dissolution behavior of FeUO compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO
compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U
with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO
as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO
compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U
dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U O
O ).
).
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2023-004, 45 Pages, 2023/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. To understand the chemical stability of simulated waste glasses, XANES spectra of B K-edge, Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO
-edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO ) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO
) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO ) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L
) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na
-edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
Sato, Hisashi*; Takayama, Yusuke; Suzuki, Hideaki*; Sato, Daisuke*
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-010, 47 Pages, 2023/09
When a high-level radioactive waste repository is constructed in a coastal area, it is necessary to fully evaluate the impact of seawater-based groundwater on engineered barriers, including buffer materials. In this report, one-dimensional saltwater infiltration tests were conducted to obtain data to understand the impact of seawater-based groundwater on the migration phenomena of water and solutes in the buffer material during the transient period. As a result, it was confirmed that the infiltration rate increased as the NaCl concentration in the infiltration solution increased. And it was confirmed that the water content ratio distribution changed as the NaCl concentration in the infiltration solution increased. As a result of analysis of the chloride ion concentration of the post-test specimens confirmed that chloride ion enrichment was occurred with infiltration. As a result of verifying the mechanism by which chloride ion enrichment occurs, it was confirmed that the phenomenon of chloride ion enrichment due to infiltration depends on the initial water content ratio.
Nagai, Takayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Katsuoka, Nanako; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Sato, Nobuaki*
2022-Nendo "Busshitsu, Debaisu Ryoiki Kyodo Kenkyu Kyoten" Kenkyu Seika, Katsudo Hokokusho (Internet), 1 Pages, 2023/09
no abstracts in English
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.603 - 613, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Yohei*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Miyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Terauchi, Masami*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(5), p.950 - 954, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dilute Mg-Zn-Y alloy with a mille-feuille structure (MFS) exhibits a mechanical strength comparable to Mg-Zn-Y alloy with long period stacking/ordered (LPSO) structure through kink deformation. In order to deepen understanding the thermal stability of the MFS-type Mg alloys, it is required to clarify the solute cluster structures composed of Zn and Y in solute enriched stacking faults (SESFs). In this study, electron energy-loss and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy based on scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM-EELS/EDS) were conducted to investigate the electronic structure and composition of Zn and Y in the SESFs of the MFS-Mg alloy. Zn-L2,3 spectra indicated that the valence charges of Zn in the dilute Mg alloy were different from that of the LPSO-type Mg-Zn-Y alloy. In addition, the intensity ratio of L3/L2 in Y-L2,3 spectrum of the dilute MFS-Mg alloy was larger than that of the LPSO-Mg alloy, reflecting the electron occupancies of 4d3/2 and 4d5/2 orbitals of Y atoms were different from those of the LPSO-Mg alloys. STEM-EELS analysis of the SESF composition in the dilute MFS-Mg alloy indicated that the Zn/Y ratio should be lower than that of the LPSO-Mg alloy, which was confirmed also by STEM-EDS measurements. These results indicate that the cluster structure in the SESFs of the dilute MFS-Mg alloy should be different from the ideal Zn6Y8 cluster in the LPSO-type Mg-Zn-Y alloys.
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:87.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Suzuki, Hideaki*; Takayama, Yusuke; Sato, Hisashi*; Watahiki, Takanori*; Sato, Daisuke*
JAEA-Research 2022-013, 41 Pages, 2023/03
It is anticipated that the coupled thermal-hydraulic-mechanical and chemical (THMC) processes will occur, involving an interactive process with radioactive decay heat arising from the vitrified waste, infiltration of groundwater from the host rock into the buffer material, swelling pressure of buffer material due to its saturation and chemical reaction between bentonite and pore-water in the near-field of a geological disposal system for high-level radioactive waste repository. In order to evaluate these phenomena in the near-field, the THMC model has been developed. In this study, For the purpose of evaluating the near-field infiltration behavior in seawater-type groundwater environment, a hydraulic model was set in which the permeability of the buffer material change depending on the salt concentration in the pore-water. In order to evaluate the drying phenomenon of the buffer material due to waste heat, a temperature gradient water transfer model was set in consideration of the dependence of temperature and pore-water saturation. The THMC analysis of the in-situ experiment of engineered barrier system (EBS) experiment at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory was carried out. The validity of the model was then checked through comparison with measured data.
Takayama, Yusuke; Sato, Daisuke*; Kikuchi, Hirohito*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 29(2), p.101 - 111, 2022/12
Swelling pressure tests have been conducted to understand the swelling properties of bentonite which is planned to be used as a buffer material in repositories for the geological disposal of radioactive waste. It has been reported that the swelling pressure obtained by swelling pressure test increases monotonically or temporarily decreases after increasing with the passage of the time depending on the initial water content. In this study, swelling pressure tests were conducted under several different initial water content conditions, and the change in wet density distribution inside the specimen during the swelling pressure tests was observed by X-ray CT measurement. It was confirmed that the presence or absence of collapse behavior and its magnitude affect the shape of the change in swelling pressure. When the collapse deformation was large, the amount of temporary decrease in swelling pressure was large. On the other hand, swelling pressure increased monotonically when there was no deformation due to collapse.
Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 569, p.153921_1 - 153921_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
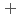 U
U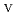
 Fe
Fe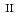
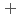 U
U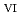 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
 , Zr, and stainless-steel
, Zr, and stainless-steelKirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 567, p.153842_1 - 153842_15, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:81.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand the chemical structure and stability of nuclear fuel debris consisting of UO , Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO
, Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO -SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600
-SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600 C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O
C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O ) atmospheres.
) atmospheres.  Np and
Np and  Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M
Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO
ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO  -SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U
-SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U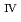 O
O (s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO
(s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO -SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
-SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
 O
O solution
solutionKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.961 - 971, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)We investigated potential degradation of fuel debris caused by H O
O , which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H
, which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H O
O solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H
solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H O
O . Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H
. Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H O
O reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO
reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO improves the stability of fuel debris against H
improves the stability of fuel debris against H O
O reaction.
reaction.