Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Hideaki; Nakama, Shigeo; Fujita, Tomoo; Imai, Hisashi; Sazarashi, Masami
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 19(2), p.39 - 50, 2012/12
For the safety assessment of a geological disposal system for high-level radioactive waste, it is necessary to quantify coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) processes in the near-field. The current study investigated the geochemical changes arising from the infiltration of groundwater into the bentonite buffer under a thermal regime of radiogenic heating arising from the vitrified waste with the computer simulated assistance of a developed THMC model. In the case of infiltration by a saline groundwater, sulfate precipitates as gypsum around the overpack in the bentonite buffer and the Na-type bentonite changes to Ca-type by exposure to Ca ions released from concrete supports. In addition, the temporal evolution of the bentonite buffer porewater composition can be obtained to assess its contribution to the corrosion of the overpack.
Kimura, Makoto*; Sazarashi, Masami; Fujita, Tomoo; Nakama, Shigeo; Suzuki, Hideaki
JAEA-Research 2010-034, 131 Pages, 2010/10
Numerical model which can quantify the complex evolution of the coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical processes in the near-field of a HLW repository has been developed and the outline of the model considering heat flow, fluid flow, mass transport and a variety of chemical reactions such as mineral dissolution/precipitation, gas dissolution/exsolution, ion-exchange and surface complexation are described. The applicability of the numerical model was shown by the following three efforts. (1) Intercomparison analysis against another coupled model, TOUGHREACT which has been developed in the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. (2) Comparison with the measured data in the designed laboratory tests for the salt accumulation/precipitation. (3) Perspective simulation on chemical changes in the near-field involving the radioactive decay heat arising from the vitrified waste and infiltration of ground water into the buffer material.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Tomoko*; Sato, Hisao*; Sazarashi, Masami
JAEA-Research 2010-030, 64 Pages, 2010/09
It is necessary to evaluate the alteration behavior of buffer material by interactions of overpack (iron) and buffer (bentonite) materials for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste. In the present study, laboratory experiments were carried out for the better understanding of phenomena caused by iron-bentonite (smectite) interactions. Before conducting the experiments, literature survey was performed to summarize the existing knowledge about iron-bentonite interactions and to identify the dominant factors affecting the alteration behavior. As the results of experiment, experimental conditions caused remarkable alteration, secondary minerals suggested as alteration product, different behavior of alteration between batch and compacted systems etc. were revealed.
Fujita, Tomoo; Yui, Mikazu; Suzuki, Hideaki*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi; Sazarashi, Masami*
JAEA-Research 2007-017, 47 Pages, 2007/03
This report describes the results of a joint research entitled "Study on Simulation of Salt Accumulation" which was conducted under the collaboration between the Institute of Research and Innovation and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In the experiments for salt accumulation, accumulation of 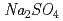 and
and 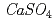 was observed near the heater surface. Based on the facts from experiments, we have made hypothesis for mechanism of salt accumulation, and developed the model for it. Then, we conducted numerical simulations for salt accumulation phenomena under the saturated condition using the geochemical code "PHREEQC". It became clear that salt accumulation behavior can be evaluated qualitatively from these simulations, but quantitative evaluation requires more realistic modeling. Moreover we evaluated salt accumulation phenomena by simulations using coupled thermo - hydro - mechanical and chemical model / code assuming the unsaturated and / or saturated condition. A series of simulations were conducted focusing on accumulation of gypsum, and the result showed that tendency of salt accumulation phenomena was in agreement with that of experiments, but the profile of distribution of accumulated gypsum was not in agreement. In conclusion, it became clear that more realistic boundary condition should be considered and problems on coupled model / code were identified for further study.
was observed near the heater surface. Based on the facts from experiments, we have made hypothesis for mechanism of salt accumulation, and developed the model for it. Then, we conducted numerical simulations for salt accumulation phenomena under the saturated condition using the geochemical code "PHREEQC". It became clear that salt accumulation behavior can be evaluated qualitatively from these simulations, but quantitative evaluation requires more realistic modeling. Moreover we evaluated salt accumulation phenomena by simulations using coupled thermo - hydro - mechanical and chemical model / code assuming the unsaturated and / or saturated condition. A series of simulations were conducted focusing on accumulation of gypsum, and the result showed that tendency of salt accumulation phenomena was in agreement with that of experiments, but the profile of distribution of accumulated gypsum was not in agreement. In conclusion, it became clear that more realistic boundary condition should be considered and problems on coupled model / code were identified for further study.
Sazarashi, Masami*; ; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*; ;
PNC TJ1564 97-002, 20 Pages, 1997/03
None
Sazarashi, Masami*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*; ;
PNC TJ1564 96-002, 19 Pages, 1996/03
None
Sazarashi, Masami*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*
PNC TJ1564 93-003, 17 Pages, 1993/02
The present study has been carrisd out to establish the final disposal methods for e wastes containing radioactive iodines. In the previous studies, cinnabar (spain) a montmorillonite containing Ag-thiourea complex were selected as the arificial barri materials. In the present report, the adsorption mechanisms of two adsorbents were udied in more detail. Furthermore, various synthetic inorganic ion exchangers were ao examined as the model materials of I ion adsorbents. The results are summarized afollow : 1. Detail examination for I
ion adsorbents. The results are summarized afollow : 1. Detail examination for I ion adsorption behavior of cinnabar (1) In avaible cinnabars, only spain one has an adsorptivity to I
ion adsorption behavior of cinnabar (1) In avaible cinnabars, only spain one has an adsorptivity to I ion. (2) The cinnabar adsorde has the selective adsorptivity to I
ion. (2) The cinnabar adsorde has the selective adsorptivity to I ion. (3) It takes 40 days to reach the adsorpti equilibrium. (4) The amount of adsorbed I
ion. (3) It takes 40 days to reach the adsorpti equilibrium. (4) The amount of adsorbed I ions decreases with the rise of pH, and t desorption of I
ions decreases with the rise of pH, and t desorption of I ions from cinnadar is not observed. These results suggest that thedsorption of I
ions from cinnadar is not observed. These results suggest that thedsorption of I ions on cinnabar is not due to the ion exchange but the compo
ions on cinnabar is not due to the ion exchange but the compo
Sazarashi, Masami*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*
PNC TJ1564 93-002, 23 Pages, 1993/02
None
Sazarashi, Masami*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Kumagai, Mikio*
PNC TJ1262 91-001, 168 Pages, 1991/05
None
Suzuki, Hideaki; Nakama, Shigeo; Fujita, Tomoo; Imai, Hisashi; Sazarashi, Masami
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sazarashi, Masami; Suzuki, Hideaki; Fujita, Tomoo; Yamashita, Ryo*; Imai, Hisashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Taniguchi, Naoki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Kawasaki, Manabu; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*; Sazarashi, Masami
no journal, ,
Immersion tests of carbon steel were carried out in bentonite saturated with synthetic seawater between 30-160  C. The corrosion depth was measured by weight loss of the specimens. The results showed that the initial corrosion rates increased with increasing temperature, and that the most protective corrosion product film was formed at 80-120
C. The corrosion depth was measured by weight loss of the specimens. The results showed that the initial corrosion rates increased with increasing temperature, and that the most protective corrosion product film was formed at 80-120  C. In order to evaluate the possibility of hydrogen embrittlement, the content of absorbed hydrogen (diffusive hydrogen) in specimens were analyzed. The results showed a tendency of decreasing the content of absorbed hydrogen with increasing temperature.
C. In order to evaluate the possibility of hydrogen embrittlement, the content of absorbed hydrogen (diffusive hydrogen) in specimens were analyzed. The results showed a tendency of decreasing the content of absorbed hydrogen with increasing temperature.
Sazarashi, Masami; Taniguchi, Naoki; Naito, Morimasa; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagatani, Mutsumi; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*; Sazarashi, Masami; Fujita, Tomoo; Chijimatsu, Masakazu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Makoto; Fujita, Tomoo; Sazarashi, Masami
no journal, ,
For the purpose of developing of the coupled Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical-Chemical(THMC) simulation code which is available to the prediction of the salt accumulation/precipitation, a chemical reaction model paid attention to unsaturated buffer material is discussed. In the THMC simulation code, chemical reaction model such as ion-exchange and surface complexation which are based on water-retention form and infiltration history under the unsaturated condition is considered. Some results of THMC simulation against the laboratory test are shown and it is found that mass-transport under the unsaturated/saturated condition is suitable but necessary to consider the change of solid/liquid ratio for the chemical reaction.
Kimura, Makoto; Fujita, Tomoo; Sazarashi, Masami; Suzuki, Hideaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sazarashi, Masami; Imai, Hisashi; Suzuki, Hideaki; Fujita, Tomoo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sazarashi, Masami; Imai, Hisashi; Suzuki, Hideaki; Fujita, Tomoo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Sazarashi, Masami; Ishii, Tomoko*; Sato, Hisao*; Kato, Hiroyasu*
no journal, ,
To investigate bentonite-iron interaction under high temperature condition, alteration experiments considering several factors (smectite composition, solution chemistry, iron-bentonite ratio) which were believed to affect on bentonite alteration were conducted with different experimental conditions. As the results, it was suggested that the factors considered in this study could also significantly affect on bentonite alteration in addition to temperature condition.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Sazarashi, Masami; Ishii, Tomoko*; Sato, Hisao*; Kato, Hiroyasu*
no journal, ,
To investigate bentonite-iron interaction under high temperature condition, alteration experiments considering several factors (smectite composition, solution chemistry, iron-bentonite ratio) which were believed to affect on bentonite alteration were conducted with different experimental conditions. As the results, it was suggested that the factors considered in this study could also significantly affect on bentonite alteration in addition to temperature condition.