Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kikuchi, Shin; Kondo, Toshiki; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Ogawa, Kengo*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
Koie, Ryusuke*; Kawaguchi, Munemichi*; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*; Seino, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/08
In order to investigate removal mechanisms of cesium aerosol from noble gas bubble in sodium pool, we performed a water simulation test to measure the decontamination factors of simulant aerosols with nitrogen gas bubbles rising through the water pool. As a result, it was found that the decontamination factors increased with the increase in the aerosol diameter and the water pool depth.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(2), p.198 - 206, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Miyahara, Shinya*; Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Seino, Hiroshi; Atsumi, Takuto*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/08
In a postulated accident of fuel pin failure of sodium cooled fast reactor, a fission product cesium will be released from the failed pin as an aerosol such as cesium iodide and/or cesium oxide together with a fission product noble gas such as xenon and krypton. As the result, the xenon and krypton released with cesium aerosol into the sodium coolant as bubbles have an influence on the removal of cesium aerosol by the sodium pool in a period of bubble rising to the pool surface. In this study, cesium aerosol removal behavior due to inertial deposition, sedimentation and diffusion from a noble gas bubble rising through liquid sodium pool was analyzed by a computer program which deals with the expansion and the deformation of the bubble together with the aerosol absorption considering the effects of particle size distribution and agglomeration in aerosols. In the analysis, initial bubble diameter, sodium pool depth and temperature, aerosol particle diameter and density, initial aerosol concentration in the bubble were changed as parameter, and the results for the sensitivities of these parameters on decontamination factor (DF) of cesium aerosol were compared with the results of the previous study in which the effects of particle size distribution and agglomeration in aerosols were not considered. From the results, it was concluded that the sensitivities of initial bubble diameter, the aerosol particle diameter and density to the DF became significant due to the inertial deposition of agglomerated aerosols. To validate these analysis results, the simulation experiments have been conducted using a simulant particles of cesium aerosol under the condition of room temperature in water pool and air bubble systems. The experimental results were compared with the analysis results calculated under the same condition.
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu*; Onishi, Takashi; Ishikawa, Takashi; Hirosawa, Takashi; Katsuyama, Kozo; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Tokoro, Daishiro*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 536, p.152119_1 - 152119_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to obtain the release rate coefficients from fuels for fast reactors (FRs), heating tests and the subsequent analyses of the fission products (FPs) and actinides that are released were carried out using samples of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel pellets irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo. Three heating tests targeting temperatures of 2773, 2973 and 3173 K were conducted using an FP release behavior test apparatus equipped with a high-frequency induction furnace and solid FP sampling systems consisting of a thermal gradient tube (TGT) and filters. Irradiated fuel pellets were placed into a tungsten crucible, then loaded into the induction furnace. The temperature was raised continuously at a heating rate of 10 K/s to the targeted temperature and maintained for 500 s in a flowing argon gas atmosphere. The FPs and actinides released from the MOX fuels and deposited in the TGT and filters were quantified by gamma-ray spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis. Based on the analysis, the release rates of radionuclides from MOX fuels for FR were obtained and compared with literature data for light water reactor (LWR) fuels. The release rate coefficients of FPs obtained in this study were found to be similar to or lower than the literature values for LWR fuels. It was also found that the release rate coefficient data for actinides were within the range of variation of literature values for LWR fuels.
Miyahara, Shinya*; Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Seino, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
In a postulated accident of fuel pin failure of sodium cooled fast reactor, a fission product cesium will be released as an aerosol such as cesium iodide and/or oxide together with xenon and/or krypton. In this study, cesium aerosol removal behavior due to inertial deposition, sedimentation and diffusion was analyzed by a computer program which deals with the expansion and the deformation of the bubble together with the aerosol absorption. Initial bubble diameter, sodium pool depth and temperature, aerosol particle diameter and density, initial aerosol concentration were changed as parameter. From the results, it was concluded that the initial bubble diameter was most sensitive parameter to the decontamination factor (DF). It was found that the sodium pool depth, the aerosol particle diameter and density have also important effect on the DF, but the sodium temperature has a marginal effect. To meet these results, the experiments are under planning to validate the results.
Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.521 - 532, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.2098 - 2107, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.30(Nuclear Science & Technology)A sodium concrete reaction (SCR) is one of the important phenomena to cause the structural concrete ablation and the release of H gas in the case of sever accident of sodium cooled fast reactors. In this study, the long-time SCR test had been carried out to investigate the self-termination mechanism. The results showed the SCR terminated even if the enough amount of Na remained on the concrete. The quantitative data were collected on the SCR terminating such as temperature and H
gas in the case of sever accident of sodium cooled fast reactors. In this study, the long-time SCR test had been carried out to investigate the self-termination mechanism. The results showed the SCR terminated even if the enough amount of Na remained on the concrete. The quantitative data were collected on the SCR terminating such as temperature and H generation. The reaction products, which became the small solids in liquid Na were transferred with slurry state by generated H
generation. The reaction products, which became the small solids in liquid Na were transferred with slurry state by generated H bubbles. Though the Na transfers actively and ablated the concrete surface with the high H
bubbles. Though the Na transfers actively and ablated the concrete surface with the high H generation rate, the mass exchange coefficient defined as
generation rate, the mass exchange coefficient defined as 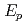 decreased and the reaction products settled gradually with decreasing the H
decreased and the reaction products settled gradually with decreasing the H generation rate. Therefore, the Na concentration decreased at the reaction front and resulted in the SCR terminating naturally.
generation rate. Therefore, the Na concentration decreased at the reaction front and resulted in the SCR terminating naturally.
Kikuchi, Shin; Koga, Nobuyoshi*; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(5), p.682 - 691, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:81.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), if considering hypothetical severe accidental condition such as the steel liner failure of structural concrete caused by intensive leakage of liquid sodium (Na) coolant, the liquid sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) may take place. The major consequences of SCR are hydrogen release, energy release and concrete ablation. Thus, it is important to understand the phenomenology of SCR. As a part of a series of studies on SCR, this study focused on the reaction between sodium oxide (Na O) and silica (SiO
O) and silica (SiO ). Through thermoanalytical and X-ray diffraction measurements, it was revealed that Na
). Through thermoanalytical and X-ray diffraction measurements, it was revealed that Na O-SiO
O-SiO reaction to form sodium orthosilicate (Na
reaction to form sodium orthosilicate (Na SiO
SiO ) occurs at significantly lower temperature in comparison with Na-SiO
) occurs at significantly lower temperature in comparison with Na-SiO reaction.
reaction.
Kikuchi, Shin; Koga, Nobuyoshi*; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 121(1), p.45 - 55, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:46.45(Thermodynamics)In this study, the kinetic behavior of the sodium (Na)-silica (SiO ) reaction was investigated for an assessment method of reactivity/stability of siliceous concrete against the sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) by postulating a severe accidental condition in the sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). The reaction behavior was tracked using a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) equipped with a videoscope for viewing the changes in the sample during the reaction. From detail kinetic analysis, it was revealed that the kinetic results determined from the kinetic data at the maximum reaction rate can be interpreted as is for the major reaction stage. In addition, the k value at a constant temperature calculated using the Arrhenius parameters determined by the simplified Kissinger method can be used for the reactivity/stability assessment of the siliceous concrete in view of the kinetics of the major reaction stage of the Na-SiO
) reaction was investigated for an assessment method of reactivity/stability of siliceous concrete against the sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) by postulating a severe accidental condition in the sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). The reaction behavior was tracked using a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) equipped with a videoscope for viewing the changes in the sample during the reaction. From detail kinetic analysis, it was revealed that the kinetic results determined from the kinetic data at the maximum reaction rate can be interpreted as is for the major reaction stage. In addition, the k value at a constant temperature calculated using the Arrhenius parameters determined by the simplified Kissinger method can be used for the reactivity/stability assessment of the siliceous concrete in view of the kinetics of the major reaction stage of the Na-SiO reaction.
reaction.
Seino, Hiroshi; Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Izumi, Keitaro*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
As a part of development of CONTAIN-LMR, CORCON and VANESA models for calculating the debris-concrete interaction (MCCI) have been improved taking into account the influence of soudium-pool existence. In this study, the following LMFR specific models in the code have been developed and improved: (1) chemical reaction in sodium pool, (2) aerosol decontamination in sodium pool, and (3) heat conduction in concrete. These models have been also confirmed and validated with experimental results. As a result, improved CORCON and VANESA can represent the MCCI behavior reasonably well. Further improvement and validation of CONTAIN-LMR will be continued in order to apply to the ex-vessel accident progression of LMFRs.
Miyahara, Shinya; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Konishi, Kensuke
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
A CONTAIN-LMR code has been developed in JAEA for application to PRA of LMFRs since the original CONTAIN code had been introduced from SNL of U.S. in 1982. The code is a best-estimate, integrated analysis tool for predicting the physical, chemical and radiological conditions inside a containment building of LMFRs following a severe accident with reactor vessel melt-through. The code is also able to predict the source term to the environment in the accident. This code can treat many important phenomena consistently such as sodium fire, radioactive aerosol behavior, hydrogen burn, sodium-concrete reaction and core debris-concrete interaction occurred in the accident with inter-cell heat and mass flow under the multiple cell geometry. This paper describes the chronology of the code development in JAEA briefly as an introduction, and after that, the outline of computational models in the code, the examples of the code validation, and the future plan of the code application are described.
Doi, Daisuke; Ono, Isao*; Seino, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Doi, Daisuke; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
CONTAIN-LMR code is an integrated analysis tool to predict the consequence of severe accident in a liquid metal fast reactor. A sodium-concrete reaction is one of the most important phenomena, and Sodium-Limestone Concrete Ablation Model (SLAM) has been installed into the original CONTAIN code. The SLAM treats chemical reaction kinetics between the sodium and the concrete compositions mechanistically, the application is limited to the limestone concrete. In order to apply SLAM to the siliceous concrete which is an ordinary structural concrete in Japan, the chemical reaction kinetics model has been improved. The improved model was validated to analyze a series of sodium-concrete experiments which were conducted in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It has been found that relatively good agreement between calculation and experimental results is obtained and the CONTAIN-LMR code has been validated with regard to the sodium-concrete reaction phenomena.
Kikuchi, Shin; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji
Proceedings of 10th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 13 Pages, 2014/12
For countermeasure against sodium leak, structural concrete is protected by steel liner in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. However, if considering severe accidental condition such as breach of steel liner by intensive sodium leak, the reaction of concrete with liquid sodium potentially may occur. The sodium-concrete reaction (SCR) may result in significant damage of structural concrete elements, the release of hydrogen and exothermic heat. Thus it is important to understand mechanism of SCR in terms of soundness of reactor structure. However, finding on the reaction kinetics is quite limited due to the experimental difficulty. In this study, kinetics of Na O-SiO
O-SiO reaction as subsequent reaction was focused. Based on the measured results by DSC equipment, kinetic parameters such as activation energy and frequency factor were obtained by the laws of chemical kinetics. XRD analysis was also performed to identify the reaction products and to discuss possible overall reactions.
reaction as subsequent reaction was focused. Based on the measured results by DSC equipment, kinetic parameters such as activation energy and frequency factor were obtained by the laws of chemical kinetics. XRD analysis was also performed to identify the reaction products and to discuss possible overall reactions.
Ohno, Shuji; Makino, Toru; Ono, Isao*; Seino, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2014/05
The CONTAIN-LMR code is being developed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to utilize for the quantitative assessment of accident consequences considered in sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) plant. Out of various physical and chemical behaviors treated in the code, this paper describes sodium fire related study issues such as computational modeling and its validation activities with focusing on important evaluating targets. Sodium pool and spray fire model validation practices are presented through the numerical analyses of sodium leak and fire experiments performed in the SAPFIRE facility.
Kikuchi, Shin; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 79(808), p.2650 - 2654, 2013/12
For countermeasure against sodium leak, structural concrete is protected by steel liner in a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). However, if considering severe and unexpected accidental condition such as breach of steel liner by intensive sodium leak, the reaction with liquid sodium and concrete potentially may occur. For the purpose of elucidating the mechanism of the sodium-concrete reaction in SFRs, kinetic study of the sodium (Na)-silica (SiO ) reaction has been carried out by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) technique. The Na-SiO
) reaction has been carried out by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) technique. The Na-SiO reaction temperaturewas identified from DSC curves. It was found that reactivity of Na-SiO
reaction temperaturewas identified from DSC curves. It was found that reactivity of Na-SiO reaction is similar with the reaction between Na and aggregate of practical used concrete. Based on the measured reaction temperature, rate constant of Na-SiO
reaction is similar with the reaction between Na and aggregate of practical used concrete. Based on the measured reaction temperature, rate constant of Na-SiO reaction was obtained. Thermal analysis results indicated that Na-SiO
reaction was obtained. Thermal analysis results indicated that Na-SiO reaction could occur under the elevated temperature in the timeframe of sodium-concrete reaction.
reaction could occur under the elevated temperature in the timeframe of sodium-concrete reaction.
Kikuchi, Shin; Seino, Hiroshi; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 7(2), p.79 - 93, 2013/06
For the purpose of elucidating the mechanism of the sodium-water surface reaction in a steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactors, kinetic study of the sodium (Na)-sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reaction has been carried out by using Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) technique. The parameters, including melting points of Na and NaOH, phase transition temperature of NaOH, Na-NaOH reaction temperature, and decomposition temperature of sodiumhydride (NaH) have been identified from DTA curves. Na, NaOH and Na O as major chemicalspecies were identified from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the residues after the DTA experiment. It was inferred that Na
O as major chemicalspecies were identified from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the residues after the DTA experiment. It was inferred that Na O could be generated as a reaction product. Based on the measured reaction temperature, the rate constant of sodium monoxide (Na
O could be generated as a reaction product. Based on the measured reaction temperature, the rate constant of sodium monoxide (Na O) generation was obtained by the application of the laws of chemical kinetics. From the estimated rate constant, it was confirmed that Na
O) generation was obtained by the application of the laws of chemical kinetics. From the estimated rate constant, it was confirmed that Na O generation should be considered during the sodium-water reaction.
O generation should be considered during the sodium-water reaction.
Kikuchi, Shin; Seino, Hiroshi; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 79(799), p.271 - 275, 2013/03
For the purpose of elucidating the mechanism of the sodium-water surface reaction in a steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactors, kinetic study of the sodium (Na)-sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reaction has been carried out by using Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) technique. It was reconfirmed that sodium monoxide (Na O) generation should be considered during the sodium-water reaction in spite of variation of volume fraction (Na:NaOH). Na, NaOH and Na
O) generation should be considered during the sodium-water reaction in spite of variation of volume fraction (Na:NaOH). Na, NaOH and Na O as major chemical species were identified from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the residues after the DTA experiment. From XRD analysis, it seems that Na
O as major chemical species were identified from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the residues after the DTA experiment. From XRD analysis, it seems that Na O is reaction product and reaction ratio is less than 100 percent.
O is reaction product and reaction ratio is less than 100 percent.