Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Yukiko*; Arakawa, Masato*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Fujinami, So*; Shibata, Motoki*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Yamada, Masako*; Seto, Hideki*; et al.
Polymer, 333, p.128662_1 - 128662_8, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Imai, Tatsuya*; Kawai, Atsuki*; Ito, Eri*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Miyata, Noboru*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16(48), p.66782 - 66791, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Miyata, Noboru*; Arima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Shibata, Motoki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Yamada, Norifumi*; et al.
Colloids and Surfaces A; Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 701, p.134928_1 - 134928_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Arakawa, Masato*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Kida, Takumitsu*; Tokumitsu, Katsuhisa*; Tanaka, Ryo*; et al.
Langmuir, 40(30), p.15758 - 15766, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Tsuji, Hayato*; Nakahata, Masaki*; Hishida, Mafumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Inoue, Takeru*; Egawa, Yasunobu*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(49), p.11235 - 11241, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.28(Chemistry, Physical)Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Shibata, Motoki*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*
Soft Matter, 19(11), p.2082 - 2089, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:50.64(Chemistry, Physical)Shimokita, Keisuke*; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; Miyata, Noboru*; Arima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Takenaka, Mikihito*; Shibata, Motoki*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; et al.
Langmuir, 38(41), p.12457 - 12465, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.88(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) structural analysis of an aligning agent additive for the alignment of nematic liquid crystals on solid substrates
structural analysis of an aligning agent additive for the alignment of nematic liquid crystals on solid substratesNemoto, Fumiya*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Hino, Masahiro*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Seto, Hideki*
Soft Matter, 18(3), p.545 - 553, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.49(Chemistry, Physical)Kumar, S.*; Saha, D.*; Takata, Shinichi; Aswal, V. K.*; Seto, Hideki
Applied Physics Letters, 118(15), p.153701_1 - 153701_7, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.19(Physics, Applied)Singh, H.*; Ray, D.*; Kumar, S.*; Takata, Shinichi; Aswal, V. K.*; Seto, Hideki
Physical Review E, 102(6), p.062601_1 - 062601_11, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.07(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Seto, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 562, p.148 - 154, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.06(Physics, Condensed Matter)Seto, Hideki; Ito, Shinichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Shibata, Kaoru; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; General Subjects, 1861(1), p.3651 - 3660, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)J-PARC, Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex provides short pulse proton beam at a repetition rate 25 Hz and the maximum power is expected to be 1 MW. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments have already been operated or under construction / commissioning. There are 6 inelastic / quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectrometers and the complementary use of these spectrometers will open new insight for life science.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 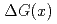 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 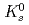 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Kanaya, Toshiji*; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Nishida, Koji*; Seto, Hideki*; Nagao, Michihiro*; Takeda, Takayoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(1), p.676 - 681, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.79(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report neutron spin-echo measurements on three types of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) gels. The first is PVA gel in a mixture of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and water with volume ratio 60/40, the second is PVA gel in an aqueous borax solution and the third is chemically cross-linked PVA gel. The observed normalized intermediate scattering functions I(Q,t)/I(Q,0) were very different among them. The I(Q,t)/I(Q,0) of the first and third gels showed a non-decaying component in addition to a decaying component, but the second one did not have the non-decaying one. This clearly indicates that the fluctuations in the first and third PVA gels consist of static and dynamic fluctuations whereas the second PVA gel does include only the dynamic fluctuations. The dynamic and static fluctuations of the PVA gels were analyzed in terms of a restricted motion in the gel network and the Zimm motion, respectively.
Tominaga, Taiki; Takata, Shinichi; Suzuki, Junichi*; Seto, Hideki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Seto, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
no journal, ,
Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Nishida, Koji*; Seto, Hideki*; Nagao, Michihiro*; Takeda, Takayoshi*
no journal, ,
We have extensively studied nano-scale structure and dynamics of three types of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) gels by using small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and neutron spin-echo (NSE) techniques; two physical gels and one chemical gel. The first one was a PVA gel in a mixture of deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6) and D2O with volume fraction of DMSO-d6 being 0.6, in which cross-links were made of crystallites. On the basis of NSE results, SANS intensity was divided into static and dynamic fluctuations to find that the former contribution was dominant in the present wave vector (Q) range. The latter, dynamic fluctuations were analyzed in terms of fluctuations of cross-links in the quasi-equilibrium position. The second gel was PVA in aqueous borax solution. The intermediate scattering functions of the gel as well as the sol were well described by Zimm mode and gel mode in Q regions of above and below a critical wave vector (Qc). The last one was the chemically cross-linked PVA gel. The intermediate scattering function was also described by Zimm mode in a short-time region, suggesting that it behaves like polymer solution. However, in a long-time region, the data points deviated from Zimm-scaled master curve, suggesting that it was restricted by the cross-links made of covalent bonds.