Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niu, X.*; Elakneswaran, Y.*; Li, A.*; Seralathan, S.*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Walkley, B.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 190, p.107814_1 - 107814_17, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)Tanizaki, Shiho*; Kubo, Tomohiro*; Bito, Yosuke*; Mori, Shigeki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Sato, Kotaro*
RSC Sustainability (Internet), 3(4), p.1714 - 1720, 2025/04
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:94.96(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
Sato, Yuriko*; Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Sano, Tomokazu*; Ogino, Yosuke*
Communications Materials (Internet), 5, p.147_1 - 147_9, 2024/08
The flow dynamics of current-carrying molten metal jet breakup during arc discharge serves as mass and heat sources in wire-arc-based metal deposition processes, thereby optimizing the resultant product quality. However, the spatiotemporal flow interaction between the molten metal jet and the surrounding arc plasma remains unclear. Here, using in-situ synchrotron X-ray imaging, we simultaneously track surface deformation and internal flow in molten aluminum jets during argon arc discharge. We reveal that modulating the magnitude and path of the arc discharge current can accelerate the jet velocity by 200  300% beyond its initial injection speed, thereby facilitating significant jet elongation. Our results provide consistent evidence that the jet flow dynamics are predominantly governed by the interaction between the arc discharge current and its coaxial self-induced magnetic field. This study establishes a framework at the intersection of fluid dynamics and electromagnetism, contributing to optimized control and precision in wire-arc-based applications.
300% beyond its initial injection speed, thereby facilitating significant jet elongation. Our results provide consistent evidence that the jet flow dynamics are predominantly governed by the interaction between the arc discharge current and its coaxial self-induced magnetic field. This study establishes a framework at the intersection of fluid dynamics and electromagnetism, contributing to optimized control and precision in wire-arc-based applications.
Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Wei, T.*; Tatsumi, Yuta*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:75.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Matsuya, Yusuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kusumoto, Tamon*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Seino, Ryosuke*; Miwa, Misako*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Matsuyama, Shigeo*; Fukunaga, Hisanori*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.16696_1 - 16696_14, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.15(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a unique radiotherapy to selectively eradicate tumor cells using boron compounds (e.g., 4-borono-L-phenylalanine [BPA]) that are heterogeneously taken up at the cellular level. However, the impacts of tempo-spatial heterogenicity on cell killing remain unclear. With the technical combination of radiation track detector, cell cycle analysis, and biophysical simulations, we demonstrated the cell cycle-dependent heterogenicity of BPA uptake and following biological impacts of  B(n,
B(n,  )
) Li reactions in HeLa cells expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-based Cell Cycle Indicators (FUCCI), as well as its modification effects of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). As a result, we revealed that the intracellular BPA concentration in the S/G2/M phase was higher than that in the G1/S phase and that PVA modified the cell cycle dependence. Further, these findings lead to the development of the first BPA-PVA-based model for predicting BNCT treatment effects. These outcomes may contribute to more precision of therapeutic efficacy, when BNCT is combined with PVA and/or cell cycle-specific anticancer agents.
Li reactions in HeLa cells expressing Fluorescent Ubiquitination-based Cell Cycle Indicators (FUCCI), as well as its modification effects of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). As a result, we revealed that the intracellular BPA concentration in the S/G2/M phase was higher than that in the G1/S phase and that PVA modified the cell cycle dependence. Further, these findings lead to the development of the first BPA-PVA-based model for predicting BNCT treatment effects. These outcomes may contribute to more precision of therapeutic efficacy, when BNCT is combined with PVA and/or cell cycle-specific anticancer agents.
Saito, Yuki*; Ishiwata, Tobimaru*; Horiuchi, Misato*; Nishiki, Yuto*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Otake, Tsubasa*; Kawakita, Ryohei; Takayama, Yusuke; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Sato, Tsutomu*
Shigen, Sozai Koenshu (Internet), 11(1), 7 Pages, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:144 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:87.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
 - and K-montmorillonite
- and K-montmorilloniteKawakita, Ryohei; Saito, Akito*; Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Otake, Tsubasa*; Sato, Tsutomu*
Applied Clay Science, 231, p.106722_1 - 106722_7, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.27(Chemistry, Physical)Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko
PLOS ONE (Internet), 17(11), p.e0276364_1 - e0276364_16, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:67.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The displacement damage dose (DDD) has been used as an index to determine the lifetime of semiconductor devices used in space radiation environments. Recently, a new index, effective DDD, has been proposed, which takes into account the defect generation efficiency of materials obtained from molecular dynamics simulations. In this study, we developed a method to calculate both conventional and effective DDD for typical semiconductor materials such as SiC, InAs, GaAs, and GaN in the PHITS code. As a result, in the arsenic compounds InAs and GaAs, the number of defects increases due to amorphization and the effective DDD is larger than the conventional DDD, while in SiC the relationship is reversed due to defect recombination. The improved PHITS can be used to calculate the effective DDD of semiconductors in cosmic ray environments, and PHITS can make a significant contribution to the evaluation of radiation damage of new semiconductor devices in space.
Xu, S.*; Odaira, Takumi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Seiner, H.*; Zoubkov , K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
, K.*; Murakami, Yasukazu*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.5307_1 - 5307_8, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:82.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kunieda, Satoshi;  elik, Y.*; Furutachi, Naoya*; Niita, Koji*
elik, Y.*; Furutachi, Naoya*; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.665 - 675, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:93.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)A benchmark study of PHITS3.24 has been conducted using neutron-shielding experiments listed in the Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database. Five neutron sources were selected, which are generated from (1) 43- and 68-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thin lithium target, (2) 52-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick graphite target, (3) 590-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick lead target, (4) 500-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick tungsten target, and (5) 800-MeV proton-induced reaction on a thick tantalum target. For all cases, overall agreements in the results are satisfactory when using the JENDL-4.0/HE to simulate neutron- and proton-induced reactions up to 200 MeV. However, discrepancies using PHITS default settings are observed in the results. For an accurate neutron-shielding design for accelerator facilities, using JENDL-4.0/HE in the particle and heavy-ion transport code system calculation is favorable.
Takahashi, Nobuo; Kubota, Shintaro; Takiya, Hiroaki; Sakaba, Ryosuke*; Sato, Koichi; Shichi, Ryo
JAEA-Testing 2021-002, 106 Pages, 2022/01
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has various nuclear facilities such as reactor facilities and reprocessing facilities. Some aged facilities will be decommissioned after their original functions ended, and it is necessary to evaluate their decommissioning cost to formulate the initial decommissioning plans and the final decommissioning plans. We have developed an evaluation method called DECOST that can efficiently calculate the decommissioning cost in a short time based on factors such as features and similarity of the facilities and dismantling methods. The decommissioning of nuclear facilities has been implemented and new achievements and findings have been reported since the development of DECOST. These findings were reflected in DECOST. In consideration of the needs of DECOST users, DECOST has been improved so that the cost of dismantling the facility can be divided into the cost of releasing the controlled area and the cost of dismantling the facility building after the release of the controlled area. This report shows the improvement of DECOST, the concept of resetting the evaluation coefficient used in the cost evaluation formula, and the validity of the evaluation coefficient after resetting. In addition, the evaluation procedure of the improved DECOST is described, since the evaluation items and evaluation contents were partially changed due to the improvement.
Sato, Yuki*; Abe, Yosuke; Okubo, Kenji*; Tanioka, Takashi*
Philosophical Magazine, 102(12), p.1152 - 1172, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using in situ observation with high-voltage electron microscope, one-dimensional (1D) migration of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters under electron irradiation at 300 K was surveyed for copper materials of five nominal purities and TEM specimens prepared with three methods. In standard (STD) specimens that were prepared through cold rolling and annealing in the vacuum, formation and 1D migration of SIA clusters did not depend much on the nominal purity. In non-annealed (NA) specimens, prepared from high purity materials through mechanical processing and electropolishing, defect structure was coarser than in STD specimens. Results of bulk annealing (BA) specimens showed that annealing of as-received block material had minor effects. Above results were discussed based on the hypothesis that impurity atoms existing in as-received materials and those induced by annealing act as traps for SIA clusters.
 -iron investigated using in situ high-voltage electron microscopy
-iron investigated using in situ high-voltage electron microscopyAbe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
Philosophical Magazine, 102(12), p.1173 - 1193, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We measured the growth rate of self-interstitial atom (SIA) clusters in electron-irradiated  -iron at 275-320 K using in situ high-voltage electron microscopy. To improve the statistical accuracy of the measurement, we used photographic films and video data. This enabled analysis of a considerable amount of data by extracting several SIA clusters and tracking their size growth using image processing techniques. By fitting the temperature-dependent cluster growth rate to the Arrhenius relations derived using rate theory analysis, we obtained vacancy migration energy of
-iron at 275-320 K using in situ high-voltage electron microscopy. To improve the statistical accuracy of the measurement, we used photographic films and video data. This enabled analysis of a considerable amount of data by extracting several SIA clusters and tracking their size growth using image processing techniques. By fitting the temperature-dependent cluster growth rate to the Arrhenius relations derived using rate theory analysis, we obtained vacancy migration energy of 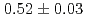 eV. In addition, the effects of impurities leading to decrease in the cluster growth rate were briefly discussed.
eV. In addition, the effects of impurities leading to decrease in the cluster growth rate were briefly discussed.
Moriguchi, Yuichi*; Sato, Yosuke*; Morino, Yu*; Goto, Daisuke*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Terada, Hiroaki; Takigawa, Masayuki*; Tsuruta, Haruo*; Yamazawa, Hiromi*
KEK Proceedings 2021-2, p.21 - 27, 2021/12
no abstracts in English