Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:94.96(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ishikawa, Akihisa; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Hirai, Yuta*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Radiological Physics and Technology, 17(2), p.553 - 560, 2024/06
 Am neutron capture cross section measurement using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline of J-PARC
Am neutron capture cross section measurement using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline of J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.459 - 477, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Mizuno, Rurie*; Niikura, Megumi*; Saito, Takeshi*; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Amato, A.*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Biswas, S.*; Chiu, I.-H.; Gianluca, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1060, p.169029_1 - 169029_14, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hata, Kuniki; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tomonori
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), 14 Pages, 2023/08
Kodama, Yu*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*; Hori, Junichi*; Shibahara, Yuji*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01024_1 - 01024_3, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) method
methodNauchi, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Suyama, Kenya; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1050, p.168109_1 - 168109_9, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Measurement of neutrons from spent nuclear fuel is performed in this study using the H method, which detects 2.223 MeV
method, which detects 2.223 MeV  rays from neutron capture reaction of hydrogen using a highly pure germanium (HPGe) detector. The detection of the 2.223 MeV
rays from neutron capture reaction of hydrogen using a highly pure germanium (HPGe) detector. The detection of the 2.223 MeV  ray is affected by intense
ray is affected by intense  ray emission from fission products (FPs) because the emission rate of
ray emission from fission products (FPs) because the emission rate of  rays from the FP is seven orders of magnitude higher than the emission rate of neutrons. To shield the intense
rays from the FP is seven orders of magnitude higher than the emission rate of neutrons. To shield the intense  ray from the FP, the HPGe detector is placed off the axis of a collimator, whereas a polyethylene block is placed on the axis. In this geometry, the detector is shielded from the intense
ray from the FP, the HPGe detector is placed off the axis of a collimator, whereas a polyethylene block is placed on the axis. In this geometry, the detector is shielded from the intense  rays from the FP, but the detector can measure 2.223 MeV
rays from the FP, but the detector can measure 2.223 MeV  rays from the H
rays from the H reactions in the polyethylene block. The measured count rate of the 2.223 MeV
reactions in the polyethylene block. The measured count rate of the 2.223 MeV  rays is consistent with the expected rate within the statistical error, which is calculated based on the nuclide composition, which is primary
rays is consistent with the expected rate within the statistical error, which is calculated based on the nuclide composition, which is primary  Cm, estimated via depletion and decay calculations. Accordingly, the H
Cm, estimated via depletion and decay calculations. Accordingly, the H method is considered feasible to quantify the number of neutron leakage from spent nuclear fuel assembly, which is applicable to certify burn up of the assembly.
method is considered feasible to quantify the number of neutron leakage from spent nuclear fuel assembly, which is applicable to certify burn up of the assembly.
 Sn nanodot
Sn nanodotSato, Yuma*; Takeuchi, Yutaro*; Yamane, Yuta*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; Kanai, Shun*; Ieda, Junichi; Ohno, Hideo*; Fukami, Shunsuke*
Applied Physics Letters, 122(12), p.122404_1 - 122404_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:56.18(Physics, Applied)Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Shoji; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Endo, Shunsuke; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00014_1 - 00014_4, 2023/03
 Am neutron capture cross section measurement and resonance analysis
Am neutron capture cross section measurement and resonance analysisRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.91 - 96, 2022/11
Xu, S.*; Odaira, Takumi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Seiner, H.*; Zoubkov , K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
, K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.5307_1 - 5307_8, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:82.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Furuta, Takuya; Koba, Yusuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Ishikawa, Akihisa*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(14), p.145002_1 - 145002_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:68.93(Engineering, Biomedical)Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. The Monte Carlo simulation is a good candidate for the tool to assess secondary cancer risk, including the contributions of secondary particles produced by nuclear reactions. We therefore developed a new dose reconstruction system implementing PHITS as the engine. In this system, the PHITS input is automatically created from the DICOM data sets recorded in the treatment planning. The developed system was validated by comparing to experimental dose distribution in water and treatment plan on an anthropomorphic phantom. This system will be used for retrospective studies using the patient data in National Institute for Quantum and Science and Technology.
 Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response function
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response functionSato, Shunsuke*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*; Suyama, Kenya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.615 - 623, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new non-destructive method for evaluating  Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.  Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which
Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which  Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of
Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.
Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.  Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified
Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified  Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
 Au with a Cr-filtered neutron beam at the ANNRI beamline of MLF/J-PARC
Au with a Cr-filtered neutron beam at the ANNRI beamline of MLF/J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.647 - 655, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect
Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effectUchimura, Tomohiro*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; Sato, Yuma*; Takeuchi, Yutaro*; Kanai, Shun*; Takechi, Ryota*; Kishi, Keisuke*; Yamane, Yuta*; DuttaGupta, S.*; Ieda, Junichi; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 120(17), p.172405_1 - 172405_5, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:88.33(Physics, Applied) Am around 23.5 keV
Am around 23.5 keVKodama, Yu*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Shibahara, Yuji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(11), p.1159 - 1164, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Chang, W.*; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(5), p.846 - 855, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.45(Biology)With the aim of developing a revaluation tool of treatment plan in carbon-ion radiotherapy using Monte Carlo (MC) simulation, we propose two methods; one is dedicated to identify realistic-tissue materials from a CT image with satisfying the well-calibrated relationship between CT numbers and stopping power ratio (SPR) provided by TPS, and the other is to estimate dose to water considering the particle- and energy-dependent SPR between realistic tissue materials and water. We validated these proposed methods by computing depth dose distribution in homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms composed of human tissue materials and water irradiated by a 400 MeV/u carbon beam with 8 cm SOBP using a MC simulation code PHITS and comparing with results of conventional treatment planning system (TPS). Our result suggested that use of water as a surrogate of real tissue materials, which is adopted in conventional TPS, is inadequate for dose estimation from secondary particles because their production rates cannot be scaled by SPR of the primary particle in water. We therefore concluded that the proposed methods can play important roles in the reevaluation of the treatment plans in carbon-ion radiotherapy.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,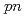 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.