Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Mika; Hidaka, Akihide; Ikuta, Yuko; Murakami, Kenta*; Tomita, Akira*; Hirose, Hiroya*; Watanebe, Masanori*; Ueda, Kinichi*; Namaizawa, Ken*; Onose, Takatoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-002, 60 Pages, 2017/03
Since 2010, IAEA has held the NEM School to develop future leaders who plan and manage nuclear energy utilization in their county. Since 2012, JAEA together with Japan Nuclear HRD Network, University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Industrial Forum and JAIF International Cooperation Center have cohosted the school in Japan in cooperation with IAEA. Since then, the school has been held in Japan every year. In 2006, Japanese nuclear technology and experience, such as lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, were provided to offer a unique opportunity for the participants to learn about particular cases in Japan. Through the school, we contributed to the internationalization of Japanese young nuclear professionals, development of nuclear human resource of other countries including nuclear newcomers, and enhanced cooperative relationship with IAEA. Additionally, collaborative relationship within the network was strengthened by organizing the school in Japan.
Hidaka, Akihide; Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Watanabe, Yoko; Yabuuchi, Yukiko; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Sawada, Makoto; Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Murakami, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2015/05
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
Proceedings of 11th Meeting of the Task Force on Shielding Aspects of Accelerators, Targets and Irradiation Facilities (SATIF-11), p.91 - 98, 2013/10
We have developed the displacement damage model in PHITS using the screened Coulomb scattering and the nuclear reaction model to evaluate the energy of the target PKA created by the projectile and the "secondary particles" which include all particles created from the sequential nuclear reactions. For the high-energy proton and neutron incident reactions, it was found that a target PKA created by the "secondary particles" is more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Recently, radiation damage models in other codes such as FLUKA, MARS, MCNP have also been developed. As there is few experimental data in a high energy region, an intercomparison of Monte Carlo codes used in the radiation damage calculation is very important for the improvement of models. In the meeting, we will also discuss the comparison between PHITS and FLUKA for the high-energy proton and neutron irradiation.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 303, p.120 - 124, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)Recently, the radiation damage model in PHITS has been developed using the screened Coulomb scattering to evaluate the energy of the target PKA (Primary Knock on Atom) created by the projectile and the "secondary particles" which include all particles created from the sequential nuclear reactions. For the high-energy proton and  He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the "secondary particles" was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment. In the meeting, we will also present DPA values and energy spectra for secondary particles created by neutrons in the energy ranges from thermal to around 1 GeV.
He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the "secondary particles" was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment. In the meeting, we will also present DPA values and energy spectra for secondary particles created by neutrons in the energy ranges from thermal to around 1 GeV.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Harada, Masahide; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu
Robutsuri No Kenkyu (Internet), (65), p.1 - 3, 2013/03
The displacement cross sections for common structural materials were calculated using the radiation damage model in PHITS. The displacement cross sections with the defect production efficiency gave good agreement with experimental data. For application to the DPA calculations at 400 MeV proton and 40 MeV deuteron, calculated cross sections were folded into calculated particle fluxes in PHITS. Thus the PHITS including the displacement cross sections can be useful to calculate the DPA values in materials used at accelerator facilities that will be exposed to intense primary and secondary particle irradiation. It will also be useful at fission and fusion reactor facilities.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei*
Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems (SMINS-2), p.273 - 279, 2012/12
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 274, p.57 - 64, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:84.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)The radiation damage model in the PHITS has been improved using the screened Coulomb scattering to evaluate the energy of the target PKA (Primary Knock on Atom) created by the projectile and the secondary particles from the nuclear reactions. For the high-energy proton and  He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the secondary particles was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Therefore, the improved PHITS can calculate DPA values at high energies and TRIM leads to severe underestimation where projectile energy is high enough to create nuclear reactions. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment.
He incident reactions, a target PKA created by the secondary particles was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile in DPA calculations. Therefore, the improved PHITS can calculate DPA values at high energies and TRIM leads to severe underestimation where projectile energy is high enough to create nuclear reactions. Thus improved PHITS is applicable to evaluate the displacement cross sections for the various particles and over a wide energy range and to calculate DPA values determined by different particles and fluxes in an irradiation environment.
Okubo, Nariaki; Sokolov, M. A.*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Hirose, Takanori; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Odette, G. R.*; Stoller, R. E.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.112 - 114, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation hardening and fracture toughness of reduced-activation ferritic/martensitic steel F82H after irradiation were investigated with a focus on changing the fracture toughness transition temperature as a result of several heat treatments. The specimens were standard F82H-IEA (IEA), F82H-IEA with several heat treatments (Mod1 series) and a higher tantalum containing (0.1%) heat of F82H (Mod3). The specimens were irradiated up to 18 dpa at 300  C in High Flux Isotope Reactor under a collaborative research program between JAEA/US-DOE. The results of hardness tests showed that irradiation hardening of IEA was comparable with that of Mod3. However, the fracture toughness transition temperature of Mod3 was lower than that of IEA. The transition temperature of Mod1 was also lower than that of the IEA heat. These results suggest that tightening of specifications on the heat treatment condition and modification of the minor alloying elements seem to be effective to reduce the fracture toughness transition temperature after irradiation.
C in High Flux Isotope Reactor under a collaborative research program between JAEA/US-DOE. The results of hardness tests showed that irradiation hardening of IEA was comparable with that of Mod3. However, the fracture toughness transition temperature of Mod3 was lower than that of IEA. The transition temperature of Mod1 was also lower than that of the IEA heat. These results suggest that tightening of specifications on the heat treatment condition and modification of the minor alloying elements seem to be effective to reduce the fracture toughness transition temperature after irradiation.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Niita, Koji*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ronningen, R. M.*; Baumann, T.*
JAEA-Conf 2011-002, p.157 - 162, 2011/09
Radiation damage measured as a function of DPA is one of the critical issues for high-intensity beams, especially heavy-ions. The DPA model in PHITS has recently been extended to include contributions from Coulomb elastic scattering of transported charged particles. For the Coulomb elastic scattering, a universal one-parameter differential scattering cross section equation introduced by J. Lindhard et al. is employed instead of the differential Rutherford cross section which is a function of six parameters; charge and mass number of incident and produced particles, kinetic energy of incident particle and scattered angle. In this work, we compare PHITS results for the 130 MeV/u  6Ge+
6Ge+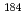 W reaction with calculated results of TRIM which is two-dimensional damage calculation code. Then we calculate DPA for different ions, targets and energies in the energy region from 100 MeV/u to 1 GeV/u and evaluate the systematics of DPA.
W reaction with calculated results of TRIM which is two-dimensional damage calculation code. Then we calculate DPA for different ions, targets and energies in the energy region from 100 MeV/u to 1 GeV/u and evaluate the systematics of DPA.
Kim, G.; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1298, p.61 - 66, 2011/04
The irradiation behaviour in two different precipitation hardening types of Ni-base alloys with the ultra high purity grade (EHP), namely, the  ' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe
' type and G phase type was investigated by multi-ion beam techniques simulated to the irradiation conditions in fuel cladding tubes used in sodium cooled FBRs. Single ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Fe or Ni
or Ni ) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni
) at 673 K. Triple ion-beam irradiation tests were conducted up to 90 dpa (by Ni , 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP(
, 90 appmHe and 1350 appmH) at 823 K. The irradiation behaviour was examined by nano-indentation tests to irradiation hardening, and the microscopic observation by TEM to the distribution of dislocations, cavities and voids. The behaviour was compared with those of PNC316. The dominating irradiation defects in EHP( ') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along
') alloy at 673 K by single ion-beam are Frank loops, perfect unfaulted loops and line dislocations. Whereas, those of EHP(WSi) alloy are the irradiation-induced G phase precipitates along 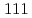 planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP(
planes. Those dominating defect structures at 823 K by triple ion-beam are classified as followings, bimodal distributions in EHP( '), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP(
'), bubbles in EHP(WSi) and voids in PNC316. The ratio of void swelling is estimated as nearly 0.01% in EHP(WSi), 0.2% in EHP( '), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
'), 3.4% in PNC316. From those results, the excellent irradiation properties of EHP(WSi) alloy is clarified as the inhibition effects of secondary irradiation defects.
Ando, Masami; Wakai, Eiichi; Okubo, Nariaki; Ogiwara, Hiroyuki; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Onuki, Somei*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 71(12), p.1107 - 1111, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.85(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Takao; Kasada, Ryuta*; Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2850 - 2855, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The impact of increasing the enrichment of  N in low activation ferritic steel, F82H, of a fusion reactor has been investigated in order to increase the fraction of low level material (LLM), which can be disposed by shallow land burial. Carbon-14, mainly produced from nitrogen, is one of the most critical nuclei for qualifying as a LLM. The concentration of nitrogen in F82H is 200 ppm in the calculations. The enrichment of
N in low activation ferritic steel, F82H, of a fusion reactor has been investigated in order to increase the fraction of low level material (LLM), which can be disposed by shallow land burial. Carbon-14, mainly produced from nitrogen, is one of the most critical nuclei for qualifying as a LLM. The concentration of nitrogen in F82H is 200 ppm in the calculations. The enrichment of  N was varied from natural abundance of 0.37% to 95%. The concentration of
N was varied from natural abundance of 0.37% to 95%. The concentration of  C at the outboard first wall decreased from 7.8
C at the outboard first wall decreased from 7.8  10
10 to 3.2
to 3.2  10
10 Bq/g by enriching
Bq/g by enriching  N, which is lower than the
N, which is lower than the  C regulation (3.7
C regulation (3.7  10
10 Bq/g) for LLM in Japan. In the permanent blanket, the highest
Bq/g) for LLM in Japan. In the permanent blanket, the highest  C concentration with 95%
C concentration with 95%  N enriched nitrogen was 1.0
N enriched nitrogen was 1.0  10
10 Bq/g. The
Bq/g. The  C concentration on the inboard side was lower than the outboard side. Therefore, with regard to the
C concentration on the inboard side was lower than the outboard side. Therefore, with regard to the  C concentration, the F82H used in the inboard and outboard blankets can qualify as a LLM by enriching
C concentration, the F82H used in the inboard and outboard blankets can qualify as a LLM by enriching  N.
N.
Shibama, Yusuke; Arai, Takashi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Suzuki, Yutaka; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Miya, Naoyuki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2462 - 2470, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The structural design of the tile as a ripple reduction for toroidal magnetic field in JT-60U was outlined. 8Cr-2W-0.2V ferritic steel plates were fabricated and mechanical and vacuum properties were evaluated to assess the design conditions. Tensile properties were uniform in yield and tensile strength at ambient temperature and sufficient strength as the structural integrity at operational temperature of 423 K and 573 K. Vacuum property was measured with the baking at 473 K and similar to the conventional stainless steel but not satisfy the JT-60 standard of the in-situ material of the vacuum vessel. The ferritic steel was judged as an installable because of that the JT-60 baking temperature is 573 K higher than this test temperature of 473 K, and of that residual out-gassing was hydrogen which was the fuel of the operational plasma.
Wakai, Eiichi; Ando, Masami; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Stroller, R. E.*; Yamamoto, Toshio; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.74 - 80, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ando, Masami; Li, M.*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Grossbeck, M. L.*; Kim, S.-W.; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Kono, Yutaka*; Koyama, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.122 - 126, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:76.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation creep behavior of the F82H and several JLF-1 steels have been measured up to 5 dpa, using helium-pressurized creep tubes irradiated in HFIR. These tubes were pressurized with helium to hoop stress levels of 0 to 400 MPa for irradiation temperature. The results of F82H and JLF-1 with 200 MPa hoop stress showed small creep strains ( 0.15%) after irradiation. Irradiation creep rate in these steels is linearly dependent on the applied stress less than 200 MPa. However, at higher hoop stress level, the creep rate of them is nonlinear. The creep compliance coefficient for F82H and JLF-1 at 300
0.15%) after irradiation. Irradiation creep rate in these steels is linearly dependent on the applied stress less than 200 MPa. However, at higher hoop stress level, the creep rate of them is nonlinear. The creep compliance coefficient for F82H and JLF-1 at 300  C is very small values. These data contribute to a part of materials database for ITER Test blanket design work.
C is very small values. These data contribute to a part of materials database for ITER Test blanket design work.
Okubo, Nariaki; Wakai, Eiichi; Matsukawa, Shingo*; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.107 - 111, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Ando, Masami; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Onuki, Somei*
Materials Transactions, 48(6), p.1427 - 1430, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:52.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Effects of helium and hydrogen production on irradiation hardening of martensitic steel F82H (Fe-8Cr-2W-0.2V-0.04Ta-0.1C) were examined by dual or triple beam experiments. The effects of tempering and cold working were also examined. The irradiations were performed at about 500 C to 50 dpa under simultaneous dual beams of 10.5 MeV-Fe and 1.05 MeV-He or triple beams of those and 380keV-H ions. The value of appm-He/dpa for the dual ion beams was about 15, and the values of appm-He/dpa and appm-H/dpa for the triple ion beams were 15 and 15 (or 150), respectively. The hardness of the irradiated specimens measured at room temperature using a micro indentation after the irradiations. Irradiation softening and hardening was observed in F82H-std, F82H+CW and a non-tempered F82H steels irradiated at about 500
C to 50 dpa under simultaneous dual beams of 10.5 MeV-Fe and 1.05 MeV-He or triple beams of those and 380keV-H ions. The value of appm-He/dpa for the dual ion beams was about 15, and the values of appm-He/dpa and appm-H/dpa for the triple ion beams were 15 and 15 (or 150), respectively. The hardness of the irradiated specimens measured at room temperature using a micro indentation after the irradiations. Irradiation softening and hardening was observed in F82H-std, F82H+CW and a non-tempered F82H steels irradiated at about 500 C to 18 and 50 dpa, respectively, by dual ion beams. The hardness of the specimens irradiated at about 500
C to 18 and 50 dpa, respectively, by dual ion beams. The hardness of the specimens irradiated at about 500 C to 18 dpa under triple ion beams was harder than that under dual ion beams.
C to 18 dpa under triple ion beams was harder than that under dual ion beams.
Kawamura, Hiroshi; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Eko Materiaru Handobukku, p.647 - 648, 2006/12
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Yusuke; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Suzuki, Yutaka; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Hayashi, Takao; Takahashi, Ryukichi*; Honda, Masao; Jitsukawa, Shiro; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49(96), p.S297 - S301, 2006/12
Installation of ferritic steel tiles was proposed in JT-60U to reduce the toroidal magnetic field ripple and to improve the fast ion loss, which degrades heating efficiency and increases heat load on plasma facing component under large volume plasma operations. We selected a 8Cr-2W-0.2V ferritic steel with the cost-effectiveness, in which concentration limits of activation elements in F82H were relaxed because of the less number of neutron generations from deuterium operations on JT-60U. The fabricated ferritic steel has clear tempered martensitic microstructure, and sufficient magnetic and mechanical properties. The saturated magnetization was estimated to 1.7 Tesla at 573 K, lower than expected, but effectiveness in JT-60U was confirmed by numerical analyses. To research the effect of material conditions, such as microstructure and heat treatment, on saturated magnetization of the ferritic steel based on 8-9Cr is important for the future fusion reactors which will be planned to install the ferritic steel as the in-vessel components.
Sawai, Tomotsugu; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 356(1-3), p.118 - 121, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A type 316 stainless steel 316F and Ti-modified type 316 stainless steel JPCA irradiated in SINQ were examined using transmission electron microscopy. Estimated irradiation temperature for two 316F specimens were 250-300 C and that for the JPCA specimen was 255
C and that for the JPCA specimen was 255 C. Irradiation damage of these specimens is calculated to be about 10 dpa. Frank loops up to 30 nm and larger perfect loops up to 50 nm were observed in 316F irradiated at 300
C. Irradiation damage of these specimens is calculated to be about 10 dpa. Frank loops up to 30 nm and larger perfect loops up to 50 nm were observed in 316F irradiated at 300 C. Frank loops observed in JPCA is somewhat smaller, suggesting lower dislocation bias in JPCA.
C. Frank loops observed in JPCA is somewhat smaller, suggesting lower dislocation bias in JPCA.