Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takagi, Rina*; Matsuyama, Naofumi*; Ukleev, V.*; Yu, L.*; White, J. S.*; Francoual, S.*; Mardegan, J. R. L.*; Hayami, Satoru*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.1472_1 - 1472_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:111 Percentile:99.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Ueno, Wakana; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.512 - 516, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.04(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*; Kato, Kosuke*; Kato, Hidemi*; Sadeghilaridjani, M.*; Otake, Yoshie*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(4), p.044001_1 - 044001_5, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)For the effective phase imaging at pulsed neutron sources, we have designed and developed the multi-colored Talbot-Lau interferometer which works at several wavelengths. At the Energy Resolved Neutron Imaging System RADEN in J-PARC, we demonstrated its operation by observing the visibilities of moire fringes derived from different wavelengths (0.25, 0.50, and 0.75 nm). We also investigated the variation of moire fringes dependent on the wavelength resolution from 18% to 50% and showed the advantage of pulsed beams. At the central wavelength of 0.5 nm, we have succeeded in interferometric imaging for the samples of metal rods made of aluminum, lead, and copper. An absorption grating as an analyzer was fabricated by imprinting of metallic glass for the first time, and showed a clear moire fringe with the high visibility of 68% and a well-controlled shape in comparison with previous ones fabricated by oblique evaporation of gadolinium.
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Ueno, Wakana; Parker, J. D.*; Samoto, Tetsuo*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*
Physics Procedia, 88, p.217 - 223, 2017/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:97.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)Mishima, Kenji*; Ino, Takashi*; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Sato, Hiromi*; Otake, Yoshie*; Omori, Hitoshi*; Muto, Suguru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.342 - 345, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new beamline for a fundamental physics experiment is under construction at BL05 port in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), this beamline is designed using novel techniques of neutron optics and it is termed "Neutron Optics and Physics". The beam from the moderator is deflected by multi-channel supermirrors and split into three branches for individual experiments. In this study, we have optimized the design of the beam optics and shields using the Monte Carlo simulation package PHITS. The neutron fluxes of beams are expected to be 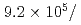 cm
cm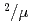 str
str s
s MW,
MW, 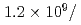 cm
cm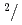 s
s MW,
MW, 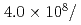 cm
cm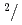 s
s MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Nakatani, Takeshi; Segawa, Mariko; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Ueno, Wakana; Seki, Yoshichika; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ueno, Wakana; Shinohara, Takenao; Seki, Yoshichika; Kai, Tetsuya; Parker, J. D.*; Sadeghilaridjani, M.*; Kato, Hidemi*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Segawa, Mariko; Nakatani, Takeshi; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Ueno, Wakana; Parker, J. D.*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Ueno, Wakana; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Samoto, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Samoto, Tetsuo*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Ueno, Wakana; Seeghilaridjani, M.*; Kato, Hidemi*; Samoto, Tetsuo*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Nakatani, Takeshi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Zhang, S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Nakatani, Takeshi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Nakatani, Takeshi; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; et al.
no journal, ,
Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hino, Masahiro*; Samoto, Tetsuo*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Nakatani, Takeshi; Seki, Yoshichika; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The Energy-Resolved Neutron Imaging System, RADEN, in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of J-PARC, has been constructed as the world's first dedicated instrument to the pulsed neutron imaging. RADEN is designed to conduct energy-resolved neutron imaging experiments like Bragg edge, resonance absorption and pulsed polarized neutron imaging by fully utilizing the short-pulsed neutron's nature, together with the conventional neutron radiography and tomography. The construction of RADEN was completed in 2014, and user operation was started from April 2015 after commissioning studies using the neutron beam. In addition to the user programs, the instrument group continues further technical developments for advanced energy-resolved neutron imaging and improving the performance of devices, especially the counting type imaging detectors.