Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation) beam at J-PARC RCS
beam at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.59 - 63, 2023/11
Domal, S. J.*; Correa-Alfonso, C. M.*; Paulbeck, C. J.*; Griffin, K. T.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Funamoto, Sachiyo*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; Endo, Akira; Hertel, N. E.*; et al.
Health Physics, 125(4), p.245 - 259, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)The RERF Working Group on Organ Dose (WGOD) has established the J45 (Japan 1945) series of high-resolution voxel phantoms, which were derived from the UF/NCI series of hybrid phantoms and scaled to match mid-1940s Japanese body morphometries. In this present study, we present the J45 pregnant female phantoms in both a kneeling and lying posture, and assess the dosimetric impact of these more anatomically realistic survivor models in comparisons to current organ doses given by the DS02 system. For the kneeling phantoms facing the bomb hypocenter, organ doses from bomb source photon spectra were shown to be overestimated by the DS02 system by up to a factor of 1.45 for certain fetal organs and up to a factor of 1.17 for maternal organs. For lying phantoms with their feet in the direction of the hypocenter, fetal organ doses from bomb source photon spectra were underestimated by the DS02 system by factors as low as 0.77 while maternal organ doses were overestimated by up to a factor of 1.38. Results from this study highlight the degree to which the existing DS02 system can differ from organ dosimetry based upon 3D radiation transport simulations using more anatomically realistic models of those survivors exposed during pregnancy while in a kneeling or lying position.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Paulbeck, C. J.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Funamoto, Sachiyo*; Lee, C.*; Griffin, K. T.*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; Endo, Akira; Hertel, N. E.*; Bolch, W. E.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 62(3), p.317 - 329, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Biology)In our prior study [Radiat Res 192, 538-561 (2019)], we presented a new J45 (Japanese 1945) series of high-resolution phantoms of the adult pregnant female at 8-week, 15-week, 25-week, and 38-week post-conception. In this present study, we extend this work using realistic angular fluences from the DS02 system for up to nine different radiation categories and five shielding conditions. General findings are that the current DS02 fetal dose surrogate overestimates values of fetal organ dose seen in the J45 phantoms towards the cranial end of the fetus, especially in the later stages of pregnancy. This work supports our previous findings that the J45 pregnant female phantom series offers significate opportunities for gestational age-dependent assessment of fetal organ dose without the need to invoke the uterine wall as a fetal organ surrogate.
Bersweiler, M.*; Sato, Hirokazu*; Adachi, Nozomu*; Todaka, Yoshikazu*; Peral, I.*; Kohlbrecher, J.*; Zaporozhets, V. D.*; Metlov, K. L.*; Michels, A.*; Oba, Yojiro
IUCrJ, 10(4), p.411 - 419, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:85.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Matsuya, Yusuke; McMahon, S. J.*; Butterworth, K. T.*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Saga, Ryo*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Prise, K. M.*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 68(9), p.095008_1 - 095008_12, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:65.01(Engineering, Biomedical)Hypoxia induces radioresistance in tumors, leading to malignant progression in intensity-modulated radiation therapy. To date, it has been shown that intercellular signalling between cells positioned inside and outside radiation field impacts on cellular radiosensitivity under hypoxia and normoxia. However, the mechanistic role of intercellular communication in hypoxia remains to be fully understood. In this study, we modelled the cell-killing effects of intercellular signalling in hypoxia to better understand the underlying mechanisms of response. We used the oxygen enhancement ratio (OER) given from early DSB yields and modelled the in- and out-of-field radiosensitivity. As a result, the model analysis provides an mechanistical interpretation that the probability of hits for releasing cell-killing signals is dependent on oxygen. Our data also suggested that the field-type independent OER value, which can be given by uniform-field exposure, can be applied when predicting both in- and out-of-field radiosensitivity. These results would contribute to more precise understanding of intercellular signalling under heterogeneous exposure to intensity-modulated radiation fields.
 laser stripping at J-PARC RCS
laser stripping at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.272 - 276, 2023/01
Watabe, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yamaya, Taiga*; Kawachi, Naoki*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 13 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Previously, we have developed DynamicMC for modelling relative movement of ORNL phantom in a radiation field for MCNP. Using this software, 3-dimensional dose distributions in a phantom irradiated by a certain mono-energetic source can be deduced through its graphical user interface (GUI). In this study, we extended DynamicMC to be used in combination with the PHITS by providing it with a higher flexibility for dynamic movement for a less sophisticated anthropomorphic phantom. We anticipate that the present work and the developed open-source tools will be in the interest of nuclear radiation physics community for research and teaching purposes.
 Sn in concrete rubble
Sn in concrete rubbleDo, V. K.; Furuse, Takahiro; Ota, Yuki; Iwahashi, Hiroyuki; Hirosawa, Takashi; Watanabe, Masahisa; Sato, Soichi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(12), p.5631 - 5640, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Chemistry, Analytical) Sn is one of the long-lived fission products that might have been released into the environment after the Fukushima nuclear accident in Japan in 2011. The presence of radionuclides must be monitored for the proper treatment of wastes obtained from decommissioning accident-related nuclear facilities and the surrounding environment. In the work, we propose a reliable method for verifying the presence of
Sn is one of the long-lived fission products that might have been released into the environment after the Fukushima nuclear accident in Japan in 2011. The presence of radionuclides must be monitored for the proper treatment of wastes obtained from decommissioning accident-related nuclear facilities and the surrounding environment. In the work, we propose a reliable method for verifying the presence of  Sn in construction materials by combining the HCl-free solid phase extraction on TEVA resin and a selective measurement by inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS). The method has been optimized and characterized step by step. More than 95% of chemical recovery was achieved for Sn from typical concrete matrixes. The interference caused by an isobar
Sn in construction materials by combining the HCl-free solid phase extraction on TEVA resin and a selective measurement by inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS). The method has been optimized and characterized step by step. More than 95% of chemical recovery was achieved for Sn from typical concrete matrixes. The interference caused by an isobar  Te and possible polyatomic interferences from matrixes were effectively suppressed by the developed chemical separation and the tandem MS/MS configuration. The total decontamination factor for the Te interference was of the order of 10
Te and possible polyatomic interferences from matrixes were effectively suppressed by the developed chemical separation and the tandem MS/MS configuration. The total decontamination factor for the Te interference was of the order of 10 . The estimated method detection limit for
. The estimated method detection limit for  Sn in concrete as measured at m/z = 160 was 12.1 pg g
Sn in concrete as measured at m/z = 160 was 12.1 pg g , which is equivalent to 6.1 mBq g
, which is equivalent to 6.1 mBq g .
.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Xu, S.*; Odaira, Takumi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Seiner, H.*; Zoubkov , K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
, K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.5307_1 - 5307_8, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:66.14(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
 Be produced by the strongest solar proton event during the holocene
Be produced by the strongest solar proton event during the holoceneSpiegl, T. C.*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Langematz, U.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Chhin, R.*; Noda, Satoshi*; Miyake, Fusa*; Kusano, Kanya*; Schaar, K.*; Kunze, M.*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 127(13), p.e2021JD035658_1 - e2021JD035658_21, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.31(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)The abundance of cosmogenic isotopes in natural archives carries important information about the complex pathways from their source in the upper atmosphere to their deposition via atmospheric transport processes. Here, we use a new modelling framework to (a) estimate the  Be production yield for the 774 CE/775 event, (b) evaluate the performance of our model framework by comparing the model results to four ice core records and (c) investigate the atmospheric pathways with a state-of-the-art climate model in detail. The results give new constraints regarding the seasonal timing of the event, underpin the role of the background conditions in the stratosphere, and highlight regional variations in the cosmogenic surface flux.
Be production yield for the 774 CE/775 event, (b) evaluate the performance of our model framework by comparing the model results to four ice core records and (c) investigate the atmospheric pathways with a state-of-the-art climate model in detail. The results give new constraints regarding the seasonal timing of the event, underpin the role of the background conditions in the stratosphere, and highlight regional variations in the cosmogenic surface flux.
Mattan, K.*; Ono, Toshio*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Nambu, Yusuke*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review B, 105(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_8, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:48.5(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spin dynamics of the spin-1/2 kagome-lattice antiferromagnet Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
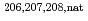 Pb(p,x)
Pb(p,x)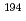 Hg and
Hg and  Bi(p,x)
Bi(p,x)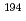 Hg excitation functions in the energy range 0.04 - 2.6 GeV
Hg excitation functions in the energy range 0.04 - 2.6 GeVTitarenko, Yu. E.*; Batyaev, V. F.*; Pavlov, K. V.*; Titarenko, A. Yu.*; Malinovskiy, S. V.*; Rogov, V. I.*; Zhivun, V. M.*; Kulevoy, T. V.*; Chauzova, M. V.*; Khalikov, R. S.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1026, p.166151_1 - 166151_9, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:33.4(Instruments & Instrumentation)The paper presents the 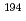 Hg production cross-sections measured by the direct gamma-spectrometry technique in the samples of lead enriched with isotopes 206, 207 and 208, as well as in the samples of natural lead and bismuth, irradiated by protons of 11 energies in the range from 0.04 to 2.6 GeV. The obtained experimental results are compared with the previous measurements, with the TENDL-2019 data-library evaluations and the simulated data by means of the high-energy transport codes MCNP6.1 (CEM03.03), PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM), Geant4 (INCL++/ABLA) and the nuclear reaction code TALYS.
Hg production cross-sections measured by the direct gamma-spectrometry technique in the samples of lead enriched with isotopes 206, 207 and 208, as well as in the samples of natural lead and bismuth, irradiated by protons of 11 energies in the range from 0.04 to 2.6 GeV. The obtained experimental results are compared with the previous measurements, with the TENDL-2019 data-library evaluations and the simulated data by means of the high-energy transport codes MCNP6.1 (CEM03.03), PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM), Geant4 (INCL++/ABLA) and the nuclear reaction code TALYS.
Zhao, Y.*; Suzuki, T.*; Iimori, T.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J. R.*; Horio, Masafumi*; Sato, Yusuke*; Fukaya, Yuki; Kanai, T.*; Okazaki, K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115304_1 - 115304_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Griffin, K. T.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Funamoto, Sachiyo*; Chizhov, K.*; Domal, S.*; Paulbeck, C.*; Bolch, W.*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; Endo, Akira; et al.
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 61(1), p.73 - 86, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:55.27(Biology)To evaluate the potential dosimetry improvements that would arise from their use in a Dosimetry System (DS) at RERF, we have evaluated organ doses in the J45 series using the environmental fluence data for twenty generalized survivor scenarios pulled directly from the current DS. The energy- and angle-dependent gamma and neutron fluences were converted to a phase space source term for use in MCNP6, a modern radiation transport code. Overall, the updated phantom series would be expected to provide dose improvements to several important organs, including the active marrow, colon, and stomach wall (up to 20%, 20%, and 15% impact on total dose, respectively). The impacts on dosimetry were especially significant for neutron dose estimates (up to a two-fold difference) and within organs which were unavailable in the previous phantom series, such as the skin, esophagus, and prostate.