Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
 Bh in the
Bh in the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 )
) Bh reaction and its decay properties
Bh reaction and its decay propertiesHaba, Hiromitsu*; Fan, F.*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Kondo, Narumi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.024625_1 - 024625_12, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.56(Physics, Nuclear)Yano, Tsuneo*; Hasegawa, Koki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hachisuka, Akiko*; Fukase, Koichi*; Hirabayashi, Yoko*
Iyakuhin Iryo Kiki Regyuratori Saiensu, 50(3), p.122 - 134, 2019/03
This report provides an overview of alpha-particle-emitting radiopharmaceuticals applied by micro-dosimetry.
Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kuwatani, Ryuta*; Kono, Masanori*; Sato, Toshinori; Kashiwaya, Koki*
Zairyo, 67(7), p.730 - 737, 2018/07
Information of confining ability of rock is important for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes. To maintain or improve the confining ability of rocks, it is important to seal pores and cracks. In this study, we investigated the precipitation of minerals on the rock surface. As rock samples, we used Berea sandstone and Toki granite in this study. It was shown that precipitation occurred on the surface of rock specimens kept in calcium hydroxide solution for 1 month if the concentration was high. Specifically, if the concentration of calcium hydroxide solution was higher than 300 mg/l, the precipitation occurred obviously. After keeping rock specimens in calcium hydroxide solution, the weight of the rock samples increased and the concentration of calcium ion decreased by the precipitation. It is considered that the calcium ion in water was used for the precipitation on rock surfaces. Since the precipitation has been recognized for rock surfaces, it is possible to seal pores and cracks in rocks. Therefore, it is also possible to keep or decrease the permeability of rocks by the precipitation of calcium compounds.
Sato, Masayuki*; Muraoka, Koji*; Hozumi, Koki*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Yamada, Tsutomu*; Torii, Tatsuo
Nihon Koku Uchu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 65(2), p.54 - 63, 2017/02
This paper is concerned with the design problem of preview altitude controller for Unmanned Airplane for Radiation Monitoring System (UARMS) to improve its control performance. UARMS has been developed for radiation monitoring around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant which spread radiation contaminant due to the huge tsunamis caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake. The monitoring area contains flat as well as mountain areas. The basic flight controller has been confirmed to have satisfactory performance with respect to altitude holding; however, the control performance for variable altitude commands is not sufficient for practical use in mountain areas. We therefore design preview altitude controller with only proportional gains by considering the practicality and the strong requirement of safety for UARMS. Control performance of the designed preview controller was evaluated by flight tests conducted around Fukushima Sky Park.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Kuwabara, Kazumichi; Ueno, Tetsuro; Onuki, Kenji*; Beppu, Shinji; Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-024, 122 Pages, 2015/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technical basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase III, as the Phase II was concluded for a moment with the completion of the excavation of horizontal tunnels at GL-500m level in February 2014. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2014.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sasao, Eiji; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ikeda, Koki; Sato, Toshinori; Osawa, Hideaki; Koide, Kaoru
JAEA-Review 2015-021, 27 Pages, 2015/10
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of geological disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment in the crystalline host rock (granite rock) at Mizunami City in Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. This report summarizes the research and development activities planned for fiscal year 2015 based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2015 and so on. On the occasion of the reform of the entire JAEA organization in 2014, JAEA identified the critical issues on the geoscientific research program: "Development of modelling technologies for mass transport", "Development of drift backfilling technologies" and "Development of technologies for reducing groundwater inflow", based on the latest results of the synthesizing R&D. Investigations on those critical issues will be performed at the MIU in fiscal year 2015.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 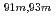 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Sasao, Eiji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Ikeda, Koki; Sato, Toshinori; Osawa, Hideaki; Koide, Kaoru
JAEA-Review 2014-035, 34 Pages, 2014/10
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host crystalline rock at Mizunami City in Gifu, central Japan. The project proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigation Phase", "Phase II: Construction Phase" and "Phase III: Operation Phase". The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase III, as the Phase II was concluded for a moment with the completion of the excavation of horizontal tunnels at GL-500m level in February 2014. The present report summarizes the research and development activities planned for fiscal year 2014 based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Tanno, Takeo*; Onoe, Hironori; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-044, 37 Pages, 2014/01
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host crystalline rock at Mizunami City in Gifu, central Japan. The project consists of major research areas, "Geoscientific Research", and proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigation Phase", "Phase II: Construction Phase" and "Phase III: Operation Phase". The present report summarizes the research and development activities planned for fiscal year 2013 based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kuboshima, Koji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Mizuno, Takashi; Sato, Toshinori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-028, 31 Pages, 2012/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase and the Operation Phase. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2012 fiscal year based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010, construction plan and research collaboration plan, etc.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-020, 178 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II. And Phase III started in 2010 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2010, as a part of the Phase II based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Mizuno, Takashi; Sato, Toshinori; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-027, 30 Pages, 2011/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). Geoscientific research and the MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase1), Construction Phase (Phase2) and Operation Phase (Phase3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase, and the Operation Phase. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2011 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010, Investigation Plan, Construction Plan and Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
Mikake, Shinichiro; Yamamoto, Masaru; Ikeda, Koki; Sugihara, Kozo; Takeuchi, Shinji; Hayano, Akira; Sato, Toshinori; Takeda, Shinichi; Ishii, Yoji; Ishida, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2010-026, 146 Pages, 2010/08
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU), one of the main facilities in Japan for research and development of the technology for high-level radioactive waste disposal, is under construction in Mizunami City. In planning the construction, it was necessary to get reliable information on the bedrock conditions, specifically the rock mass stability and hydrogeology. Therefore, borehole investigations were conducted before excavations started. The results indicated that large water inflow could be expected during the excavation around the Ventilation Shaft at GL-200m and GL-300m Access/Research Gallery. In order to reduce water inflow, pre-excavation grouting was conducted before excavation of shafts and research tunnels. Grouting is the injection of material such as cement into a rock mass to stabilize and seal the rock. This report describes the knowledge and lessons learned during the planning and conducting of pre-excavation grouting.
 Sb
Sb
Aoki, Yuji*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsunashima, Yoshino*; Yonezawa, Yuki*; Sato, Koki*; Koda, Akihiro*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki; Heffner, R. H.; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.757 - 760, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.33(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero field (ZF) and transverse field (TF) muon spin relaxation and rotation ( SR) study has been carried out in filled-skutterudite SmOs
SR) study has been carried out in filled-skutterudite SmOs Sb
Sb in order to investigate the magnetically robust heavy-fermion (HF) state and the weak ferromagnetic anomaly. A large-amplitude oscillating signal appears in the ZF-
in order to investigate the magnetically robust heavy-fermion (HF) state and the weak ferromagnetic anomaly. A large-amplitude oscillating signal appears in the ZF- SR spectra at low temperatures, confirming that the weak ferromagnetic anomaly is an intrinsic bulk property. Analysis reveals that the weak ferromagnetic moment is carried by itinerant heavy quasiparticles.
SR spectra at low temperatures, confirming that the weak ferromagnetic anomaly is an intrinsic bulk property. Analysis reveals that the weak ferromagnetic moment is carried by itinerant heavy quasiparticles.
Sato, Hideyuki*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki; Ito, Takashi; Heffner, R. H.; Saha, S. R.*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.749 - 753, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.59(Physics, Condensed Matter)Wide varieties of strongly correlated electron phenomena are performed on the stage of a filled skutterudite structure. Especially when one of the players contains a plural number of 4f electrons, the orbital degrees of freedom play a major role as a new type of nonmagnetic and/or weak-magnetic phenomena. Several examples found in Pr- and Sm-based filled skutterudites are introduced in relation to muon spin relaxation experiments.
 SR measurements on the vortex lattice of CaAlSi; Anisotropic response in magnetic penetration depth
SR measurements on the vortex lattice of CaAlSi; Anisotropic response in magnetic penetration depthKuroiwa, Sogo*; Sato, Koki*; Koda, Akihiro*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Higemoto, Wataru; Akimitsu, Jun*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 68(11), p.2124 - 2128, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.88(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The vortex state defined by two characteristic length scales, magnetic penetration depth ( ) and coherence length (
) and coherence length (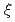 ), in a layered hexagonal superconductor CaAlSi was probed using muon spin rotation. From preliminary analysis using modified London model, we found that the in-plane
), in a layered hexagonal superconductor CaAlSi was probed using muon spin rotation. From preliminary analysis using modified London model, we found that the in-plane  increases with increasing magnetic field while inter-plane
increases with increasing magnetic field while inter-plane  is almost independent of magnetic field. The presence of field-induced quasiparticle excitation manifested in the field dependence of
is almost independent of magnetic field. The presence of field-induced quasiparticle excitation manifested in the field dependence of  suggests that CaAlSi has an anisotropic gap structure.
suggests that CaAlSi has an anisotropic gap structure.