Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD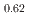 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 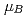 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD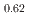 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In our previous article (Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014)), the site occupancies of D atoms dissolved in an fcc Fe metal lattice were investigated via Rietveld refinement of neutron powder diffraction patterns collected at 988 K and 6.3 GPa. The fcc metal lattice has two interstitial sites available for accommodating D atoms: octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The Rietveld refinement revealed that D atoms occupied mainly the octahedral sites with occupancy of 0.532 and slightly the tetrahedral sites with occupancy of 0.056. Subsequent density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations by Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019)) showed that the occupation energy on the tetrahedral site was significantly higher than that on the octahedral site; the tetrahedral site occupation was unlikely to occur even at temperatures as high as 988 K. We reexamined the site occupancies of D-atom by Rietveld refinement including extinction correction. As a result, the octahedral occupancy was increased to 0.60 and the tetrahedral occupancy was reduced to zero. The occupation of only the octahedral site for D atom is consistent with the DFT calculation, although in contrast to the previous results.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 587, p.412153_1 - 412153_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.28(Physics, Condensed Matter)The site occupancy of deuterium (D) atoms in face-centered-cubic nickel (fcc Ni) was measured along a cooling path from 1073 to 300 K at an initial pressure of 3.36 GPa via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms predominantly occupy the octahedral (O) sites and slightly occupy the tetrahedral (T) sites of the fcc metal lattice. The O-site occupancy increases from 0.4 to 0.85 as the temperature is lowered from 1073 to 300 K. Meanwhile, the T-site occupancy remains c.a. 0.02. The temperature-independent behavior of the T-site occupancy is unusual, and its process is not yet understood. From the linear relation between the expanded lattice volume and D content, a D-induced volume expansion of 2.09(13) 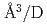 atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2
atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2 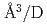 atom previously reported for Ni and Ni
atom previously reported for Ni and Ni Fe
Fe alloy.
alloy.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Iizuka, Riko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.9934_1 - 9934_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.41(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Neutron powder diffraction profiles were collected for iron deuteride (FeDx) while the temperature decreased from 1023 to 300 K for a pressure range of 4-6 GPa. The  ' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD
' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD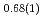 at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD
at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD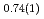 at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD
at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD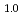 . In the dhcp FeD
. In the dhcp FeD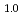 at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11
at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11  0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.12290_1 - 12290_9, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.40(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hexagonal close-packed iron hydride, hcp FeHx, is absent from the conventional phase diagram of the Fe-H system, although hcp metallic Fe exists stably over extensive temperature ( ) and pressure (
) and pressure ( ) conditions, including those corresponding to the Earth's inner core.
) conditions, including those corresponding to the Earth's inner core. 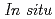 X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements at temperatures ranging from 298 to 1073 K and H pressures ranging from 4 to 7 GPa revealed that the hcp hydride was formed for FeH
X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements at temperatures ranging from 298 to 1073 K and H pressures ranging from 4 to 7 GPa revealed that the hcp hydride was formed for FeH compositions when
compositions when 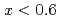 . Hydrogen atoms occupied the octahedral interstitial sites of the host metal lattice both partially and randomly. The hcp hydride exhibited a H-induced volume expansion of 2.48(5)
. Hydrogen atoms occupied the octahedral interstitial sites of the host metal lattice both partially and randomly. The hcp hydride exhibited a H-induced volume expansion of 2.48(5) 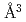 /H-atom, which was larger than that of the face-centered cubic (fcc) hydride. The hcp hydride showed an increase in
/H-atom, which was larger than that of the face-centered cubic (fcc) hydride. The hcp hydride showed an increase in  with
with  , whereas the fcc hydride showed a corresponding decrease. The present study provides guidance for further investigations of the Fe-H system over an extensive
, whereas the fcc hydride showed a corresponding decrease. The present study provides guidance for further investigations of the Fe-H system over an extensive  -
- -
- region.
region.
Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Iijima, Yuki*; Sato, Toyoto*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Miwa, Kazutoshi*; Ikeshoji, Tamio*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 54(19), p.5650 - 5653, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:69.33(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.5063_1 - 5063_6, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:87.34(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Iron hydride FeH , is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. To investigate the hydrogenation process and hydrogen state in iron hydride, it is necessary to carry out the in-situ measurement under high pressure and high temperature. In this study, we performed the in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of Fe-D system using the high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in the MLF, J-PARC, and determined the deuterium occupying sites and occupancies in fcc-FeD
, is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. To investigate the hydrogenation process and hydrogen state in iron hydride, it is necessary to carry out the in-situ measurement under high pressure and high temperature. In this study, we performed the in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of Fe-D system using the high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in the MLF, J-PARC, and determined the deuterium occupying sites and occupancies in fcc-FeD . We found the minor occupation of tetrahedral sites under high pressure and high temperature. We considered the mechanism of the minor occupation based on the Quantum-mechanical calculation.
. We found the minor occupation of tetrahedral sites under high pressure and high temperature. We considered the mechanism of the minor occupation based on the Quantum-mechanical calculation.
 RuH
RuH ; Prospect for formation of [FeH
; Prospect for formation of [FeH ]
] anion
anionTakagi, Shigeyuki*; Ikeshoji, Tamio*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Sato, Toyoto*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Orimo, Shinichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 103(11), p.113903_1 - 113903_4, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.31(Physics, Applied)Saito, Hiroyuki; Takagi, Shigeyuki*; Iijima, Yuki*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Orimo, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Iron hydride FeH , is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. Three hydride phases, bcc-FeH
, is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. Three hydride phases, bcc-FeH (
(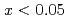 ), dhcp-FeH
), dhcp-FeH (
(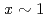 ), and fcc-FeH
), and fcc-FeH (
(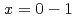 ) were confirmed at 300-2000 K and 0-20 GPa. In situ neutron diffraction measurement on their deutrides have not been reported yet. A high pressure neutron diffractometor, PLANET, constructed at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC, enables us to perform in situ neutoron diffraction measurements on deuterization process of metals at high pressure and high temperature. With PLANET, the deuteration process of iron was investigated at a pressure of about 7 GPa and temperatures up to about 1000 K. This in situ measurement was successfully made using a deuterization reaction cell developed for neutron diffraction measurement. We observed the bcc-fcc transition of pure iron around 800 K and successive deuterization of fcc-Fe around 870 K.
) were confirmed at 300-2000 K and 0-20 GPa. In situ neutron diffraction measurement on their deutrides have not been reported yet. A high pressure neutron diffractometor, PLANET, constructed at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC, enables us to perform in situ neutoron diffraction measurements on deuterization process of metals at high pressure and high temperature. With PLANET, the deuteration process of iron was investigated at a pressure of about 7 GPa and temperatures up to about 1000 K. This in situ measurement was successfully made using a deuterization reaction cell developed for neutron diffraction measurement. We observed the bcc-fcc transition of pure iron around 800 K and successive deuterization of fcc-Fe around 870 K.
 neutron diffraction measurement on the deuterization process of Fe at high temperature and high pressure
neutron diffraction measurement on the deuterization process of Fe at high temperature and high pressureMachida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English