Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:96.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,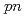 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Yoshida, Yasuhito*; Nakagawa, Ryo*; Yazawa, Shinya*; Kumada, Masashi*; Sato, Daisuke*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Chaumeix, N.*; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 16(2), p.21-00044_1 - 21-00044_13, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.68(Thermodynamics)The effects of addition of CO and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO
and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co
addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co or H
or H O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
 hypernuclear spectroscopy with the
hypernuclear spectroscopy with the 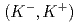 reaction
reactionGogami, Toshiyuki*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi*; Ichikawa, Yudai; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1643, p.012133_1 - 012133_6, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.36(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sekimoto, Shun*
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 105, 2019/08
To understand this structural change of a borosilicate glass by a neutron irradiation in detail, the irradiation test was carried out in KUR in 2017FY. The glass structure was estimated by using Raman spectrometry in 2018FY. Comparing with the Raman spectra of glass samples before and after irradiation, it could be observed the change of peak height of Si-O bridging structure by the irradiation.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Gogami, Toshiyuki*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Ichikawa, Yudai; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 18, p.011031_1 - 011031_6, 2017/11
Sato, Toshinori; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Eiichi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Fujita, Tomoo*; Tanai, Kenji; Nakayama, Masashi; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-025, 313 Pages, 2017/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. This report summarizes the results of the Phase II investigations carried out from April 2005 to June 2014 to a depth of 350m. Integration of work from different disciplines into a "geosynthesis" ensures that the Phase II goals have been successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to made to be addressed in the Phase II investigations Efforts are made to summarize as many lessons learnt from the Phase II investigations and other technical achievements as possible to form a "knowledge base" that will reinforce the technical basis for both implementation and the formulation of safety regulations.
Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Yokota, Hideharu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-007, 269 Pages, 2015/08
We have synthesised the research results from Mizunami/Horonobe URLs and geo-stability projects in the second mid-term research phase. It could be used as technical bases for NUMO/Regulator in each decision point from sitting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase). High quality construction techniques and field investigation methods have been developed and implemented and these will be directly applicable to the National Disposal Program (along with general assessments of hazardous natural events and processes). It will be crucial to acquire technical knowledge on decisions of partial backfilling and final closure by actual field experiments in Mizunami/Horonobe URLs as main themes for the next phases.
Sato, Isamu; Maeda, Koji; Suto, Mitsuo; Osaka, Masahiko; Usuki, Toshiyuki; Koyama, Shinichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(4), p.580 - 587, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Penetration behavior of radionuclides such as  Cs into dried concrete material, dried mortar material and epoxy paint for a few dozen days was observed using a solution containing fission products extracted from irradiated fuels to obtain fundamental information on the radionuclide penetration rate and depth. Hardly any radionuclides could penetrate into the epoxy paint. The radionuclide solution penetrated into concrete and mortar materials to a depth of a few millimeters for a few dozen days. The penetration behavior observed near the surface of concrete and mortar materials was similar to the diffusion of nuclides in media such as water-saturated concrete, bentonite and cement materials.
Cs into dried concrete material, dried mortar material and epoxy paint for a few dozen days was observed using a solution containing fission products extracted from irradiated fuels to obtain fundamental information on the radionuclide penetration rate and depth. Hardly any radionuclides could penetrate into the epoxy paint. The radionuclide solution penetrated into concrete and mortar materials to a depth of a few millimeters for a few dozen days. The penetration behavior observed near the surface of concrete and mortar materials was similar to the diffusion of nuclides in media such as water-saturated concrete, bentonite and cement materials.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Murakami, Hiroaki; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Sasao, Eiji; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-038, 137 Pages, 2014/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2013. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2013, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
 /UO
/UO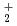 couple in Li
couple in Li MoO
MoO -Na
-Na MoO
MoO eutectic melt at 550
eutectic melt at 550 C
CNagai, Takayuki; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kofuji, Hirohide; Myochin, Munetaka; Yamana, Hajimu*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 454(1-3), p.159 - 163, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The redox equilibrium of UO /UO
/UO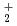 couple was measured in Li
couple was measured in Li MoO
MoO -Na
-Na MoO
MoO eutectic melt at 550
eutectic melt at 550 C by cyclic voltammetry and absorption spectrophotometry. The standard redox potential of UO
C by cyclic voltammetry and absorption spectrophotometry. The standard redox potential of UO /UO
/UO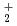 couple was approximately evaluated by cyclic voltammetry. Further, the absorption spectrum and equilibrium potential were measured, repeatedly adding UO
couple was approximately evaluated by cyclic voltammetry. Further, the absorption spectrum and equilibrium potential were measured, repeatedly adding UO source material into the melt containing UO
source material into the melt containing UO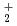 . From the correlation between the equilibrium potential of the melt and the concentration ratio [UO
. From the correlation between the equilibrium potential of the melt and the concentration ratio [UO ]/[UO
]/[UO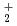 ] spectrophotometrically evaluated, the standard redox potential of UO
] spectrophotometrically evaluated, the standard redox potential of UO /UO
/UO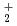 couple was determined to be -0.847
couple was determined to be -0.847 0.010 V vs. O
0.010 V vs. O /O
/O .
.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:94.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Sato, Isamu; Suto, Mitsuo; Maeda, Koji; Osaka, Masahiko; Koyama, Shinichi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sekioka, Ken*; Ishigamori, Toshio*
JAEA-Testing 2014-001, 29 Pages, 2014/05
The penetration tests with solution containing radioactive nuclides were experimented to understand basic data for floor and wall materials of Fukushima Daiichi reactor buildings. The solution prepared from irradiated fuels was used as solution containing radioactive nuclides. The solution was applied to surface of epoxy paint, dried concrete and mortar used as specimens. Dose-rate profiles of direction of depth were given by radiation measurement and grinding of the specimens. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for epoxy paint specimens were not clearly observed and the penetration depths would be within 0.4 mm. The penetrations of radioactive nuclides for dried concrete specimens proceeded. The penetration rates were substantially decreased when 16 days have elapsed from start. The dose rates of penetrated dried concrete specimens were reduced to background by grinding-2.0 mm.  -ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
-ray spectrometry measurement showed that penetration behavior of near surface concrete are different among nuclides and the penetration behavior of radioactive nuclides into dried concrete and mortar materials through solution is similar to migration behavior of ions into those water-saturated materials.
Koide, Tetsuya*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Saito, Yuichi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Okochi, Takuo*; Kotsugi, Masato*; Kinoshita, Toyohiko*; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Iwase, Akihiro*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 53(5S1), p.05FC06_1 - 05FC06_4, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:46.98(Physics, Applied)We previously reported that the magnetic state of FeRh can be controlled by irradiation with ion beams. In this paper, we evaluate possibility of magnetic patterning on FeRh thin films using energetic light ion microbeam irradiation with various shapes and dimensions. Proton microbeam irradiation with 2 MeV was performed at JAEA-Takasaki to produce micron-sized magnetic patterns. XMCD-PEEM observation was performed at SPring8 to confirm the synthesized magnetic patterns. As a result, the XMCD-PEEM images of the various micrometer sized patters in FeRh film were observed using 2 MeV H ion beam. The observed bright regions are considered to have ferromagnetic spin orders, in contrast that the gray areas have anti-ferromagnetic spin order. Since the brightness of the PEEM images is strongly correlated with the magnetization of the samples, we reveal that the magnetic state in local regions of the FeRh thin films can be controlled by changing the ion fluences.
 -wave halos at the drip-line;
-wave halos at the drip-line; 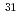 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(14), p.142501_1 - 142501_5, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:91.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Onoe, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-050, 114 Pages, 2014/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in fiscal year 2012. This report presents the results of the investigations, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2012, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Tanno, Takeo*; Onoe, Hironori; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-044, 37 Pages, 2014/01
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host crystalline rock at Mizunami City in Gifu, central Japan. The project consists of major research areas, "Geoscientific Research", and proceeds in three overlapping phases, "Phase I: Surface-based investigation Phase", "Phase II: Construction Phase" and "Phase III: Operation Phase". The present report summarizes the research and development activities planned for fiscal year 2013 based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.