Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakashita, Koichi; Arakawa, Yuto; Masuyama, Koichi; Sato, Koichi; Seki, Kazunari; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Ishii, Tetsuro
Radiation Safety Management, 23, p.7 - 15, 2025/03
 -Mo
-Mo O
O revealed by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculation
revealed by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculationSumida, Kazuki; Higaki, Sota*; Sato, Hitoshi*; Tsuru, Daichi*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Okuda, Taichi*; Kuroiwa, Yoshihiro*; Moriyoshi, Chikako*; Takase, Koichi*; Oguchi, Tamio*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(8), p.084706_1 - 084706_6, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 -iron
-ironHirayama, Shintaro*; Sato, Koichi*; Kato, Daiji*; Iwakiri, Hirotomo*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Watanabe, Yoshiyuki*; Nozawa, Takashi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101179_1 - 101179_9, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:67.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 O
O -pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawater
-pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawaterMizumachi, Takumi*; Sato, Minami*; Kaneko, Masashi; Takeyama, Tomoyuki*; Tsushima, Satoru*; Takao, Koichiro*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(16), p.6175 - 6181, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:52.57(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Based on unique 5-fold equatorial coordination of UO
 , water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H
, water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
 in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
 /CO
/CO
 , pH 8), saldian
, pH 8), saldian shows the strongest complexation with UO
shows the strongest complexation with UO
 to form UO
to form UO (saldian) (log
(saldian) (log
 = 28.05
= 28.05  0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
 from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
Takahashi, Nobuo; Kubota, Shintaro; Takiya, Hiroaki; Sakaba, Ryosuke*; Sato, Koichi; Shichi, Ryo
JAEA-Testing 2021-002, 106 Pages, 2022/01
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has various nuclear facilities such as reactor facilities and reprocessing facilities. Some aged facilities will be decommissioned after their original functions ended, and it is necessary to evaluate their decommissioning cost to formulate the initial decommissioning plans and the final decommissioning plans. We have developed an evaluation method called DECOST that can efficiently calculate the decommissioning cost in a short time based on factors such as features and similarity of the facilities and dismantling methods. The decommissioning of nuclear facilities has been implemented and new achievements and findings have been reported since the development of DECOST. These findings were reflected in DECOST. In consideration of the needs of DECOST users, DECOST has been improved so that the cost of dismantling the facility can be divided into the cost of releasing the controlled area and the cost of dismantling the facility building after the release of the controlled area. This report shows the improvement of DECOST, the concept of resetting the evaluation coefficient used in the cost evaluation formula, and the validity of the evaluation coefficient after resetting. In addition, the evaluation procedure of the improved DECOST is described, since the evaluation items and evaluation contents were partially changed due to the improvement.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t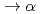 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Chen, Y.*; Sato, Masahiro*; Tang, Y.*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Oyanagi, Koichi*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Fujita, Masaki*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.5199_1 - 5199_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Torii, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; Kanda, Sotaro*; Kawagoe, Kiyotomo*; Kawall, D.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kurosawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:83.44(Optics)Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sato, Koichi; Takahashi, Kazutoshi*; Miyamoto, Yukihiro; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011144_1 - 011144_6, 2021/03
A spallation neutron source with a mercury target has been in operation at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility of J-PARC since 2008. The target vessel made of stainless steel is required to be exchanged periodically due to radiation damage etc. In this presentation, tritium gas release observed in the first series of exchange work in 2011 and the analytical results will be shown.
 for production of
for production of  Tc radioactive isotope
Tc radioactive isotopeSuematsu, Hisayuki*; Sato, Soma*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Niihara, Koichi*; Nanko, Makoto*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies (Internet), 8(4), p.1154 - 1161, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.02(Materials Science, Ceramics)Pulsed electric current sintering of molybdenum trioxide (MoO ) was carried out by one- and two-step pressuring methods for fabrication of irradiation target using production of
) was carried out by one- and two-step pressuring methods for fabrication of irradiation target using production of  Mo and
Mo and  Tc nuclear medicine. At 550
Tc nuclear medicine. At 550 C by the two-step pressurizing method, a relative density of 93.1% was obtained while, by the one-step pressurization method, the relative density was 76.9%. Direct sample temperature measurements were conducted by inserting a thermocouple in a punch. By the two-step pressurizing method, the sample temperature was higher than that by the one-step pressurizing method even almost the same die temperature. From voltage and current waveforms, it was thought that the conductivity of the sample increased by the two-step pressurizing method to increase the sample temperature and the relative density. The two-step pressurization method enables us to prepare dense targets at a low temperature from recycled and coarse-grained
C by the two-step pressurizing method, a relative density of 93.1% was obtained while, by the one-step pressurization method, the relative density was 76.9%. Direct sample temperature measurements were conducted by inserting a thermocouple in a punch. By the two-step pressurizing method, the sample temperature was higher than that by the one-step pressurizing method even almost the same die temperature. From voltage and current waveforms, it was thought that the conductivity of the sample increased by the two-step pressurizing method to increase the sample temperature and the relative density. The two-step pressurization method enables us to prepare dense targets at a low temperature from recycled and coarse-grained  Mo enriched MoO
Mo enriched MoO powder.
powder.
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.74(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Yako, Tomoki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Abe, Masashi*; Kurihara, Toshikazu*; Fukuda, Masafumi*; Sato, Masaharu*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takamiya, Koichi*; Iinuma, Yuto*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1003 - 1005, 2019/10
Permanent magnets are used as materials for beam optics elements, but it is known that radiation demagnetization occurs in neodymium magnets and samarium cobalt magnets. However, there is not enough information on the radiation demagnetization of ferrite magnets which is weak in strength but inexpensive. In order to verify the suitability of the ferrite magnet as a beam optics element, radiation demagnetization experiments by neutron irradiation of the ferrite magnet were carried out at the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR). In the experiment, neutron fluence up to 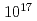 cm
cm was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Sato, Hisato; Fukasawa, Tomonori*; Fukui, Kunihiro*
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.738 - 745, 2019/09
In the MOX fuel fabrication process, the dry grinding technology of mixed oxide pellets have been developed for the effective use of nuclear fuel materials. To develop a technology to control the particle size of dry recovered powder, the performance of the buhrstone mill and the collision plate type jet mill were studied using a simulated powder of particle size distribution about 500  m. We found that the particle size can be controlled at the range of about 250
m. We found that the particle size can be controlled at the range of about 250  m or less by both by adjusting the clearance between the grinding wheels of the buhrstone mill, and the clearance and elevation angle of the clarification zone of the collision plate type jet mill. And furthermore, the collision plate type jet mill is considered to be suitable for particle size control because the operating parameters of the classifier can be finely adjusted.
m or less by both by adjusting the clearance between the grinding wheels of the buhrstone mill, and the clearance and elevation angle of the clarification zone of the collision plate type jet mill. And furthermore, the collision plate type jet mill is considered to be suitable for particle size control because the operating parameters of the classifier can be finely adjusted.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.

Yamanouchi, Michihiko*; Oyamada, Tatsuro*; Sato, Koichi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Ieda, Junichi
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 55(7), p.1400604_1 - 1400604_4, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.91(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Yano, Tsuneo*; Hasegawa, Koki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hachisuka, Akiko*; Fukase, Koichi*; Hirabayashi, Yoko*
Iyakuhin Iryo Kiki Regyuratori Saiensu, 50(3), p.122 - 134, 2019/03
This report provides an overview of alpha-particle-emitting radiopharmaceuticals applied by micro-dosimetry.