Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Furuta, Takuya; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Ishikawa, Kenichi*; Noda, Shigeho*; Takagi, Shu*; Maeyama, Takuya*; Fukunishi, Nobuhisa*; Fukasaku, Kazuaki*; et al.
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Mathematics and Computation, Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and the Monte Carlo Method (M&C + SNA + MC 2015) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/04
In Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System PHITS, two parallel computing functions are prepared to reduce the computational time. One is the distributed-memory parallelization using message passing interface (MPI) and the other is the shared-memory parallelization using OpenMP directives. Each function has advantages and disadvantages, and thus, by adopting both functions in PHITS, it is possible to conduct parallel computing suited for needs of users. It is also possible to conduct the hybrid parallelization by the intra-node OpenMP parallelization and the inter-node MPI parallelization in supercomputer systems. Each parallelization functions were explained together with some application results obtained using a workstation and a supercomputer system, K computer at RIKEN.
Yamagishi, Isao; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kato, Chiaki; Morita, Keisuke; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kamiji, Yu; Hino, Ryutaro; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.1044 - 1053, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)For safe storage of zeolite wastes generated by treatment of radioactive saline water at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, properties of the Herschelite adsorbent were studied and its adsorption vessel was evaluated for hydrogen production and corrosion. Hydrogen production depends on its water level and dissolved species because hydrogen is oxidized by radicals in water. It is possible to evaluate hydrogen production rate in Herschelite submerged in seawater or pure water by taking into account of the depth effect of the water. The reference vessel of decay heat 504 W with or without residual pure water was evaluated for the hydrogen concentration by thermal hydraulic analysis using obtained fundamental properties. Maximum hydrogen concentration was below the lower explosive limit (4 %). The steady-state corrosion potential of a stainless steel 316L increased with absorbed dose rate but its increase was repressed by the presence of Herschelite. At 750 Gy/h and  60
60 C which were values evaluated at the bottom of the vessel of 504 W, the localized corrosion of SUS316L contacted with Herschelite would not immediately occur under 20,000 ppm of Cl
C which were values evaluated at the bottom of the vessel of 504 W, the localized corrosion of SUS316L contacted with Herschelite would not immediately occur under 20,000 ppm of Cl concentration.
concentration.
Yan, X.; Noguchi, Hiroki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Hino, Ryutaro
International Journal of Energy Research, 37(14), p.1811 - 1820, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:74.42(Energy & Fuels)Existing nuclear desalination cogeneration incurs loss of nuclear plant power generation. Such loss is avoided with the plant design GTHTR300 proposed in the present study. The plant is based on a HTGR. Gas turbine is used to replace steam turbine as power generator. The gas turbine converts about a half of the reactor thermal power to electricity while rejecting the balance as sensible waste heat to be utilized in a MSF plant for desalination. A new MSF is proposed to efficiently match the sensible waste heat source. Although operating with a similar number of stages to traditional process, the new process is shown to produce 45% more water over the same temperature range.
 Cm +
Cm +  O reaction
O reactionMurakami, Masashi*; Goto, Shinichi*; Murayama, Hirofumi*; Kojima, Takayuki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 88(2), p.024618_1 - 024618_8, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:66.57(Physics, Nuclear)Production cross sections of Rf isotopes in the  Cm +
Cm +  O reaction were measured at the beam energy range of 88.2 to 101.3 MeV by use of a gas-filled recoil ion separator. The excitation functions of
O reaction were measured at the beam energy range of 88.2 to 101.3 MeV by use of a gas-filled recoil ion separator. The excitation functions of 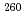 Rf,
Rf, 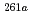 Rf, and
Rf, and  Rf were obtained together with those of spontaneously fissioning nuclides which have few-second half-lives and have been assigned to
Rf were obtained together with those of spontaneously fissioning nuclides which have few-second half-lives and have been assigned to 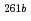 Rf and a longer-lived state of
Rf and a longer-lived state of  Rf. The excitation function of few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide exhibited the maximum cross section at the
Rf. The excitation function of few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide exhibited the maximum cross section at the  O beam energy of 94.8 MeV. The shape of the excitation function was almost the same as that of
O beam energy of 94.8 MeV. The shape of the excitation function was almost the same as that of 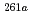 Rf, whereas it was quite different from those of
Rf, whereas it was quite different from those of 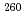 Rf and
Rf and  Rf. A few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide previously reported as
Rf. A few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide previously reported as 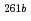 Rf and
Rf and  Rf observed in
Rf observed in Cm +
Cm +  O reaction was identified as
O reaction was identified as 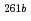 Rf.
Rf.
 ;
;  synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction study
synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction studySato, Ryutaro*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 102(9), p.091901_1 - 091901_4, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:73.44(Physics, Applied) and its synthesis; Mechanism for formation of metallic perovskite
and its synthesis; Mechanism for formation of metallic perovskiteTakagi, Shigeyuki*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Endo, Naruki; Sato, Ryutaro*; Ikeshoji, Tamio*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Miwa, Kazutoshi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 87(12), p.125134_1 - 125134_6, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:53.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) ; Adjustment of imbalanced charge by additional Li as an electron donor
; Adjustment of imbalanced charge by additional Li as an electron donorMatsuo, Motoaki*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Sato, Ryutaro*; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Miwa, Kazutoshi*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
RSC Advances (Internet), 3(4), p.1013 - 1016, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:53.62(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) 113 of the 113th element
113 of the 113th elementMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yoneda, Akira*; Tanaka, Kengo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(10), p.103201_1 - 103201_4, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:167 Percentile:97.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An isotope of the 113th element,  113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a
113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a  Zn beam on a
Zn beam on a  Bi target. We observed six consecutive
Bi target. We observed six consecutive  decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of
decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of  Db and
Db and  Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of
Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of  113,
113, 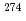 Rg (Z = 111),
Rg (Z = 111), 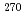 Mt (Z = 109),
Mt (Z = 109),  Bh (Z = 107),
Bh (Z = 107),  Db (Z = 105), and
Db (Z = 105), and  Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope
Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope  113, of the 113th element.
113, of the 113th element.
 Sg in the
Sg in the  Cm(
Cm( Ne,5
Ne,5 )
) Sg reaction and decay properties of two isomeric states in
Sg reaction and decay properties of two isomeric states in  Sg
SgHaba, Hiromitsu*; Kaji, Daiya*; Kudo, Yuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Sakai, Ryutaro*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Physical Review C, 85(2), p.024611_1 - 024611_11, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:91.35(Physics, Nuclear)Two isomeric states in  Sg, i.e,
Sg, i.e,  Sg
Sg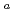 and
and  Sg
Sg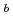 were produced in the
were produced in the  Cm(
Cm( Ne,5
Ne,5 ) reaction. Decay properties of
) reaction. Decay properties of  Sg
Sg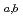 were investigated with a rotating-wheel apparatus for
were investigated with a rotating-wheel apparatus for  and spontaneous fission (SF) spectrometry under low background condition attained by a gas-jet transport system coupled to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator. Based on genetically correlated
and spontaneous fission (SF) spectrometry under low background condition attained by a gas-jet transport system coupled to the RIKEN gas-filled recoil ion separator. Based on genetically correlated  -
- (-
(- ) and
) and  -SF decay chains, 18 and 24 events were assigned to
-SF decay chains, 18 and 24 events were assigned to  Sg
Sg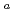 and
and  Sg
Sg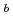 , respectively. The half-life and
, respectively. The half-life and  -particle energy of
-particle energy of  Sg
Sg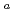 were measured to be
were measured to be 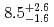 s and
s and 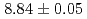 MeV, respectively, and those of
MeV, respectively, and those of  Sg
Sg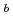 were
were 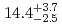 s and
s and 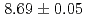 MeV.
MeV.
Yan, X.; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Hino, Ryutaro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(1), p.121 - 131, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Terada, Atsuhiko; Yan, X.; Hino, Ryutaro; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2010/05
When a primary pipe of the HTGR ruptures, helium coolant gas in the reactor blows out into the reactor confinement structure and the reactor primary system depressurizes. Consequently, the core graphite structures may be oxidized by the air and the complicated natural convection of multi component gas mixtures with chemical reactions would take place inside the reactor. Hence, JAEA studies showed the air ingress phenomena in the depressurized reactor and proposed a new passive mechanism of sustained counter air diffusion (SCAD) that has been shown effective in preventing major air ingress through natural circulation in the reactor. In the present plan, JAEA will construct an experimental reactor mockup including reactor core, the SCAD system, pressure vessel, coaxial pipe and so on. The core is made of graphite or ceramics and heated by electric heaters to allow for test operation up to 1200 C. Present status of these activities will be presented.
C. Present status of these activities will be presented.
Ogawa, Masuro; Hino, Ryutaro; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Sato, Hiroyuki
Karyoku Genshiryoku Hatsuden, 58(10), p.1029 - 1037, 2007/10
High temperature gas reactors (HTGRs) are expected to expand the application field of the nuclear energy. This report describes the salient features of the HTGRs such as various heat utilization, excellent safety features, high efficiency, high burn-up, etc. Also, development status of the HTGRs in the world was described.
Aso, Tomokazu; Monde, Masanori*; Sato, Hiroshi; Hino, Ryutaro; Tatsumoto, Hideki; Kato, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 5(3), p.179 - 189, 2006/09
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Keishi; Takahashi, Koji; Kasugai, Atsushi; Minami, Ryutaro; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Tobita, Kenji
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1263 - 1270, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:36.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masahiro*; Endo, Akira; Sato, Shigero*; Ohata, Tsutomu*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Oyama, Ryutaro*; Furuya, Hirotaka*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(3), p.213 - 218, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Ishikura, Shuichi*; Sato, Hiroshi; Harada, Masahide; Takatama, Shunichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Hino, Ryutaro; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.178 - 183, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A cross-flow type (CFT) mercury target with flow guide blades, which has been developed for JSNS, can suppress the generation of stagnant flow region especially near the beam window where the peak heat density is generated due to spallation reaction. Then, a flat type beam window has been applied to the CFT target from the viewpoint of suppressing dynamic stress caused by a pressure wave, which has been estimated with a mercury model of the linear equation of state. The recent experimental results obtained by using a proton beam incidents to mercury led that a cutoff pressure model in the equation of state of mercury caused a suitable dynamic stress with experimental results. Dynamic stress analyses were carried out with the cutoff pressure model, in which the negative pressure less than 0.15 MPa was not generated. The generated dynamic stress in the flat beam window became much larger than that in a semi-cylindrical type window. However, the generated stress in the semi-cylindrical type beam window was over the allowable stress of SS316L under the peak heat density of 668 W/cc. In order to decrease the dynamic stress in the semi-cylindrical beam window, the incident proton beam was defocused to decrease the peak heat density down to 218 W/cm . As a result, the dynamic stress could be suppressed less than the allowable stress. On the other hand, due to defocus of the proton beam, high heat density was generated on the end of the flow guide blades, which caused high thermal stress exceeding the allowable stress. To decrease the thermal stress, several shapes of the blade ends were studied analytically, which were selected so as not to affect the mercury flow distribution. A simple thin-end blade showed low thermal stress below the allowable stress.
. As a result, the dynamic stress could be suppressed less than the allowable stress. On the other hand, due to defocus of the proton beam, high heat density was generated on the end of the flow guide blades, which caused high thermal stress exceeding the allowable stress. To decrease the thermal stress, several shapes of the blade ends were studied analytically, which were selected so as not to affect the mercury flow distribution. A simple thin-end blade showed low thermal stress below the allowable stress.
Sato, Hiroshi; Aso, Tomokazu; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Hino, Ryutaro
JAERI-Tech 2004-018, 23 Pages, 2004/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute is constructing a mega-watt class spallation neutron source in cooperation with the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization. A cold moderator using liquid hydrogen is one of the key components in the system, which directly affects the neutronic performance both in intensity and pulse time structure. Since a hydrogen temperature rise in the moderator vessel affects the neutronic performance, it is necessary to suppress the recirculation and stagnant regions which would cause hot spots. A cold moderator with a poison plate (poisoned decoupled moderator) has a high possibility to generate the stagnant region on and near the poison plate. Thermal-hydraulic analyses were carried out with proposed inner structure of the poisoned cold moderator. The stagnant and recirculation regions could be reduced by making a gap between the poison plate end and the vessel bottom surface, and the local temperature rise also could be kept under the required design value.
Haga, Katsuhiro; Kaminaga, Masanori; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Sato, Hiroshi; Ishikura, Shuichi*; Torii, Yoshikatsu; Hino, Ryutaro
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-12) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/00
In the Material and Life Science Facility, which will be constructed in the J-PARC project, the spallation mercury target station will be installed. Once the target system operation starts, mercury, the target vessel and the surrounding components are highly irradiated, so that all the replacement and maintenance operations of the target vessel and its peripheral devices have to be done with remote handling. In order to meet the requirements, we designed the target system such that the target vessel and the mercury circulation system are mounted on a target trolley, which is the system carriage. The target vessel is carried with the mercury circulation system together and inserted into the target center by the target trolley during the on-beam operation. During the system maintenance period, the target trolley is withdrawn to the maintenance room of hot cell, and the component exchange or repairing work will be done using a power manipulator and some master-slave manipulators. In this paper, the present design of the mercury target and its peripheral devices for 1MW spallation neutron source including the target vessel, a mercury circulation system, and a target trolley will be reported.