Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Shima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Seiji
MRS Advances (Internet), 8(6), p.243 - 249, 2023/06
In the intermediate depth disposal of relatively high-level radioactive waste, a method to confirm whether the borehole for monitoring is properly sealed should be developed in advance. In this study, groundwater flow analyses were performed for the hydrogeological structures with backfilled boreholes, assuming sedimentary rock area, to understand what backfill design conditions could prevent significant water pathways in the borehole, and to identify the confirmation points of borehole sealing. The results indicated the conditions to prevent water pathways in the borehole and BDZ (Borehole Disturbed Zone), such as designing the permeability of bentonite material less than or equal to that of the host rock, and grouting BDZ.
Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Mukai, Masayuki; Sawaguchi, Takuma
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-012, 122 Pages, 2022/01
Reducing public dose is required when radioactive wastes such as high-level and from reactor core internals etc. are disposed of by means of multi barrier system consist of engineered and natural barriers. In these barriers, engineered barrier is expected to bring out confinement function of waste's radionuclides in the barrier. Materials used as the engineered barriers are altered and performances of the barrier materials are degraded in course of time. To estimate properly the degraded performances, analytical evaluation of long-term change of the engineered barrier state is important. Change state of the engineered barrier is given by mass-transport and geochemical-reaction inside the barrier materials and these phenomena are interrelated, it is necessary to calculate the state by means of coupled analysis procedure. We have developed a coupled mass-transport and geochemical-reaction calculation code (MC- BUFFER) to evaluate alteration of engineered barrier specially targeted for water permeability of bentonite buffer material as one of most important performances to engineered barrier. This report describes functions expected for the engineered barrier, influence parameters for the functions, implementation models in MC-BUFFER, structure and functions of MC-BUFFER, input file format and output examples, execution method of MC-BUFFER, and sample run with MC-BUFFER.
Shimada, Asako; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Health Physics, 120(5), p.517 - 524, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Sawaguchi, Takuma
"Yugai Haikibutsu, Hoshasei Haikibutsu Eno Semento, Konkurito Gijutsu No Tekiyo Kenkyu Iinkai" Hokokusho (CD-ROM), p.165 - 173, 2020/12
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Asako; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Research 2020-005, 47 Pages, 2020/06
After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, large quantities of radiocesium-contaminated soil were generated from decontamination activities in the Fukushima prefecture. The removed soil has been stored in the prefecture until its final disposal. To complete the final disposal outside Fukushima prefecture, reducing the disposal volume through recycling can prove effective. The Ministry of the Environment, Japan (MOE) has presented a policy to recycle low-radioactive removed soil as recycled materials under the management of public authority. The recycling is limited to civil engineering structures in public projects. In this study, to contribute to guideline development for removed soil recycling by MOE, dose estimation in recycling of removed soil as embankment materials of seaside protection forest was conducted. First, additional doses to workers and the public in construction and service scenarios were evaluated. From the result, the radioactive cesium concentration level of recycled materials, where all additional doses meet the radiation criterion of 1 mSv/y, was derived to be 5,000 Bq/kg. Then, construction conditions were reviewed to reduce additional doses to the public in a service scenario. With the derived radioactivity level of 5,000 Bq/kg, the covered soil thickness of 39 cm or more limited the doses to less than 10  Sv/y. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were evaluated. The doses were confirmed to be below 1 mSv/y when the removed soil of 5,000 Bq/kg was used.
Sv/y. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were evaluated. The doses were confirmed to be below 1 mSv/y when the removed soil of 5,000 Bq/kg was used.
Shimada, Asako; Nemoto, Hiromi*; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00569_1 - 19-00569_17, 2020/06
After treatments such as sieve classification and washing of decontamination soil taken in Fukushima prefecture, recycling of the treated soil in which radioactivity concentration level is relatively low to public engineering works is invented to reduce the amount of the decontamination soil that must be disposed of. In the present study, dose estimation for workers and the public was conducted from the viewpoint of application of recycling material of decontamination soil for land reclamation by considering exposure pathways from the construction to the servicing of the land as a greenery-covered area. In the case of revegetation with trees, uptake of Cs into trees was considered and the exposure from trees, trimmed or thinned trees, and organic deposit made from litter fall were evaluated. From the results, the concentration levels of radiocesium,  Cs and
Cs and  Cs, for which the annual effective exposure dose does not exceed 1 mSv/y was calculated. In addition, the thickness of the cover soil required to maintain the exposure dose lower than 10
Cs, for which the annual effective exposure dose does not exceed 1 mSv/y was calculated. In addition, the thickness of the cover soil required to maintain the exposure dose lower than 10  Sv/y for the public during servicing was ascertained. Furthermore, disasters were considered; for instance, by considering that tsunamis, fires, and concentrated heavy rain can increase exposure doses based on changes in the conditions of the reclamation land, we confirmed that the additional exposure dose during disaster and rehabilitation is lower than 1 mSv/y. Based on these evaluation results, we determined the concentration levels amenable to recycling.
Sv/y for the public during servicing was ascertained. Furthermore, disasters were considered; for instance, by considering that tsunamis, fires, and concentrated heavy rain can increase exposure doses based on changes in the conditions of the reclamation land, we confirmed that the additional exposure dose during disaster and rehabilitation is lower than 1 mSv/y. Based on these evaluation results, we determined the concentration levels amenable to recycling.
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Asako; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 188(1), p.1 - 7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident, most of radiocesium-contaminated soil generated from decontamination activities outside Fukushima prefecture has been stored at decontamination sites such as schools, parks and residential lands (storage at sites) according to the Decontamination Guidelines. However, additional exposure due to the present storage has not been evaluated. Moreover, entering storage sites, which is not restricted for storage at sites, was not considered in safety assessment conducted in the guidelines. To continue the storage and confirm the effectiveness, understanding of present possible exposures is important. In this study, we evaluated exposure doses for residents and users of storage sites based on the present situation. As a result, annual doses due to residence were 10 to 10
to 10 mSv y
mSv y and doses due to annual entries were of the order of 10
and doses due to annual entries were of the order of 10 mSv y
mSv y . Hence, we confirmed that the exposure due to present storage outside Fukushima is significantly less than 1 mSv y
. Hence, we confirmed that the exposure due to present storage outside Fukushima is significantly less than 1 mSv y .
.
Shimada, Asako; Nemoto, Hiromi*; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
no abstracts in English
Takai, Shizuka; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Health Physics, 115(4), p.439 - 447, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.93(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Nuclear Power Station accident, large quantities of radiocesium-contaminated soil generated from decontamination activities have been stored in the Fukushima Prefecture. To reduce the disposal volume, the Ministry of the Environment of Japan has presented a policy to recycle low-radioactive decontamination soil limited to civil engineering structures. However, there has been no practical instance or safety assessment of decontamination soil recycling. In this study, the way of ensuring the safety for decontamination soil recycling for road embankments was discussed. First, based on Japanese construction standards, additional doses to workers and the public in construction and service scenarios were evaluated. From the result, the radioactive cesium concentration level of recycled materials, where all additional doses meet the radiation criterion of 1 mSv y , was derived to be 6,000 Bq kg
, was derived to be 6,000 Bq kg . To confine additional doses to the public in a service scenario below 0.01 mSv y
. To confine additional doses to the public in a service scenario below 0.01 mSv y , soil slope protection of 40 cm or more was needed. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were confirmed to be below 1 mSv y
, soil slope protection of 40 cm or more was needed. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were confirmed to be below 1 mSv y .
.
Takai, Shizuka; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposia 2018 (WM2018) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2018/03
After the Fukushima Nuclear Power Station accident, large quantities of radiocesium-contaminated soil generated from decontamination activities have been stored in the Fukushima prefecture. To complete the final disposal of decontamination soil, the Ministry of the Environment of Japan presented policy to reduce the disposal volume by using low-level decontamination soil as recycled materials. The use will be limited to civil engineering structures in public projects, such as coastal levee and road embankment. However, there has been no example or safety assessment of recycling of decontamination soil. To contribute to guideline development for the recycling by the Ministry of the Environment, we conducted the safety assessment for recycling of decontamination soil as coastal levee. First, we evaluated additional doses to workers and the public in the case of construction and service of coastal levee. From the result, the radioactive cesium concentration level of recycled materials was derived to be 6,800 Bq/kg. For general designs of coastal levee in Japan, additional doses to the public in the case of service were below 0.01 mSv/y with derived radioactivity level. Finally, we confirmed additional doses in the case of disaster to be below 1 mSv/y.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Takeda, Seiji; Okada, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(8), p.445 - 447, 2017/08
, 59(8), p.445 - 447, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(5), P. 815, 2016/12
ERRATUM; Effects of OH activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditionsSawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.267 - 278, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:24.33(Chemistry, Physical)The dependences of the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite on activity of OH (a
(a -) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (
-) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (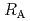 ) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as
) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as 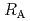 = 10
= 10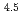 (a
(a -)
-)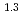 e
e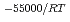 , was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures:
, was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures: 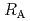 = 3500 (a
= 3500 (a -)
-)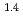 e
e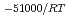 . The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a
. The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a - in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a
- in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a - is achieved somehow.
- is achieved somehow.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Hoshino, Seiichi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.279 - 287, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:24.33(Chemistry, Physical)Alteration of bentonite-cement interfaces and accompanying changes in diffusivity of tritiated water was experimentally investigated using intact hardened cement specimens. The alteration by carbonate solution was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 70% of the initial value after 180-day period. Another alteration under silicate system contacting hardened cement and compacted bentonite was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 71% of the initial value after 600-day period. The changes in the diffusivity were much less than those observed for mixed specimens of granulated hardened cement and bentonite where the diffusivity decreased down to 20% of the initial value over 180 days. The results were extrapolated to 15 years under simple assumptions and showed good agreement with those observed in the cement-argillite interface at Tournemire URL. Such an explanation enhances our confidence in our assessment of alteration of cement-bentonite systems and can be a base for using our data and models in long term assessment of radioactive waste disposal.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo; Tanaka, Tadao
Hoken Butsuri, 50(1), p.36 - 49, 2015/03
It is desirable that the disaster wastes contaminated by radioactive cesium after the severe accident at the Fukushima Nuclear Plant are reused as much as possible in order to minimize the quantity to be disposed of. Ministry of the Environment showed the policy that the wastes containing cesium of higher concentration than the clearance level (100 Bq/kg) were reusable as materials of construction such as subbase course materials of pavements under controlled condition with measures to lower exposure doses. In this study, in order to provide technical information for making a guideline on the use of contaminated concrete materials recycled from disaster wastes as pavement, doses for workers and the public were estimated, and the reusable concentration of radioactive cesium in the wastes was evaluated. It was shown that the external exposure of the public (children) residing near the completed pavement gave the minimum radiocesium concentration in order to comply with the dose criteria. The recycled concrete materials whose average concentration of cesium lower than 2,700 Bq/kg can be used as the subbase course materials of pavements.
Takeda, Seiji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Kimura, Hideo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1665, p.103 - 109, 2014/09
Some kinds of material in the environment due to the accident at the Fukushima Nuclear Plant have been contaminated by radioactive cesium, which are represented by dehydrated sludge, surface soil, disaster wastes generated by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake and so on. Treatment (transportation, temporary storage or incineration) and disposal of the contaminated materials should be carried out while ensuring the safety of radiation for the workers and the public. In this study, in order to provide the technical information for making the guideline, the dose estimate for scenarios on the treatment and disposal is conducted, based on the method used for driving the clearance levels in Japan. Minimum activity concentration in contaminated material is calculated from the dose results, corresponding to the effective dose criterions indicated by the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan (June 3, 2011). From the calculation result, it is suggested that it is necessary to forbid reusing the disposal site as construction, resident and agriculture in which the calculated doses for the public are higher than those in the other exposure pathways. Minimum activity concentration of radioactive cesium is derived to be 8.9 Bq/g for exposure pathway in landfill work under the condition of limited reuse of the site. In the case of the activity concentration below 8.9 Bq/g, the calculated dose of the resident due to direct and sky-shine radiation from the temporary storage place is less than 1 mSv/y, irrespective of the distance from the storage place.
Sawaguchi, Takuma
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 21(1), P. 56, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Kadowaki, Mitsushi*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki; Tanaka, Tadao
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 20(2), p.71 - 78, 2013/12
The dissolution rate for montmorillonite under compacted condition was studied in order to evaluate long-term alteration behavior of bentonite buffer materials by highly alkaline groundwater. The dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite was found to be larger than that of montmorillonite in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures at 130  C, which revealed that the dissolution of montmorillonite was inhibited by decreasing the activity of hydroxide ions (
C, which revealed that the dissolution of montmorillonite was inhibited by decreasing the activity of hydroxide ions (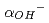 ) in the compacted mixtures including accessory minerals such as silica. In order to provide reliability for the analysis of bentonite-alteration using a formula of dissolution rate of montmorillonite, it is important to quantify the decrease of
) in the compacted mixtures including accessory minerals such as silica. In order to provide reliability for the analysis of bentonite-alteration using a formula of dissolution rate of montmorillonite, it is important to quantify the decrease of 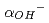 in the compacted mixtures and to formulate the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite.
in the compacted mixtures and to formulate the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Kadowaki, Mitsushi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.403 - 410, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:29.71(Chemistry, Physical)Montmorillonite is the main constituent of bentonite clay buffer materials in radioactive waste repositories. Highly alkaline environments induced by cement based materials are likely to alter montmorillonite, and to deteriorate the physical and/or chemical properties of the buffer materials. The deterioration may cause variation in hydraulic conductivity of the buffer and induce major uncertainties in the radionuclide migration analysis. Empirical data on the variation of hydraulic conductivity are, however, scarce mainly because the alteration of compacted buffer materials, sand-bentonite mixture specimen, is extremely slow. In this study, laboratory experiments were performed to observe changes in hydraulic conductivity of sand-bentonite mixtures accompanied with their alkaline alteration using NaOH based solutions at 80-90  C. Three types of experiments proved that the alkaline alteration of bentonite buffer can increase the hydraulic conductivity. The data obtained in this study are useful for verification of the code that will be used for assessing the alteration.
C. Three types of experiments proved that the alkaline alteration of bentonite buffer can increase the hydraulic conductivity. The data obtained in this study are useful for verification of the code that will be used for assessing the alteration.